Abstract
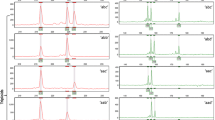
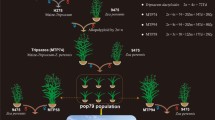
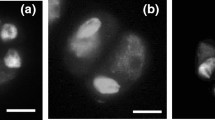
Diploid gametes are usually applied to produce triploids of Populus [originating from first-division restitution (FDR), second-division restitution (SDR), and postmeiotic restitution (PMR) 2n eggs]. Three types of 2n gametes transmitted different parental heterozygosities in Populus. Failed spindle formation and no chromosomal separation to opposite poles during meiosis I mean that FDR 2n gametes carry nonsister chromatids that are potentially heterozygous. By contrast, SDR 2n gametes result from failed sister chromatid separation in meiosis II, and therefore, they carry sister chromatid that are potentially homozygous. Completely homozygous 2n gametes can arise from the PMR mechanism. The alteration of gene expression resulting from allopolyploidization is a prominent feature in plants. We compared gene expression in the full-sib progeny of three allotriploid Populus populations (triploid-F, triploid-S, and triploid-P) with that in its parent species, and their full-sib diploid F1 hybrid. Genome-wide expression level dominance was biased toward the maternal in the diploid F1 hybrid and three allotriploid populations, whereas our data indicated important, but different, effects of the transmission of different heterozygosity by 2n female gametes in the expression patterns of allopolyploids. Because of the higher level of heterozygosity, the triploids had higher rates of non-additive and transgressive expression patterns in the triploid-F than in triploid-S and triploid-P. Compared with diploid F1, about 30-fold more genes (251) were differently expressed in the triploid-F than in the triploid-S (9) and triploid-P (8), respectively. These findings indicate that hybridization and polyploidization have immediate and distinct effects on the large-scale patterns of gene expression, and different effects on the transmission of heterozygosity by three 2n female gametes.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams KL (2007) Evolution of duplicate gene expression in polyploid and hybrid plants. J Hered 98:136–141
Adams KL, Wendel JF (2004) Exploring the genomic mysteries of polyploidy in cotton. Biol J Linn Sco 82:573–581
Adams KL, Cronn R, Percifield R, Wendel JF (2003) Genes duplicated by polyploidy show unequal contributions to the transcriptome and organ-specific reciprocal silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4649–4654
Akhunova AR, Matniyazov RT, Liang H, Akhunov ED (2010) Homoeolog-specific transcriptional bias in allopolyploid wheat. BMC Genom 11:505
Albertin W, Balliau T, Brabant P, Chevre AM, Eber F, Malosse C, Thiellement H (2006) Numerous and rapid nonstochastic modifications of gene products in newly synthesized Brassica napus allotetraploids. Genetics 173:1101–1113
Bao J, Lee S, Chen C, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Liu S, Clark T, Wang J, Cao M, Yang H et al (2005) Serial analysis of gene expression study of a hybrid rice strain (LYP9) and its parental cultivars. Plant Physiol 138:1216–1231
Bastiaanssen HJM, Van Den Berg PMMM, Lindhout P, Jacobsen E, Ramanna MS (1998) Postmeiotic restitution in 2n-egg formation of diploid potato. Heredity 81:20–27
Bottley A, Xia GM, Koebner RMD (2006) Homoeologous gene silencing in hexaploid wheat. Plant J 47:897–906
Bretagnolle F, Thompson JD (1995) Tansley review no. 78. Gametes with the somatic chromosome number: mechanisms of their formation and role in the evolution of autopolyploid plants. New Phytol 129:1–22
Chelaifa H, Monnier A, Ainouche M (2010) Transcriptomic changes following recent natural hybridization and allopolyploidy in the salt marsh species Spartina × townsendii and Spartina anglica (Poaceae). New Phytol 186:161–174
Chelaifa H, Chagué V, Chalabi S, Mestiri I, Arnaud D, Deffains D, Lu Y, Belcram H, Huteau V, Chiquet J, Coriton O et al (2013) Prevalence of gene expression additivity in genetically stable wheat allohexaploids. New Phytol 197:730–736
Chen ZJ (2007) Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms for gene expression and phenotypic variation in plant polyploids. Annu Rev Plant Biol 8:377–406
Chen ZJ (2010) Molecular mechanisms of polyploidy and hybrid vigor. Trends Plant Sci 15:57–71
Chen ZJ (2013) Genomic and epigenetic insights into the molecular bases of heterosis. Nat Rev Genet 14:471–482
Comai L (2005) The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid. Nat Rev Genet 6:836–846
Davenport CB (1908) Degeneration, albinism and inbreeding. Science 28:454–455
De Storme N, Geelen D (2013) Sexual polyploidization in plants–cytological mechanisms and molecular regulation. New Phytol 198:670–684
Dong CB, Suo YJ, Kang XY (2014a) Assessment of the genetic composition of triploid hybrid Populus using SSR markers with low recombination frequencies. Can J For Res 44:692–699
Dong CB, Mao JF, Suo YJ, Shi L, Wang J, Zhang PD, Kang XY (2014b) A strategy for characterization of persistent heteroduplex DNA in higher plants. Plant J 80:282–291
East EM (1908) Inbreeding in corn. Conn Agric Exp Stn 1907:419–428
Einspahr DW (1984) Production and utilization of triploid hybrid aspen. Iowa State J Res 58:401–409
Flagel LE, Wendel JF (2010) Evolutionary rate variation, genomic dominance and duplicate gene expression evolution during allotetraploid cotton speciation. New Phytol 186:184–193
Groszmann M, Greaves IK, Fujimoto R, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES (2013) The role of epigenetics in hybrid vigour. Trends Genet 29:684–690
Grover CE, Gallagher JP, Szadkowski EP, Yoo MJ, Flagel LE, Wendel JF (2012) Homoeolog expression bias and expression level dominance in allopolyploids. New Phytol 196:966–971
Guo M, Rupe MA, Yang X, Crasta O, Zinselmeier C, Smith OS, Bowen B (2006) Genome-wide transcript analysis of maize hybrids: allelic additive gene expression and yield heterosis. Theor Appl Genet 113:831–845
Hegarty MJ, Barker GL, Wilson ID, Abbott RJ, Edwards KJ, Hiscock SJ (2006) Transcriptome shock after interspecific hybridization in senecio is ameliorated by genome duplication. Curr Biol 16:1652–1659
Hegarty MJ, Barker GL, Brennan AC, Edwards KJ, Abbott RJ, Hiscock SJ (2008) Changes to gene expression associated with hybrid speciation in plants: further insights from transcriptomic studies in Senecio. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:3055–3069
Heike L, Kristina U, Dietrich E (2015) FDR and SDR processes in meiosis and diploid gamete formation in poplars (Populus L.) detected by centromere-associated microsatellite markers. Tree Genet Genomes 11:801
Huang Y, Zhang L, Zhang J, Yuan D, Xu C, Li X, Zhou D, Wang S, Zhang Q (2006) Heterosis and polymorphisms of gene expression in an elite rice hybrid as revealed by a microarray analysis of 9198 unique ESTs. Plant Mol Biol 62:579–591
Ilut DC, Coate JE, Luciano AK, Owens TG, May GD, Farmer A, Doyle JJ (2012) A comparative transcriptomic study of an allotetraploid and its diploid progenitors illustrates the unique advantages and challenges of RNA-seq in plant species. Am J Bot 99:383–396
Kang XY, Zhu ZT, Zhang ZY (2000) Suitable period of high temperature treatment for 2n pollen of Populus tomentosa × P. bolleana. J Beijing For Univ 22:1–4
Koh J, Chen S, Zhu N, Yu F, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2012) Comparative proteomics of the recently and recurrently formed natural allopolyploid Tragopogon mirus (Asteraceae) and its parents. New Phytol 196:292–305
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25
Li ZK, Luo LJ, Mei HW, Wang DL, Shu QY, Tabien R, Zhong DB, Ying CS, Stansel JW, Khush GS, Paterson AH (2001) Overdominant epistatic loci are the primary genetic basis of inbreeding depression and heterosis in rice. I. Biomass and grain yield. Genetics 158:1737–1753
Li YH, Kang XY, Wang SD, Zhang ZH, Chen HW (2008) Triploid induction in Populus alba × P. glandulosa by chromosome doubling of female gametes. Silvae Genet 57:37–40
Li A, Liu D, Wu J, Zhao X, Hao M, Geng S, Yan J, Jiang X, Zhang L, Wu J et al (2014) mRNA and small RNA transcriptomes reveal insights into dynamic homoeolog regulation of allopolyploid heterosis in nascent hexaploid wheat. Plant Cell 26:1878–1900
Liesebach H, Ulrich K, Ewald D (2015) FDR and SDR processes in meiosis and diploid gamete formation in poplars (Populus L) detected by centromere-associated microsatellite markers. Tree Genetics Genomes 11:801
Liu B, Wendel J (2002) Non-Mendelian phenomenon in allopolyploid genome evolution. Curr Genom 3:489–505
Lu M, Zhang P, Kang X (2013) Induction of 2n female gametes in Populus adenopoda Maxim by high temperature exposure during female gametophyte development. Breed Sci 63:96–103
Lynch M, Force A (2000) The probability of duplicate gene preservation by subfunctionalization. Genetics 154:459–473
Mashkina OS, Burdaeva LM, Belozerova MM, Vyunova LN (1989) Method of obtaining diploid pollen of woody species. Lesoved 1:19–25
Mason AS, Pires JC (2015) Unreduced gametes: meiotic mishap or evolutionary mechanism? Trends Genet 31:5–10
Mayfield D, Chen ZJ, Pires JC (2011) Epigenetic regulation of flowering time in polyploids. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:174–178
Mendiburu AO, Peloquin SJ (1976) Sexual polyploidization and depolyploidization: some terminology and definitions. Theor Appl Genet 48:137–143
Miller M, Zhang C, Chen ZJ (2012) Ploidy and hybridity effects on growth vigor and gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana hybrids and their parents. G3 2:505–513
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5:621–628
Müntzing A (1936) The chromosomes of a giant Populus tremula. Hereditas 21:383–393
Nilsson-Ehle H (1936) Note regarding the gigas form of Populus tremula found in nature. Hereditas 21:372–382
Osborn TC, Pires JC, Birchler JA, Auger DL, Chen ZJ et al (2003) Understanding mechanisms of novel gene expression in polyploids. Trends Genet 19:141–147
Peloquin SJ, Boiteux LS, Simon PW, Jansky SH (2008) A chromosome-specific estimate of transmission of heterozygosity by 2n gametes in potato. J Hered 99:177–181
Pumphrey M, Bai J, Laudencia-Chingcuanco D, Anderson O, Gill BS (2009) Nonadditive expression of homoeologous genes is established upon polyploidization in hexaploid wheat. Genetics 181:1147–1157
Qi B, Huang W, Zhu B, Zhong X, Guo J, Zhao N, Xu C, Zhang H, Pang J, Han F, Liu B (2012) Global transgenerational gene expression dynamics in two newly synthesized allohexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum) lines. BMC Biol 26:3
Rambani A, Page JT, Udall JA (2014) Polyploidy and the petal transcriptome of Gossypium. BMC Plant Biol 14:3
Randolph LF (1932) Some effects of high temperature on polyploidy and other variations in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 18:222–229
Rapp RA, Udall JA, Wendel JF (2009) Genomic expression dominance in allopolyploids. BMC Biol 7:18
Shen H, He H, Li J, Chen W, Wang X, Guo L, Peng Z, He G, Zhong S, Qi Y et al (2012) Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression changes in two Arabidopsis ecotypes and their reciprocal hybrids. Plant Cell 24:875–892
Shen Y, Zhao Q, Zou J, Wang W, Gao Y, Meng J, Wang J (2014) Characterization and expression patterns of small RNAs in synthesized Brassica hexaploids. Plant Mol Biol 85:287–299
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3. Article 3
Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Tate JA (2003) Advances in the study of polyploidy since plant speciation. New Phytol 161:173–191
Song GS, Zhai HL, Peng YG, Zhang L, Wei G, Chen XY, Xiao YG, Wang L, Chen YJ, Wu B et al (2010) Comparative transcriptional profiling and preliminary study on heterosis mechanism of super-hybrid rice. Mol Plant 3:1012–1025
Stupar RM, Springer NM (2006) Cis-transcriptional variation in maize inbred lines B73 and Mo17 leads to additive expression patterns in the F1 hybrid. Genetics 173:2199–2210
Swanson-Wagner RA, Jia Y, DeCook R, Borsuk LA, Nettleton D, Schnable PS (2006) All possible modes of gene action are observed in a global comparison of gene expression in a maize F1 hybrid and its inbred parents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6805–6810
Taylor G (2002) Populus. Arabidopsis for forestry. Do we need a model tree? Ann Bot 90:681–689
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25:1105–1111
Tuskan GA, DiFazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Ralph S, Rombauts S, Salamov A et al (2006) The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 313:1596–1604
Udall JA, Wendel JF (2006) Polyploidy and crop improvement. Crop Sci 46:S3–S14
Veilleux R (1985) Diploid and polyploid gametes in crop plants: mechanisms of formation and utilization in plant breeding. Plant Breed Rev 3:253–288
Vuylsteke M, Van Eeuwijk F, Van Hummelen P, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (2005) Genetic analysis of variation in gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 171:1267–1275
Wang J, Kang XY (2009) Distribution of microtubular cytoskeletons and organelle nucleoids during microsporogenesis in a 2n pollen producer of hybrid Populus. Silvae Genetica 58:220–226
Wang J, Kang XY, Li DL, Chen HW, Zhang PD (2010) Induction of diploid eggs with colchicine during embryo sac development in Populus. Silvae Genet 59:40–48
Wang J, Li DL, Kang XY (2012) Induction of unreduced megaspores with high temperature during megasporogenesis in Populus. Ann For Sci 15:1–9
Wang J, Shi L, Song SY, Tian J, Kang XY (2013) Tetraploid production through zygotic chromosome doubling in Populus. Silva Fenn 2:1–12
Washburn JD, Birchler JA (2014) Polyploids as a ‘model system’ for the study of heterosis. Plant Reprod 27:1–5
Wei G, Tao Y, Liu G, Chen C, Luo R, Xia H, Gan Q, Zeng H, Lu Z, Han Y et al (2009) A transcriptomic analysis of superhybrid rice LYP9 and its parents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:7695–7701
Weisgerber H, Rau HM, Gartner EJ, Baumeister G, Kohnert H, Karner L (1980) 25 Years of forest tree breeding in Hessen. Allg For 26:665–712
Wendel JF (2000) Genome evolution in polyploids. Plant Mol Biol 42:225–249
Wu RL (2000) Quantitative genetic variation of leaf size and shape in a mixed diploid and triploid population of Populus. Genet Res 75:215–222
Wulschleger S, Jansson S, Taylor G (2002) Genomics and forest biology—Populus emerges as the perennial favourite. Plant Cell 14:2651–2655
Yao H, Dogra Gray A, Auger DL, Birchler JA (2013) Genomic dosage effects on heterosis in triploid maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:2665–2669
Yoo MJ, Szadkowski E, Wendel JF (2013) Homoelog expression bias and expression level dominance in allopolyploid cotton. Heredity 110:171–180
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16:284–287
Zhang XZ, Liu GJ, Yan LY, Zhao YB, Chang RF, Wu LP (2002) Creating triploid germplasm via induced 2n pollen in Capsicum L. J Horticult Sci Biotechnol 78:84–88
Zhu ZT, Lin HB, Kang XY (1995) Studies on allotriploid breeding of Populus tomentosa B301 clones. Sci Silvae Sin 31:499–505
Zhu ZT, Kang XY, Zhang ZY (1998) Studies on selection of natural triploids of Populus tomentosa. Sci Silave Sin 34:22–31
Zhuang Y, Adams KL (2007) Extensive allelic variation in gene expression in populus F1 hybrids. Genetics 177:1987–1996
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Guanjing Hu in Department of Ecology, Evolution, and Organismal Biology, Iowa State University, Ames IA, for her critical reading of the manuscript. We are grateful to Dai Chen and Bo Zhang (Novel Bioinformatics Ltd., Co, Shanghai, China) for their technical assistance in bioinformatics analysis, and to three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. Research was supported by Special Fund for Forest Scientific Research in the Public Welfare (201404113), a National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470667), and 111 Project (B13007).
Author contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Xiangyang Kang. Performed the experiments: Shiping Cheng. Analyzed the data: Shiping Cheng, Jun Yang, Ting Liao, Xiaohu Zhu, Yujing Suo, Pingdong Zhang, Jun Wang. Wrote the paper: Shiping Cheng, Xiangyang Kang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, S., Yang, J., Liao, T. et al. Transcriptomic changes following synthesis of a Populus full-sib diploid and allotriploid population with different heterozygosities driven by three types of 2n female gamete. Plant Mol Biol 89, 493–510 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0384-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0384-0