Abstract
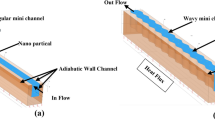
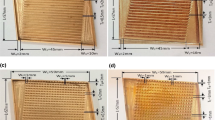
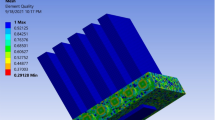
The present research investigates the performance of a proposed variable channel width double-layered minichannel heat sink (VWC DL-MCHS) with advanced coolants. Nanofluids such as Al2O3–water and CuO–water with nanoparticle concentration (Øp) of 1%, 5% and 9% and n-octadecane–water NEPCM slurries with particle concentration (Cm) of 5%, 10% and 20% are used as advanced coolants. Along with that, the effect of the dimensionless stepped fin length (λ) on the thermal performance of a VWC DL-MCHS is investigated by considering various values of λ (0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1). The results show that VWC DL-MCHS performs better as compared to conventional DL-MCHS. A VWC DL-MCHS with zero overlap and λ = 0.8 using CuO–water (Øp = 1%) nanofluid as coolant turns out the best configuration. Therefore, a VWC DL-MCHS with λ = 0.8 and zero overlap with advanced coolants would serve as an efficient thermal management solution for microelectronics devices.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naqiuddin NH, Saw LH, Yew MC, Yusof F, Ng TC, Yew MK. Overview of micro-channel design for high heat flux application. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;82:901–14.
Vafai K, Zhu L. Analysis of two-layered micro-channel heat sink concept in electronic cooling. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1999;42:2287–97.
Lu S, Vafai K. A comparative analysis of innovative microchannel heat sinks for electronic cooling. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:271–84.
Sharma D, Garg H, Singh PP, Karar V. Numerical study on the performance of double layer microchannel with liquid gallium and water. Adv Mech Eng. 2013;2013:32458. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/324578.
Azizi Z, Alamdari A, Malayeri MR. Thermal performance and friction factor of a cylindrical microchannel heat sink cooled by Cu-water nanofluid. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;99:970–8.
Radwan A, Ahmed M, Ookawara S. Performance enhancement of concentrated photovoltaic systems using a microchannel heat sink with nanofluids. Energy Convers Manag. 2016;119:289–303.
Arabpour A, Karimipour A, Toghraie D. The study of heat transfer and laminar flow of kerosene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) nanofluid in the microchannel heat sink with slip boundary condition. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131(2):1553–66.
Mashayekhi R, Khodabandeh E, Akbari OA, Toghraie D, Bahiraei M, Gholami M. CFD analysis of thermal and hydrodynamic characteristics of hybrid nanofluid in a new designed sinusoidal double-layered microchannel heat sink. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;134(3):2305–15.
Khodabandeh E, Rozati SA, Joshaghani M, Akbari OA, Akbari S, Toghraie D. Thermal performance improvement in water nanofluid/GNP–SDBS in novel design of double-layer microchannel heat sink with sinusoidal cavities and rectangular ribs. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136(3):1333–45.
Wang SL, Chen LY, Zhang BX, Yang YR, Wang XD. A new design of double-layered microchannel heat sinks with wavy microchannels and porous-ribs. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09317-3.
Mohd-Ghazali N, Estellé P, Halelfadl S, Maré T, Siong TC, Abidin U. Thermal and hydrodynamic performance of a microchannel heat sink with carbon nanotube nanofluids: effect of concentration and channel section. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138(2):937–45.
Heidarshenas A, Azizi Z, Peyghambarzadeh SM, Sayyahi S. Experimental investigation of the particle size effect on heat transfer coefficient of Al2O3 nanofluid in a cylindrical microchannel heat sink. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09033-7.
Chamkha AJ, Molana M, Rahnama A, Ghadami F. On the nanofluids applications in microchannels: a comprehensive review. Powder Technol. 2018;332:287–322.
Chai L, Shaukat R, Wang L, Wang HS. A review on heat transfer and hydrodynamic characteristics of nano/microencapsulated phase change slurry (N/MPCS) in mini/microchannel heat sinks. Appl Thermal Eng. 2018;135s:334–49.
Patel N, Mehta HB. Stacked minichannel heat sink. The filed design patent is granted and published in the Indian Patent Journal No. 28/2019 with Application No. 303545.
Patel N, Mehta HB. Investigations on a variable channel width double layered minichannel heat sink. IEEE Trans Compon Packag Manuf Technol. 2019;09(10):2036–45.
Lorenzini-gutierrez D, Kandlikar SG. Variable fin density flow channels for effective cooling and mitigation of temperature nonuniformity in three-dimensional integrated circuits. J Electron Packag. 2014;136:1–11.
Khanafer K, Vafai K. A critical synthesis of thermophysical characteristics of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54(19–20):4410–28.
Nguyen CT, Desgranges F, Roy G, Galanis N, Maré T, Boucher S, Angue MH. Temperature and particle-size dependent viscosity data for water-based nanofluids—hysteresis phenomenon. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2007;28(6):1492–506.
Rimbault B, Nguyen CT, Galanis N. Experimental investigation of CuO–water nanofluid flow and heat transfer inside a microchannel heat sink. Int J Therm Sci. 2014;84:275–92.
Wei X, Joshi Y, Patterson MK. Experimental and numerical study of a stacked microchannel heat sink for liquid cooling of microelectronic devices. J Heat Transf. 2007;129:1432–44.
Peyghambarzadeh SM, Hashemabadi SH, Chabi AR, Salimi M. Performance of water based CuO and Al2O3 nanofluids in a Cu-Be alloy heat sink with rectangular microchannels. Energy Convers Manag. 2014;86:28–38.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, Government of India under the Core Research Grant Sanction No. SERB/EMR/2017/000429.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Thermophysical properties of CuO–water nanofluid
The equations reported by Minsta et al. [20] are shown below.
-
For Øp = 9.3% → \(k_{\text{eff}}\) = 0.003 \(T_{\text{f}}\) (°C) + 0.61
-
For Øp = 6.1% → \(k_{\text{eff}}\) = 0.0032 \(T_{\text{f}}\) (°C) + 0.59
-
For Øp = 3.3% → \(k_{\text{eff}}\) = 0.0044 \(T_{\text{f}}\) (°C) + 0.53.
From these equations, Nguyen and Rimbault et al. [20] have interpolated and determined the following correlations.
-
For Øp = 4.5% → \(k_{\text{eff}}\) = (1.041E − 17)\(T_{\text{f}}^{2}\)(°C) + 0.00388571428571341000 \(T_{\text{f}}\) + 0.555714285714301
-
For Øp = 1.03% → \(k_{\text{eff}}\) = 0.00223214447146814000 \(T_{\text{f}}\)(°C) + 0.63975654568569
-
For Øp = 0.24% → \(k_{\text{eff}}\) = 0.00147769254744161000 \(T_{\text{f}}\)(°C) + 0.57579978104837900000.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, N., Mehta, H.B. Investigations on a variable channel width double-layered minichannel heat sink using advanced coolants. J Therm Anal Calorim 145, 3359–3379 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09904-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09904-4