Abstract
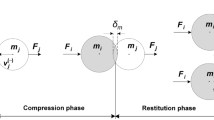
In this work, a new dissipative contact force model, based on the foundation of Hertz contact law, is presented for impact analysis in multibody dynamics. A hysteresis damping force is introduced in the model for capturing the energy loss during the contact process. An approximate function, representing the relationship between the deformation velocity and deformation, is used to calculate the energy loss due to the damping force. The difference between the compression phase and restitution phase during the contact process is taken into account in the energy loss calculation. For illustration, four different contact force models are applied in a numerical example to compare their behaviors. The results are presented in the form of dynamic simulations in a multibody system, which allow comparison of the differences and similarities among the four contact models. They show the validity of our model for soft or hard contact problems.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- i,j :
-
solid sphere
- \(v_{i}^{ ( - )},v_{j}^{ ( - )}\) :
-
initial velocity
- \(v_{i}^{ ( + )},v_{j}^{ ( + )}\) :
-
separation velocity
- t (−) :
-
time of initial contact
- t (+) :
-
time of separation
- t (m) :
-
time of maximum deformation
- R i ,R j :
-
radius of solid sphere
- F N :
-
normal contact force
- δ :
-
deformation or indentation
- K :
-
generalized stiffness
- n :
-
Hertz’s contact force exponent
- T (−),T (+) :
-
kinetic energies of the two spheres before and after impact
- E :
-
Young’s modulus
- λ :
-
Poisson’s ratio
- \(\dot{\delta}^{ ( + )}\) :
-
relative separation velocity
- ΔE :
-
energy loss
- e :
-
coefficient of restitution
- m :
-
equivalent mass
- \(\dot{\delta}^{ ( - )}\) :
-
initial deformation velocity
- D :
-
hysteresis damping coefficient
- c :
-
hysteresis damping factor
- δ m :
-
maximum deformation
- \(\dot{\delta}\) :
-
relative normal velocity
- ΔE c ,ΔE r :
-
energy loss for compression or restitution
References
Greenwood, D.T.: Principles of Dynamics. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1965)
Dubowsky, S., Deck, J.F., Costello, H.: The dynamic modeling of flexible spatial machine systems with clearance connections. J. Mech. Transm.—T. ASME 109(1), 87–94 (1987)
Shabana, A.A.: Dynamics of Multibody Systems. Wiley, New York (1989)
Pfeiffer, F., Glocker, C.: Multibody Dynamics with Unilateral Contacts. Wiley, New York (1996)
Bai, Z.F., Zhao, Y.: Dynamic behaviour analysis of planar mechanical systems with clearance in revolute joints using a new hybrid contact force model. Int. J. Mech. Sci. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2011.10.009
Tian, Q., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Flores, P.: Dynamics of spatial flexible multibody systems with clearance and lubricated spherical joints. Comput. Struct. 87(13–14), 913–929 (2009)
Mukras, S., Mauntler, N.A., Kim, N.H., Schmitz, T.L., Sawyer, W.G.: Modeling a slider–crank mechanism with joint wear. SAE Int. J. Passeng. 2(1), 600 (2009)
Erkaya, S., Uzmay, İ.: Optimization of transmission angle for slider–crank mechanism with joint clearances. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 37(5), 493–508 (2009)
Wojtkowski, M., Pecen, J., Horabik, J., Molenda, M.: Rapeseed impact against a flat surface: Physical testing and DEM simulation with two contact models. Powder Technol. 198(1), 61–68 (2010)
Machado, M., Flores, P., Claro, J., Ambrósio, J., Silva, M., Completo, A., Lankarani, H.: Development of a planar multibody model of the human knee joint. Nonlinear Dyn. 60(3), 459–478 (2010)
Flores, P., Lankarani, H.: Spatial rigid-multibody systems with lubricated spherical clearance joints: modeling and simulation. Nonlinear Dyn. 60(1), 99–114 (2010)
Zhao, Y., Bai, Z.F.: Dynamics analysis of space robot manipulator with joint clearance. Acta Astronaut. 68(7–8), 1147–1155 (2011)
Flores, P.: A parametric study on the dynamic response of planar multibody systems with multiple clearance joints. Nonlinear Dyn. (2010). doi:10.1007/s1171-010-9676-71-010-8
Flores, P., Leine, R., Glocker, C.: Modeling and analysis of planar rigid multibody systems with translational clearance joints based on the non-smooth dynamics approach. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 23(2), 165–190 (2010)
Flores, P., Machado, M., Silva, M., Martins, J.: On the continuous contact force models for soft materials in multibody dynamics. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 25(3), 357–375 (2011)
Tasora, A., Anitescu, M., Negrini, S., Negrut, D.: A compliant visco-plastic particle contact model based on differential variational inequalities. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 53, 2–12 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2013.01.010
Bai, Z.F., Zhao, Y.: A hybrid contact force model of revolute joint with clearance for planar mechanical systems. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 48, 15–36 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2012.07.003
Lin, Y., Haftka, R.T., Queipo, N.V., Fregly, B.J.: Surrogate articular contact models for computationally efficient multibody dynamic simulations. Med. Eng. Phys. 32(6), 584–594 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2010.02.008
Anitescu, M., Potra, F.A., Stewart, D.E.: Time-stepping for three-dimensional rigid body dynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 177(3–4), 183–197 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0045-7825(98)00380-6
Pang, J., Stewart, D.: Differential variational inequalities. Math. Program. 113(2), 345–424 (2008). doi:10.1007/s10107-006-0052-x
Tasora, A., Negrut, D., Anitescu, M.: Large-scale parallel multi-body dynamics with frictional contact on the graphical processing unit. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Proc., Part K, J. Multi-Body Dyn. 222(4), 315–326 (2008)
Lankarani, H.M., Nikravesh, P.E.: A contact force model with hysteresis damping for impact analysis of multibody systems. J. Mech. Des. 112(3), 369–376 (1990)
Flores, P.: Compliant contact force approach for forward dynamic modeling and analysis of biomechanical systems. Proc. IUTAM 2, 58–67 (2011)
Machado, M., Moreira, P., Flores, P., Lankarani, H.M.: Compliant contact force models in multibody dynamics: Evolution of the Hertz contact theory. Mech. Mach. Theory 53, 99–121 (2012)
Ravn, P.: A continuous analysis method for planar multibody systems with joint clearance. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2, 1–24 (1998)
Lankarani, H.M., Nikravesh, P.E.: Continuous contact force models for impact analysis in multibody systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 5(2), 193–207 (1994)
Hunt, K.H., Crossley, F.R.E.: Coefficient of restitution interpreted as damping in vibroimpact. J. Appl. Mech. 42(2), 440–445 (1975)
Herbert, R.G., Mcwhannell, D.C.: Shape and frequency composition of pulses from an impact pair. J. Eng. Ind. 99(3), 513–518 (1977)
Lee, T.W., Wang, A.C.: On the dynamics of intermittent-motion mechanisms. Part 1: Dynamic model and response. J. Mech. Transm.—T. ASME 105(3), 534–540 (1983)
Gonthier, Y., Mcphee, J., Lange, C., Piedbœuf, J.: A regularized contact model with asymmetric damping and dwell-time dependent friction. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 11(3), 209–233 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:MUBO.0000029392.21648.bc
Zhiying, Q., Qishao, L.: Analysis of impact process based on restitution coefficient. J. Dyn. Control 4, 294–298 (2006)
Jackson, R., Green, I., Marghitu, D.: Predicting the coefficient of restitution of impacting elastic-perfectly plastic spheres. Nonlinear Dyn. 60(3), 217–229 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11071-009-9591-z
Seifried, R., Schiehlen, W., Eberhard, P.: The role of the coefficient of restitution on impact problems in multi-body dynamics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Proc., Part K, J. Multi-Body Dyn. 224(3), 279–306 (2010)
Braccesi, C., Landi, L.: A general elastic–plastic approach to impact analysis for stress state limit evaluation in ball screw bearings return system. Int. J. Impact Eng. 34(7), 1272–1285 (2007)
Zhang, X., Vu-Quoc, L.: Modeling the dependence of the coefficient of restitution on the impact velocity in elasto-plastic collisions. Int. J. Impact Eng. D 27(3), 317–341 (2002)
Ye, K., Zhu, H.: A note on the Hertz contact model with nonlinear damping for pounding simulation. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 38(9), 1135–1142 (2008)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the financial supports form the Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, S., Guo, X. A dissipative contact force model for impact analysis in multibody dynamics. Multibody Syst Dyn 35, 131–151 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-015-9453-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-015-9453-z