Abstract
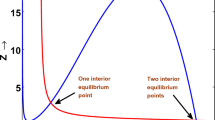
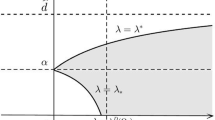
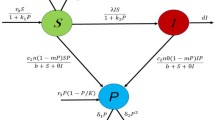
In this paper, we have investigated the effects of spatial diffusion in the pattern formation of a predator–prey system with quadratic mortality rate of the predator in the presence of habitat complexity. Using linear stability analysis, the regions of parameter space are plotted, and several kinds of instability regions are identified. Special attention has been given to investigate the selection of spatio-temporal patterns in the neighborhood of a critical parameter using the amplitude equation formalism. Choosing control parameter from the Turing space, the existence conditions for stable patterns are derived using the amplitude equations. Results obtained from theoretical analysis of amplitude equations agree very well with the numerical simulation results near the critical parameter value. Numerical simulations are done to show the existence of different spatio-temporal patterns. Spiral patterns are obtained in the suitable parameter region. It is shown that varying only the death rate of the predator, the spatio-temporal chaos can be controlled. Our investigations show that patterns are sensitive to the variation of habitat complexity and death rate of predator and patterns can be controlled by tuning the death rate of the predator.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levin, S.A.: The problem of pattern and scale in ecology: the Robert H MacArthur award lecture. Ecology 73(6), 1943–1967 (1992)
MacArthur, R.H.: Geographical Ecology: Patterns in the Distribution of Species. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1972)
Rietkerk, M., Koppel, J.V.D.: Regular pattern formation in real ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 23(3), 169–175 (2008)
Solé, R.V., Bascompte, J.: Self-Organization in Complex Ecosystems. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2006)
Turing, A.M.: On the chemical basis of morphogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B: Biol. Sci. 237, 37–72 (1952)
Sen, S., Ghosh, P., Riaz, S.S., Ray, D.S.: Spatial periodicity induced by a chemical wave train. Phys. Rev. E 81(1), 017101 (2010)
Cross, M.C., Hohenberg, P.C.: Pattern formation outside of equilibrium. Rev. Mod. Phys. 65(3), 851–1112 (1993)
Segel, L.A., Jackson, J.L.: Dissipative structure: an explanation and an ecological example. J. Theor. Biol. 37(3), 545–559 (1972)
Medvinsky, A.B., Petrovskii, S.B., Tikhonova, I.A., Malchow, H., Li, B.L.: Spatiotemporal complexity of plankton and fish dynamics. SIAM Rev. 44(3), 311–370 (2002)
Zhao, H., Huang, X., Zhang, X.: Turing instability and pattern formation of neural networks with reaction–diffusion terms. Nonlinear Dyn. 76(1), 115–124 (2014)
Ghorai, S., Poria, S.: Turing patterns induced by cross-diffusion in a predator–prey system in presence of habitat complexity. Chaos Solitons Fractals 91, 421–429 (2016)
Ma, J., Xu, Y., Ren, G., Wang, C.: Prediction for breakup of spiral wave in a regular neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 84(2), 497–509 (2016)
Chen, J.X., Guo, M.M., Ma, J.: Termination of pinned spirals by local stimuli. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 113(3), 38004 (2016)
Xu, Y., Jin, W., Ma, J.: Emergence and robustness of target waves in a neuronal network. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 29(23), 1550164 (2015)
Qin, H., Wu, Y., Wang, C., Ma, J.: Emitting waves from defects in network with autapses. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 23(1), 164–174 (2015)
Liu, T.B., Ma, J., Zhao, Q., Tang, J.: Force exerted on the spiral tip by the heterogeneity in an excitable medium. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 104(5), 58005 (2014)
Chattopadhyay, J., Tapaswi, P.K.: Effect of cross-diffusion on pattern formation—a nonlinear analysis. Acta Appl. Math. 48(1), 1–12 (1997)
Chaudhuri, S., Chattopadhyay, J., Venturino, E.: Toxic phytoplankton-induced spatiotemporal patterns. J. Biol. Phys. 38(2), 331–348 (2012)
Wang, T.: Pattern dynamics of an epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate. Nonlinear Dyn. 77(1–2), 31–40 (2014)
Chakraborty, K., Manthena, V.: Modelling and analysis of spatio-temporal dynamics of a marine ecosystem. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(4), 1895–1906 (2015)
Xu, J., Yang, G., Xi, H., Su, J.: Pattern dynamics of a predator–prey reaction–diffusion model with spatiotemporal delay. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(4), 2155–2163 (2015)
Newell, A.C., Whitehead, J.A.: Finite bandwidth, finite amplitude convection. J. Fluid Mech. 38(02), 279–303 (1969)
Wang, W., Lin, Y., Rao, F., Zhang, L., Tan, Y.: Pattern selection in a ratio-dependent predator–prey model. J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp. 2010(11), P11036 (2010)
Sun, G., Jin, Z., Liu, Q., Li, L.: Pattern formation induced by cross-diffusion in a predator–prey system. Chin. Phys. B 17(11), 3936–3941 (2008)
Yuan, S., Xu, C., Zhang, T.: Spatial dynamics in a predator–prey model with herd behavior. Chaos 23(3), 033102 (2013)
Zhang, T., Xing, Y., Zang, H., Han, M.: Spatio-temporal dynamics of a reaction–diffusion system for a predator–prey model with hyperbolic mortality. Nonlinear Dyn. 78(1), 265–277 (2014)
Orth, R.J.: The importance of sediment stability in seagrass communities. Ecol. Mar. Benthos 6, 281–300 (1977)
Stoner, A.W.: Species-specific predation on amphipod crustacea by the pinfish Lagodon rhomboides: mediation by macrophyte standing crop. Mar. Biol. 55(3), 201–207 (1979)
Savino, J.F., Stein, A.: Predator–prey interaction between largemouth bass and bluegills as influenced by simulated, submersed vegetation. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 111(3), 255–266 (1982)
Savino, J.F., Stein, R.A.: Behavioural interactions between fish predators and their prey: effects of plant density. Anim. Behav. 37, 311–321 (1989)
Anderson, O.: Optimal foraging by largemouth bass in structured environments. Ecology 65(3), 851–861 (1984)
Ryer, C.H.: Pipefish foraging Effects of fish size, prey size and altered habitat complexity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 48(1), 37–45 (1988)
Pennings, S.C.: Predator–prey interactions in opisthobranch gastropods: effects of prey body size and habitat complexity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 62, 95–101 (1990)
Grabowski, J.H.: Habitat complexity disrupts predator–prey interactions but not the trophic cascade on oyster reefs. Ecology 85(4), 995–1004 (2004)
Sahoo, B., Poria, S.: Effects of additional food in a delayed predator–prey model. Math. Biosci. 261, 62–73 (2015)
Luckinbill, L.S.: Coexistence in laboratory populations of Paramecium aurelia and its predator Didinium nasutum. Ecology 54(6), 1320–1327 (1973)
Edwards, A.M., Brindley, J.: Oscillatory behaviour in a three-component plankton population model. Dyn. Stab. Syst. 11(4), 347–370 (1996)
Baurmann, M., Gross, T., Feudel, U.: Instabilities in spatially extended predator–prey systems: spatio-temporal patterns in the neighborhood of Turing–Hopf bifurcations. J. Theor. Biol. 245(2), 220–229 (2007)
Jana, D., Bairagi, N.: Habitat complexity, dispersal and metapopulations: macroscopic study of a predator–prey system. Ecol. Complex. 17, 131–139 (2014)
Kot, M.: Elements of Mathematical Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Sahoo, B., Poria, S.: Effects of additional food on an ecoepidemic model with time delay on infection. Appl. Math. Comput. 245, 17–35 (2014)
Fulton, E.A., Smith, A.D., Johnson, C.R.: Mortality and predation in ecosystem models: is it important how these are expressed? Ecol. Model. 169(1), 157–178 (2003)
Ghorai, S., Poria, S.: Pattern formation and control of spatiotemporal chaos in a reaction diffusion prey–predator system supplying additional food. Chaos Solitons Fractals 85, 57–67 (2016)
Wang, W., Liu, Q.X., Jin, Z.: Spatiotemporal complexity of a ratio-dependent predator–prey system. Phys. Rev. E 75(5), 051913 (2007)
Dufiet, V., Boissonade, J.: Dynamics of Turing pattern monolayers close to onset. Phys. Rev. E 53(5), 4883 (1996)
Wang, W., Zhang, L., Wang, H., Li, Z.: Pattern formation of a predator–prey system with Ivlev-type functional response. Ecol. Model. 221(2), 131–140 (2010)
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorai, S., Poria, S. Emergent impacts of quadratic mortality on pattern formation in a predator–prey system. Nonlinear Dyn 87, 2715–2734 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3222-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3222-2