Abstract
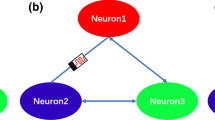
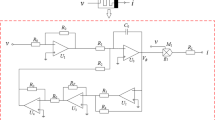
Synaptic crosstalk is ubiquitous in many brain regions, but its effect on firing activities of neural network has rarely been studied. In this study, a heterogeneous neural network constructed with one Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model and one Fitzhugh–Nagumo neuron model is developed, in which the synaptic crosstalk is emulated by two mutually coupled memristors. The effect of crosstalk intensities on the firing activities of the neural network are discussed by time series, phase diagrams, Lyapunov exponents, and dynamic mapping. For different crosstalk intensities, the coexisting periodic firing and chaotic firing, the coexisting periodic firing and periodic firing, the coexisting chaotic firing and periodic firing, and the coexisting chaotic firing and chaotic firing are observed in the neural network under different memristor’s initial values. Furthermore, the effect of crosstalk intensity on synchronous firing between two neurons is also revealed and it is found that the two heterogeneous neurons transit from initially oscillate independently to gradually achieve fully synchronous firing behavior as the crosstalk intensities decrease. Finally, the numerical simulations are verified by circuit simulation experiment based on Multisim.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
M Wang et al Neuron. 77 736 (2013)
J Ma J Tang Nonlinear Dynamics. 89 1569 (2017)
Y Xu, J Ma, X Zhan, L Yang, Y Jia Cognitive Neurodynamics. 13 601 (2019)
H Wang, Q Lu, Q Wang Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation. 13 1668 (2008)
J L Hindmarsh, R M Rose Nature. 296 162 (1982)
Z Wang, Q Hong, X Wang IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems. 13 631 (2019)
T R Chay, Y S Fan, S Lee International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos. 5 595 (1995)
Q Xu and X Tan Solitons & Fractals. 141 110353 (2020)
J L Hindmarsh, R M Rose Proceedings of the Royal society of London. Series B. Biological sciences. 221 87 (1984)
Y Yao et al Complexity. 2018 1 (2018)
Y Yao, J Ma Cognitive Neurodynamics. 12 343 (2018)
F Wu, J Ma, G Zhang Applied Mathematics and Computation. 347 590 (2019)
D B Strukov et al Nature. 453 80 (2008)
K Wu, T Luo, H Lu, Y Wang Neural Computing and Applications 27 739 (2016)
E M Ngouonkadi et al Chaos, Solitons & Fractals. 85 151 (2016)
B Bao et al Nonlinear Dynamics. 92 1695 (2018)
S Binczak et al Neural Network. 19 684 (2006)
D Ding et al Chaos, Solitons & Fractals. 158 112014 (2022)
J Ma et al Applied Mathematics and Computation. 307 321 (2017)
Z Li, Z Guo, M Wang, M Ma International Journal Electronic Communication. 142 153995 (2021)
T Stegall, K A Krolick Journal of Neuroimmunology. 119 377 (2001)
H Gu, B Pan, G Chen, L Duan Nonlinear Dynamics. 78 391 (2014)
M Ma et al Chinese Physics B. 32 058701 (2023)
M Ma et al Mathematics. 11 375 (2023)
H Lin, C Wang, Q Hong, Y Sun IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs. 67 3472 (2020)
M Ma et al Nonlinear Dynamics. 107 2935 (2022)
Q Wan, F Li and S Chen Solitons & Fractals. 169 113259 (2023)
Y Leng et al Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science. 30 033108 (2020)
F Wu, Y Zhang, X Zhang Nonlinear Dynamics. 98 971 (2019)
R Li, Z Wang, E Dong Nonlinear Dynamics. 104 4459 (2021)
Y Xu et al Chaos, Solitons & Fractals. 104 435 (2017)
H Bao, Y Zhang, W Liu, B Bao Nonlinear Dynamics. 100 937 (2020)
Z Li, H Zhou, M Wang, M Ma Nonlinear Dynamics. 104 1455 (2021)
T Kloek, The effect of dendritic spine morphology on synaptic crosstalk: Two multi-synapse models, integrating diffusion on curved surfaces (2015)
M Kawahara, M Kato-Negishi, K Tanaka Metallomics. 9 619 (2017)
A N Shrivastava, A Triller, W Sieghart Frontiers in cellular neuroscience. 5 7 (2011)
Q Li, S Tang, H Zeng, T Zhou Nonlinear Dynamics. 78 1087 (2014)
H Wang, Q Lu, X Shi Chinese Physics B. 19 060509 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China under Grant No. 62171401 and 62071411 and the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 2022JJ30572.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Peng, C., Wang, M. et al. Dynamic behavior in memristor coupled Hindmarsh–Rose and Fitzhugh–Nagumo neurons with synaptic crosstalk. Indian J Phys 98, 1043–1059 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02845-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02845-2