Abstract
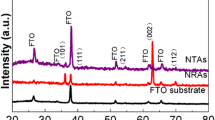
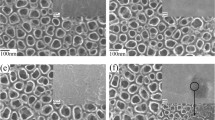
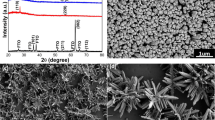
Anatase TiO2 nanoplates, with average side length ranging from 90 to 200 nm and average thickness ranging from 20 to 60 nm, were successfully fabricated by annealing anodized TiO2 nanotubes with different heating rates. The as-synthesized TiO2 nanoplates and nanotubes were analyzed by field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. To investigate the growth mechanism of the TiO2 nanoplates dominated by highly reactive {001} facets, different heating rates were applied appropriately during the thermal treatment. The results revealed that the heating rate during thermal treatment is critical in determining the nanostructure of anatase TiO2. The fast heating rate (samples were annealed when the temperature heated up to 450 °C) and the brittle property are the main reasons for the collapse of the anodized TiO2 nanotubes. The nanosized TiO2 species grow into TiO2 nanoplates with the exposed 60 % of {001} facets because the fluorated surface of TiO2 species can direct the formation of TiO2 nanoplates with exposed {001} facets. The photoactivity of the TiO2 nanoplates is higher than that of TiO2 nanotubes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger S, Kunze J, Schmuki P, Valota AT, LeClere DJ, Skeldon P, Thompson GE (2010) Influence of water content on the growth of anodic TiO2 nanotubes in fluorine-containing ethylene glycol electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 157:18–23
Cochran RE, Shyue JJ, Padture NP (2007) Template-based, near-ambient synthesis of crystalline metal-oxide nanotubes, nanowires and coaxial nanotubes. Acta Mater 55:3007–3014
Crawford GA, Chawla N (2009) Porous hierarchical TiO2 nanostructures: processing and microstructure relationships. Acta Mater 57:854–867
Formo E, Lee E, Campbell D, Xia YN (2008) Functionalization of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers with Pt nanoparticles and nanowires for catalytic applications. Nano Lett 8:668–672
Grimes CA (2007) Synthesis and application of highly ordered arrays of TiO2 nanotubes. J Mater Chem 17:1451–1457
Han XG, Kuang Q, Jin MS, Xie ZX, Zheng LS (2009) Synthesis of titania nanosheets with a high percentage of exposed (001) facets and related photocatalytic properties. J Am Chem Soc 131:3152–3153
Hirakata H, Ito KJ, Yonezu A, Tsuchiya H, Fujimoto SJ, Minoshima KJ (2010) Strength of self-organized TiO2 nanotubes arrays. Acta Mater 58:4956–4967
Koo HJ, Kim YJ, Lee YH, Lee WI, Kim YK, Park NG (2008) Nano-embossed hollow spherical TiO2 as bifunctional material for high-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv Mater 20:195–199
Kumar A, Jose R, Fujihara K, Wang J, Ramakrishna S (2007) Structural and optical properties of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers. Chem Mater 19:6536–6542
Liu SW, Yu JG, Jaroniec M (2011) Anatase TiO2 with dominant high-energy 001 facets: synthesis, properties, and applications. Chem Mater 23:4085–4093
Macak JM, Zlamal M, Krysa J, Schmuki P (2007) Self-organized TiO2 nanotube layers as highly efficient photocatalysts. Small 3:300–304
Park JH, Lee TW, Kang MG (2008) Growth, detachment and transfer of high-ordered TiO2 nanotubes arrays: use in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Commun 25:2867–2869
Regonini D, Jaroenworaluck A, Stevens R, Bowen CR (2010) Effect of heat treatment on the properties and structure of TiO2 nanotubes: phase composition and chemical composition. Surf Interface Anal 42:139–144
Robel I, Kuno M, Kamat PV (2007) Size-dependent electron injection from excited CdSe quantum dots into TiO2 nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 129:4136–4137
Roy P, Kim D, Lee K, Spiecker E, Schmuki P (2009) TiO2 nanotubes and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 2:45–59
Roy P, Berger S, Schmuki P (2011) TiO2 nanotubes: synthesis and applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:2904–2939
Shokuhfar T, Arumugam GK, Heiden PA, Yassar RS, Friedrich C (2009) Direct compressive measurements of individual titanium dioxide nanotubes. ACS Nano 3:3098–3102
Stein FS, Thiemann S, Berger S, Hahn R, Schmuki P (2010) Mechanical properties of anatase and semi-metallic TiO2 nanotubes. Acta Mater 58:6317–6323
Stergiopoulos T, Ghicov A, Likodimos V, Tsoukleris DS, Kunze J, Schmuki P, Falaras P (2008) Dye-sensitized solar cells based on thick highly ordered TiO2 nanotubes produced by controlled anodic oxidation in non-aqueous electrolytic media. Nanotechnology 19:235602–235609
Tang J, Redl F, Zhu YM, Siegrist T, Brus LE, Steigerwald ML (2005) An organometallic synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles. Nano Lett 5:543–548
Taveira LV, Macak JM, Tsuchiya H, Dick LFP, Schmuki P (2005) Initiation and growth of self-organized TiO2 nanotubes anodically formed in NH4F/(NH4)2SO4 electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 152:B405–B410
Wang CY, Bahnemann DW, Dohrmann JK (2000) A novel preparation of iron-doped TiO2 nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem Commun 16:1539–1540
Wang D, Liu Y, Yu B, Zhou F, Liu WM (2009a) TiO2 Nanotubes with tunable morphology, diameter, and length: synthesis and photo-electrical/catalytic performance. Chem Mater 21:1198–1206
Wang D, Yu B, Wang CW, Zhou F, Liu WM (2009b) A novel protocol toward perfect alignment of anodized TiO2 nanotubes. Adv Mater 21:1964–1967
Xiang QJ, Lv KG, Yu JG (2010) Pivotal role of fluorine in enhanced photocatalytic activity of anatase TiO2 nanosheets with dominant (001) facets for the photocatalytic degradation of acetone in air. Appl Catal B 96:557–564
Xiang QJ, Yu JG, Wang WG, Jaroniec M (2011) Nitrogen self-doped nanosized TiO2 sheets with exposed 001 facets for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Chem Commun 47:6906–6908
Yan JF, Zhou F (2011) TiO2 nanotubes: structure optimization for solar cells. J Mater Chem 21:9406–9418
Yang HG, Sun CH, Qiao SZ, Zou J, Liu G, Smith SC, Jin Z, Cheng HM, Lu GQ (2008) Anatase TiO2 single crystals with a large percentage of reactive facets. Nature 453:06964–06968
Yang HG, Liu G, Qiao SZ, Sun CH, Jin YG, Smith SC, Cheng HM, Lu GQ (2009) Solvothermal synthesis and photoreactivity of anatase TiO2 nanosheets with dominant 001 facets. J Am Chem Soc 131:4078–4083
Yang WG, Li JM, Wang YL, Zhu F, Shi WM, Wan FR, Xu DS (2011a) A facile synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanosheets-based hierarchical spheres with over 90% 001 facets for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Commun 47:1809–1811
Yang XH, Li Z, Liu G, Xing J, Sun CH, Yang HG, Li CZ (2011b) Ultra-thin anatase TiO2 nanosheets dominated with 001 facets: thickness-controlled synthesis, growth mechanism and water-splitting properties. Cryst Eng Comm 13:1378–1383
Yu JG, Fan JJ, Lv K (2010) Anatase TiO2 nanosheets with exposed (001) facets: improved photoelectric conversion efficiency in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 2:2144–2149
Yu JG, Dai GP, Xiang QJ, Jaroniec M (2011a) Fabrication and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of carbon self-doped TiO2 sheets with exposed 001 facets. J Mater Chem 21:1049–1057
Yu JG, Fan JJ, Cheng B (2011b) Dye-sensitized solar cells based on anatase TiO2 hollow spheres/carbon nanotube composite films. J Power Sources 196:7891–7898
Zheng Q, Zhou BX, Bai J, Li LH, Jin ZJ, Zhang JL, Li JH, Liu YB, Cai WM, Zhu XY (2008) Self-organized TiO2 nanotube array sensor for the determination of chemical oxygen demand. Adv Mater 20:1044–1049
Acknowledgments
Financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51172159) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Cui, Z., Zhu, S. et al. Fabrication, characterization, and photocatalytic properties of anatase TiO2 nanoplates with exposed {001} facets. J Nanopart Res 16, 2191 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2191-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2191-3