Abstract
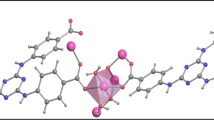
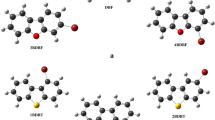
Two different single crystals of 1,3,5-trinitro-4,6-diazidobenzene (C6HN9O6) were measured by X-ray single-crystal diffraction. The molecular weight of C6HN9O6 is 295.16. Crystal I system is orthorhombic, and space groups are Pbca, a = 10.5199 (19) nm, b = 13.436 (3) nm, c = 15.235 (3) nm, β = 90°, V = 2153.4 (7) nm3, Z = 8, Dc = 1.821 g cm−3, μ = 0.164 mm−1, F(000) = 1184. Crystal II system is tetragonal, and space groups are P42/no a = b = 19.412 (5) nm, c = 5.9603 (17) nm, β = 90°, V = 2246.0 (13) nm3, Z = 8, Dc = 1.746 g cm−3, μ = 0.157 mm−1, F(000) = 1184. Enthalpy of formation and detonation properties were calculated at the DFT-B3LYP/6-311++G ** level. It shows that these two compounds all have good detonation performance, among which crystal I has higher detonation velocity (8.81 km s−1) and detonation pressure (34.65 GPa) than those of crystal II. The thermal behavior of the crystal I was studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)–thermal gravimetric (TG) analysis, melting peak is at 94.80 °C, and two decomposition exothermic peaks are at 126.39 °C and 212.10 °C, respectively, in DSC curve. According to the Kissinger and Flynn–Wall–Ozawa methods, the activation energy (E) calculated for the first decomposition of the crystal I is 109.25 kJ mol−1 and 110.67 kJ mol−1, respectively, and second decomposition is 121.05 kJ mol−1 and 124.35 kJ mol−1, respectively. In addition, the accelerating rate calorimeter (ARC) was used to further study the adiabatic decomposition behavior. The E of the two decompositions is 128.70 kJ mol−1 and 302.55 kJ mol−1, respectively, and the pre-exponential (A) is 1.02 × 1016 s−1 and 2.01 × 1035 s−1, respectively, by ARC data. The mechanism functions were f(α) = 2α0.5 (first decomposition) and f(α) = 3α2/3 (second decomposition).















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chavez DE, Hiskey MA, Gilardi RD. 3,3′-Azobis(6-amino-1,2,4,5-tetrazine): a novel high-nitrogen energetic material. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2000;39:1791.
Yang SQ, Xu SL, Huang HJ, Zhang W, Zhang XG. High nitrogen compounds and energetic materials. Prog Chem. 2008;20:526–37.
Jiang YB, Qi CX, Han CM. Advances in the synthesis of organic azides. Chin J Org Chem. 2016;32:2231–8.
Li YC, Zhang XJ, Fu W, Pang SP, Zhang CL. Synthesis, characterization and thermal decomposition of 4,4′,6,6′-tetraazidoazo-1,3,5-triazine (TAAT). Chin J Org Chem. 2012;31:1484–9.
Gao FL, Ji YP, Liu WX, Wang YL, Chen B, Liu YJ, Ding F. Synthesis and characterization of pentanol-3-nitraza-5-azidonitrate. Chin J Energy Mater. 2015;23:302–3.
Li YC, Zhang XJ, Fu W, Pang SP, Zhao CL. Synthesis, characterization and thermal decomposition mechanism of 4,4′,6,6′-tetra(azido)azo-1,3,5-triazine (TAAT). Chin J Org Chem. 2011;31:1484–9.
Pourmortazavi SM, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Kohsari I, Hajimirsadeghi SS. Non-isothermal kinetic studies on thermal decomposition of energetic materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110(2):857–63.
Abusaidi H, Ghaieni HR, Pourmortazavi SM, et al. Effect of nitro content on thermal stability and decomposition kinetics of nitro-HTPB. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:935–41.
Pourmortazavi SM, Mirzajani V, Farhadi K. Thermal behavior and thermokinetic of double-base propellant catalyzed with magnesium oxide nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;137:93–104.
Mirzajani V, Farhadi K, Pourmortazavi SM. Catalytic effect of lead oxide nano- and microparticles on thermal decomposition kinetics of energetic compositions containing TEGDN/NC/DAG. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:937–48.
Li J, Chen LZ, Wang JL, Lan GC, Hou H, Li M. Crystal structure and thermal decomposition kinetics of byproduct of synthesis of RDX: 3,5-dinitro-1-oxygen-3,5-diazacyclohexane. Acta Phys Chim Sin. 2015;31:2049–56.
Zhang CY, Jin SH, Ji JW, Jing BC, Bao F, Zhang GY, Shu QH. Thermal hazard assessment of TNT and DNAN under adiabatic condition by using accelerating rate calorimeter (ARC). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;131:89–93.
Bailey AS, Case JR. 4:6-dinitrobenzofuroxan, nitrobenzodifuroxan and benzotrifuroxan: a new series of complex-forming reagents for aromatic hydrocarbons. Tetrahedron. 1958;3:113–31.
Lu CY, Sheng DL, Chen LK, Huo H, Zhu YH, Yang B. Preparation of ultrafine CL-18 and research on its narrow pulse detonation performance. Chin J Explos Propell. 2013;36:47–50.
Huo H, Wang BZ, Zhou C, Zhou YS, Luo YF. Synthesis, characterization and performances of 7-amino-6-nitrobenzodifuroxans. Chin J Org Chem. 2011;31:701–7.
Cheng CS, Qin FT, Wei ZY. Chemical safety production and reaction risk assessment. 1st ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2011.
Budyka FM. Photodissociation of aromatic azides. Russ Chem Rev. 2008;77(8):709–23.
Sheldrick GM. SHELXS-97, program for X-ray crystal structure refinement. Göttingen: Göttingen University; 1997.
Sheldrick GM. SHELXS-97, program for X-ray crystal structure solution. Göttingen: Göttingen University; 1997.
Li YL, Liu TY, Cao DL, Wang JL. Theoretical study on structure and properties of tetranitropyrrole and its derivatives. J Energy Mater. 2017;25:291–7.
Tou JC, Whiting LF. The thermokinetic performance of an accelerating rate calorimeter. Thermochim Acta. 1981;48:21–42.
Zhao GL, Yan GX. Estimation of thermodynamic data of organic matter. Beijing: Higher Education Publishing Society; 1983. p. 113–4.
Allen FH, Kennard O, Watson DG. Tables of bond lengths determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Part I. Bond lengths in organic compounds. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1987;7:1–19.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29(11):1702.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38(11):1881.
Chen LZ, Liu W, Wang JL, Cao DL. Crystal structure and thermal decomposition kinetics of 3-nitro-4-diazo-5-oxygenpyrazole. Chin J Struct Chem. 2018;37:1807–902.
Liu W, Liu ZX, Wang JL, Cao DL, Chen LZ. Adiabatic decomposition analysis of 3,4-dinitropyrazole based on accelerating calorimeter. Sci Technol Eng. 2018;18:126–30.
Sivapirakasam SP, Nalla Mohamed M, Surianarayanan M, Sridhar VP. Evaluation of thermal hazards and thermo-kinetic parameters of a matchhead composition by DSC and ARC. Thermochim Acta. 2013;557:13–9.
Bao F, Zhang GZ, Jin SH. Thermal decomposition behavior and thermal stability of DABT·2DMSO. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:3185–91.
Hu RZ, Gao SL, Zhao FQ, Shi QZ, Zhang TL, Zhang JJ. Kinetics of thermal analysis. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press; 2008. p. 79–83.
Zhang GY, Jin SH, Li LJ, Li ZH, Shu QH, Wang DQ, Zhang B, Li YK. Evaluation of thermal hazards and thermo-kinetic parameters of 3-amino-4-amidoximinofurazan by ARC and TG. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:1223–30.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Center of Testing and Analysis, Shanghai Institute, for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Wang, J. & Wang, J. Crystal structure and thermal decomposition kinetics of 1,3,5-trinitro-4,6-diazidobenzene. J Therm Anal Calorim 143, 3983–3995 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09339-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09339-x