Abstract
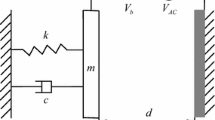
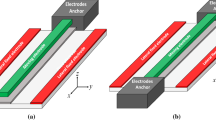
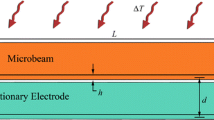
We report on the lateral pull-in in capacitive MEMS transducers that employ a repulsive electrostatic force. The moving element in this system undergoes motion in two dimensions. A two degree-of-freedom mathematical model is developed to investigate the pull-in quantitatively. The nonlinear electrostatic force, which is a vector function of two spatial coordinates, is determined by calculating the potential energy of the system using a boundary element approach. The equilibrium points are found by numerically solving the nonlinear coupled static equations. A stability analysis reveals that depending on the values of the lateral and transverse stiffness, the system undergoes different bifurcations when the voltage on the side electrodes is considered as the control parameter. Three-dimensional bifurcation diagrams are presented and discussed to elucidate the nonlinear nature of the system. The results establish important criteria for designing MEMS transducers with reliable and robust performance.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guney, M.G., Li, X., Chung, V.P.J., paramesh, J., Mukherjee, T., Fedder, G.K.: High dynamic range CMOS-MEMS capacitive accelerometer array. In: 2018 IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), pp. 992–995 (2018)
Mukhiya, R., Agarwal, R., Badjatya, S., Garg, M., Gaikwad, P., Sinha, S., Singh, A.K., Gopal, R.: Design, modelling and system level simulations of DRIE-based MEMS differential capacitive accelerometer. Microsyst. Technol. 25(9), 3521–3532 (2019)
Yang, C., Tang, S., Tavassolian, I.: Utilizing gyroscopes towards the automatic annotation of seismocardiograms. IEEE Sens. J. 17(7), 2129–2136 (2017)
Sheikhaleh, A., Jafari, K., Abedi, K.: Design and analysis of a novel MOEMS gyroscope using an electrostatic comb-drive actuator and an optical sensing system. IEEE Sens. J. 19(1), 144–150 (2019)
Pallay, M., Miles, R.N., Towfighian, S.: A tunable electrostatic MEMS pressure switch. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2019.2956377
Wang, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, W., Han, J.: Dynamic analysis of a micro beam-based tactile sensor actuated by fringing electrostatic fields. Micromachines (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050324
Miles, R.N., Cui, W., Su, Q.T., Homentcovschi, D.: A MEMS low-noise sound pressure gradient microphone with capacitive sensing. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 24(1), 241–248 (2015)
Ozdogan, M., Towfighian, S., Miles, R.N.: Fabrication and experimental characterization of a MEMS microphone using electrostatic levitation. In: 2019 IEEE sensors conference (2019)
Pallay, M., Towfighian, S.: A reliable MEMS switch using electrostatic levitation. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5053090
Iannacci, J.: Reliability of MEMS: a perspective on failure mechanisms, improvement solutions and best practices at development level. Displays 37, 62–71 (2014)
Ramini, A., Bellaredj, M.L.F., Hafiz, M.A.A., Younis, M.I.: Experimental investigation of snap-through motion of in-plane MEMS shallow arches under electrostatic excitation. J. Micromech. Microeng. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/26/1/015012
Derakhshani, M., Berfield, T.A.: Snap-through and mechanical strain analysis of a MEMS bistable vibration energy harvester. Shock Vib. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6743676
Maani Miandoab, E., Nejat Pishkenari, H., Meghdari, A., Fathi, M.: A general closed-form solution for the static pull-in voltages of electrostatically actuated MEMS/NEMS. Physica E Low-dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 90, 7–12 (2017)
SoltanRezaee, M., Afrashi, M.: Modeling the nonlinear pull-in behavior of tunable nano-switches. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 109, 73–87 (2016)
Ozdogan, M., Towfighian, S., Miles, R.N.: Modeling and characterization of a pull-in free MEMS microphone. IEEE Sens. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.2976527
Godara, R.K., Joglekar, M.M.: Alleviation of residual oscillations in electrostatically actuated variable-width microbeams using a feedforward control strategy. Microsyst. Technol. 23, 4441–4457 (2016)
Godara, R.K., Joglekar, M.M.: Suppression of contact bounce in beam-type microelectromechanical switches using a feedforward control scheme. J. Vib. Control 24(23), 5502–5513 (2018)
Lee, K.B., Cho, Y.: Laterally driven electrostatic repulsive-force microactuators using asymmetric field distribution. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 10(1), 128–136 (2001)
Towfighian, S., Seleim, A., Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Heppler, G.R.: A large-stroke electrostatic micro-actuator. J. Micromech. Microeng. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/21/7/075023
Park, S., Khater, M., Effa, D., Abdel-Rahman, E., Yavuz, M.: Detection of cyclic-fold bifurcation in electrostatic MEMS transducers by motion-induced current. J. Micromech. Microeng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6439/aa77bd
Ak, C., Yildiz, A.: A novel closed-form expression obtained by using differential evolution algorithm to calculate pull-in voltage of MEMS cantilever. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 27(3), 392–397 (2018)
Zehnder, A.T., Rand, R.H., Krylov, S.: Locking of electrostatically coupled thermo-optically driven MEMS limit cycle oscillators. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 102, 92–100 (2018)
Caruntu, D.I., Botello, M.A., Reyes, C.A., Beatriz, J.S.: Voltage-amplitude response of superharmonic resonance of second order of electrostatically actuated MEMS cantilever resonators. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4042017
Guha, K., Laskar, N.M., Gogoi, H.J., Chanda, S., Baishnab, K.L., Rao, K.S., Maity, N.P.: An improved analytical model for static pull-in voltage of a flexured MEMS switch. Microsyst. Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3911-5
Younis, Mohammad I.: MEMS Linear and Nonlinear Statics and Dynamics. Springer, New York (2011)
Zhang, W., Yan, H., Peng, Z., Meng, G.: Electrostatic pull-in instability in MEMS/NEMS: a review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 214, 187–218 (2014)
Bian, W., Zhao, J., You, Z.: Low voltage, high speed and small area in-plane MEMS switch. J. Micromech. Microeng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6439/ab1635
Firouzi, B., Zamanian, M.: The effect of capillary and intermolecular forces on instability of the electrostatically actuated microbeam with T-shaped paddle in the presence of fringing field. Appl. Math. Model. 71, 243–268 (2019)
Sharma, A.K., Godara, R.K., Joglekar, M.M.: Static and DC dynamic pull-in analysis of curled microcantilevers with a compliant support. Microsyst. Technol. 25(3), 965–975 (2019)
Nayfeh, A.H., Younis, M.I., Eihab, A.M.: Dynamic pull-in phenomenon in MEMS resonators. Nonlinear Dyn. 48(1), 153–163 (2007)
Rocha, L.A., Cretu, E., Wolffenbuttel, R.F.: Behavioural analysis of the pull-in dynamic transition. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 37–42 (2004)
Sharma, M., Sarraf, E.H., Cretu, E.: A novel dynamic pull-in MEMS gyroscope. Procedia Eng. 25, 55–58 (2011)
Pallay, M., Daeichin, M., Towfighian, S.: Dynamic behavior of an electrostatic MEMS resonator with repulsive actuation. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(2), 1525–1538 (2017)
Pallay, M., Towfighian, S.: Feasibility study of a capacitive MEMS filter using electrostatic levitation. In: International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Aug 2019. American Society of Mechanical Engineers (2019)
Daeichin, M., Ozdogan, M., Towfighian, S., Miles, R.N.: Dynamic response of a tunable MEMS accelerometer based on repulsive force. A Phys. Sens. Actuators 289, 34–43 (2019)
Ozdogan, M., Daeichin, M., Ramini, A., Towfighian, S.: Parametric resonance of a repulsive force MEMS electrostatic mirror. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 265, 20–31 (2017)
Miles, R.N.: A compliant capacitive sensor for acoustics: avoiding electrostatic forces at high bias voltages. IEEE Sens. J. 18(14), 5691–5698 (2018)
Miles, R.N.: Physical Approach to Engineering Acoustics. Springer, New York (2019)
Daeichin, M., Miles, R.N., Towfighian, S.: Experimental characterization of the electrostatic levitation force in MEMS transducers. J. Vib. Acoust. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4046625
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of this study by the National Science Foundation (NSF) through Grant ECCS 1608692.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daeichin, M., Miles, R. & Towfighian, S. Lateral pull-in instability of electrostatic MEMS transducers employing repulsive force. Nonlinear Dyn 100, 1927–1940 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05614-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05614-6