Abstract
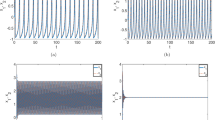
The heterogeneous coupled network has shown its research values in brain science and bionics. In this paper, a novel small heterogeneous coupled network through a memristive synapse is proposed and investigated. The model is constructed by coupling a 2D Hindmarsh–Rose (HR) neuron with a 3D Hopfield neural network (HNN) through a memristive synapse. Subsequently, the complex dynamical behaviors exhibited by the network were investigated. Specifically, we varied the coupling parameter k12 of the 3D HNN and found that the membrane potentials of the 2D HR neuron possess seven stable firing patterns. Then, by varying the coupling parameter k1 between the 2D HR neuron and the 3D HNN, the membrane potentials of the 2D HR neuron generated five stable firing patterns. Furthermore, by fixing the coupling parameters and varying the initial values of the network, multistability behavior was exhibited by the network. These findings have potential applications in brain science and bionics. Finally, a circuit is designed to realize the network in both simulation and experiments.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500 (1952)
Tsumoto, K., Kitajima, H., Yoshinaga, T., et al.: Bifurcations in Morris-Lecar neuron model. Neurocomputing 69(4–6), 293–316 (2006)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.M.: A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296(5853), 162–164 (1982)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.M.: A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Series B Biol. Sci. 221(1222), 87–102 (1984)
Izhikevich, E.M., FitzHugh, R.: Fitzhugh-nagumo model. Scholarpedia. 1(9), 1349 (2006)
Pham, V.T., Volos, C., Jafari, S., et al.: Coexistence of hidden chaotic attractors in a novel no-equilibrium system. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(3), 2001–2010 (2017)
Cang, S., Li, Y., Zhang, R., et al.: Hidden and self-excited coexisting attractors in a Lorenz-like system with two equilibrium points. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(1), 381–390 (2019)
Pisarchik, A.N., Feudel, U.: Control of multistability. Phys. Rep. 540(4), 167–218 (2014)
Parastesh, F., Jafari, S., Azarnoush, H.: Traveling patterns in a network of memristor-based oscillators with extreme multistability. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228(10), 2123–2131 (2019)
Xu, Y., Jia, Y., Ma, J., et al.: Synchronization between neurons coupled by memristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 104, 435–442 (2017)
Lu, L., Jia, Y., Liu, W., et al.: Mixed stimulus-induced mode selection in neural activity driven by high and low frequency current under electromagnetic radiation. Complexity (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7628537
Ge, M., Jia, Y., Xu, Y., et al.: Mode transition in electrical activities of neuron driven by high and low frequency stimulus in the presence of electromagnetic induction and radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(1), 515–523 (2018)
Xu, F., Zhang, J., Fang, T., et al.: Synchronous dynamics in neural system coupled with memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 92(3), 1395–1402 (2018)
Zhang, G., Wang, C., Alzahrani, F., et al.: Investigation of dynamical behaviors of neurons driven by memristive synapse. Chaos Solitons Fractals 108, 15–24 (2018)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., et al.: A novel no-equilibrium HR neuron model with hidden homogeneous extreme multistability. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 145, 110761 (2021)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., et al.: Multi-scroll hidden attractor in memristive HR neuron model under electromagnetic radiation and its applications. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 31(1), 011101 (2021)
Li, Z., Guo, Z., Wang, M., et al.: Firing activities induced by memristive autapse in Fitzhugh-Nagumo neuron with time delay. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 142, 153995 (2021)
Bao, B., Qian, H., Xu, Q., et al.: Coexisting behaviors of asymmetric attractors in hyperbolic-type memristor based Hopfield neural network. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 11, 81 (2017)
Li, C., Yang, Y., Yang, X., et al.: A tristable locally active memristor and its application in Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 108(2), 1697–1717 (2022)
Bao, B., Qian, H., Wang, J., et al.: Numerical analyses and experimental validations of coexisting multiple attractors in Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 90(4), 2359–2369 (2017)
Chen, C., Bao, H., Chen, M., et al.: Non-ideal memristor synapse-coupled bi-neuron Hopfield neural network: numerical simulations and breadboard experiments. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 111, 152894 (2019)
Chen, C., Chen, J., Bao, H., et al.: Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(4), 3385–3399 (2019)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Tan, Y.: Hidden extreme multistability with hyperchaos and transient chaos in a Hopfield neural network affected by electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(3), 2369–2386 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C.: Influences of electromagnetic radiation distribution on chaotic dynamics of a neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 369, 124840 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yao, W., et al.: Chaotic dynamics in a neural network with different types of external stimuli. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 90, 105390 (2020)
Li, R., Ding, R.: A novel locally active time-delay memristive Hopfield neural network and its application. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231, 3005–3017 (2022)
Shen, H., Yu, F., Kong, X., et al.: Dynamics study on the effect of memristive autapse distribution on Hopfield neural network. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32(8), 083133 (2022)
Li, Z., Zhou, H., Wang, M., et al.: Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(2), 1455–1473 (2021)
Njitacke, Z.T., Tsafack, N., Ramakrishnan, B., et al.: Complex dynamics from heterogeneous coupling and electromagnetic effect on two neurons: application in images encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 153, 111577 (2021)
Yu, F., Shen, H., Wang, C., et al.: Firing mechanism based on single memristive neuron and double memristive coupled neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 110, 3807–3822 (2022)
Njitacke Tabekoueng, Z., Shankar Muni, S., Fonzin Fozin, T., et al.: Coexistence of infinitely many patterns and their control in heterogeneous coupled neurons through a multistable memristive synapse. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32(5), 053114 (2022)
Njitacke, Z.T., Awrejcewicz, J., Ramakrishnan, B., et al.: Hamiltonian energy computation and complex behavior of a small heterogeneous network of three neurons: circuit implementation. Nonlinear Dyn. 107(3), 2867–2886 (2022)
Uzuntarla, M.: Firing dynamics in hybrid coupled populations of bistable neurons. Neurocomputing 367, 328–336 (2019)
Calim, A., Torres, J.J., Ozer, M., et al.: Chimera states in hybrid coupled neuron populations. Neural Netw. 126, 108–117 (2020)
Palabas, T., Longtin, A., Ghosh, D., et al.: Controlling the spontaneous firing behavior of a neuron with astrocyte. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32(5), 051101 (2022)
Ma, J.: Biophysical neurons, energy, and synapse controllability: a review. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A. 24(2), 109–129 (2023)
Xie, Y., Zhou, P., Ma, J.: Energy balance and synchronization via inductive-coupling in functional neural circuits. Appl. Math. Model. 113, 175–187 (2023)
Xie, Y., Yao, Z., Ren, G., et al.: Estimate physical reliability in Hindmarsh–Rose neuron. Phys. Lett. A 464, 128693 (2023)
Zhou, Y., Li, C., Li, W., Li, H., Feng, W., Qian, K.: Image encryption algorithm with circle index table scrambling and partition diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn. 103(2), 2043–2061 (2021)
Li, C.L., Zhou, Y., Li, H.M., Feng, W., Du, J.R.: Image encryption scheme with bit-level scrambling and multiplication diffusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 80, 18479–18501 (2021)
Dou, G., Zhao, K., Guo, M., Mou, J. et al.: Memristor-based LSTM network for text classification. Fractals. 2340040 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62071411) and the Research Foundation of Education Department of Hunan Province, China (Grant No.20B567).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Peng, J., Zhang, X. et al. Firing activities analysis of a novel small heterogeneous coupled network through a memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 15397–15415 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08626-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08626-0