Abstract
The vibration-based damage identification method utilizes changes in the vibration properties of a structure to detect damages. The presence of noise makes the use of these methods unreliable. Therefore, it is necessary to develop and apply a robust technique in noisy conditions. The main purpose of the proposed method in this study is to investigate the effect of noise on highway bridges and reduce its effects in determining the precise and correct location and severity of damages on these types of bridges. Therefore, a dual-criteria method based on modal flexibility change (MF) and modal strain energy (MSE) damage index is considered as the bases for training convolution neural network (CNN). This method aims to identify more accurate the damage location and intensity with and without the effect of noise. The feasibility of the proposed method is indicated on a validated FE model applied to the portion of the I-40 bridge as a sample of steel girders highway bridge by its application to a range of damage scenarios. The numerical simulation of damage scenarios is utilized to achieve both noise-polluted damage indexes for training CNN. The well-trained CNN is then applied to double-check the location and attain the intensity of unknown single and multiple damages (up to four simultaneous damages) in noisy conditions. The results demonstrate that dual criteria damage indexes along with CNN can practically and accurately identify unspecified location and severity of single and multiple damage scenarios in the presence of noise.



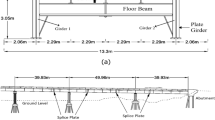
(adapted from Farrar et al. [51])
























Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
We will provide data and materials to anyone who requests them from us.
References
Beskhyroun, S., Oshima, T., Mikami, S.: Wavelet-based technique for structural damage detection. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 17(5), 473–494 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.316
Li, J., Dackermann, U., Xu, Y.L., Samali, B.: Damage identification in civil engineering structures utilizing PCA-compressed residual frequency response functions and neural network ensembles. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 18(2), 207–226 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.369
Das, S., Saha, P.: Performance of hybrid decomposition algorithm under heavy noise condition for health monitoring of structure. J. Civ. Struct. Heal. Monit. 10, 679–692 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13349-020-00412-5
Das, S., Saha, P.: Structural health monitoring techniques implemented on IASC–ASCE benchmark problem: a review. J. Civ. Struct. Heal. Monit. 8, 689–718 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13349-018-0292-5
Li, L., Betti, R.: A machine learning-based data augmentation strategy for structural damage classification in civil infrastructure system. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13349-023-00705-5
Bayata, M., Ahmadi, H.R., Mahdavib, N.: Application of power spectral density function for damage diagnosis of bridge piers. Struct. Eng. Mech. 71(1), 57–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2019.71.1.057
Khodabandehlou, H., Pekcan, G., Fadali, M.S.: Vibration-based structural condition assessment using convolution neural networks. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 26(2), e2308 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2308
Mousavi, Z., Varahram, S., Ettefagh, M.M., Sadeghi, M.H., Razavi, S.N.: Deep neural networks–based damage detection using vibration signals of finite element model and real intact state: an evaluation via a lab-scale offshore jacket structure. Struct. Health Monit. 20(1), 379–405 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/1475921720932614
Azimi, M., Eslamlou, A.D., Pekcan, G.: Data-driven structural health monitoring and damage detection through deep learning: State-of-the-art review. Sensors 20(10), 2778 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102778
Wang, Z., Cha, Y.-J.: Unsupervised deep learning approach using a deep auto-encoder with a one-class support vector machine to detect damage. Struct. Health Monit. 20(1), 406–425 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/1475921720934051
Wang, Z., Cha, Y.J.: Unsupervised machine and deep learning methods for structural damage detection: a comparative study. Eng. Rep. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/eng2.12551
Cha, Y.-J., Wang, Z.: Unsupervised novelty detection–based structural damage localization using a density peaks-based fast clustering algorithm. Struct. Health Monit. 17(2), 313–324 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1475921717691260
Cha, Y.J., Choi, W., Büyüköztürk, O.: Deep learning-based crack damage detection using convolutional neural networks. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 32(5), 361–378 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/mice.12263
Cha, Y.J., Choi, W., Suh, G., Mahmoudkhani, S., Büyüköztürk, O.: Autonomous structural visual inspection using region-based deep learning for detecting multiple damage types. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct Eng. 33(9), 731–747 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/mice.12334
Avci, O., Abdeljaber, O., Kiranyaz, S., Hussein, M., Gabbouj, M., Inman, D.J.: A review of vibration-based damage detection in civil structures: from traditional methods to Machine Learning and Deep Learning applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 147, 107077 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.107077
Zhang, H., Lin, J., Hua, J., Gao, F., Tong, T.: Data anomaly detection for bridge SHM based on CNN combined with statistic features. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 41(1), 28 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-022-00857-2
Shih, H.W., Thambiratnam, D., Chan, T.: Vibration based structural damage detection in flexural members using multi-criteria approach. Sound Vib. 323(3–5), 645–661 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2009.01.019
Cornwell, P., Doebling, S.W., Farrar, C.R.: Application of the strain energy damage detection method to plate-like structures. Sound Vib. 224(2), 359–374 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1006/jsvi.1999.2163
Rizos, P., Aspragathos, N., Dimarogonas, A.: Identification of crack location and magnitude in a cantilever beam from the vibration modes. Sound Vib. 138(3), 381–388 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-460X(90)90593-O
Hong, J.-C., Kim, Y., Lee, H., Lee, Y.: Damage detection using the Lipschitz exponent estimated by the wavelet transform: applications to vibration modes of a beam. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39(7), 1803–1816 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7683(01)00279-7
Contursi, T., Messina, A., Williams, E.J.: A multiple-damage location assurance criterion based on natural frequency changes. J. Vib. Control 4(5), 619–633 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1177/107754639800400505
Shi, Z., Law, S., Zhang, L.: Damage localization by directly using incomplete mode shapes. J. Eng. Mech. 126(6), 656–660 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2000)126:6(656)
Ahmadi, H.R., Anvari, D.: Health monitoring of pedestrian truss bridges using cone-shaped kernel distribution. Smart Struct. Syst. 22(6), 699–709 (2018). https://doi.org/10.12989/sss.2018.22.6.699
Shih, W., Thambiratnam, D., Chan, T.: Damage detection in truss bridges using vibration based multi-criteria approach. Struct. Eng. Mech. 39(2), 187–206 (2011). https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2011.39.2.187
Caicedo, J.M., Dyke, S.J.: Experimental validation of structural health monitoring for flexible bridge structures. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 12(3–4), 425–443 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.78
Jayasundara, N., Thambiratnam, D., Chan, T., Nguyen, A.: Vibration-based dual-criteria approach for damage detection in arch bridges. Struct. Health Monit. 18(5–6), 2004–2019 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1475921718810011
Tan, Z.X., Thambiratnam, D.P., Chan, T.H., Gordan, M., Abdul, R.H.: Damage detection in steel-concrete composite bridge using vibration characteristics and artificial neural network. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 16(9), 1247–1261 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15732479.2019.1696378
Nick, H., Aziminejad, A., Hosseini, M.H., Laknejadi, K.: Damage identification in steel girder bridges using modal strain energy-based damage index method and artificial neural network. Eng. Fail. Anal. 119, 105010 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.105010
Nick, H., Aziminejad, A.: Vibration-based damage identification in steel girder bridges using artificial neural network under noisy conditions. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 40, 1–22 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-020-00744-8
Jayasundara, N., Thambiratnam, D., Chan, T., Nguyen, A.: Damage detection and quantification in deck type arch bridges using vibration based methods and artificial neural networks. Eng. Fail. Anal. 109, 104265 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2019.104265
Pailes, B.M., Gucunski, N.: Understanding multi-modal non-destructive testing data through the evaluation of twelve deteriorating reinforced concrete bridge decks. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 34, 1–14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-015-0308-6
Pandey, A., Biswas, M.: Damage detection in structures using changes in flexibility. Sound Vib. 169(1), 3–17 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1006/jsvi.1994.1002
Sung, S.-H., Koo, K.-Y., Jung, H.-J.: Modal flexibility-based damage detection of cantilever beam-type structures using baseline modification. Sound Vib. 333(18), 4123–4138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2014.04.056
Gao, Y., Spencer, B.: Damage localization under ambient vibration using changes in flexibility. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 1, 136–144 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-002-0017-x
Moragaspitiya, H.P., Thambiratnam, D.P., Perera, N.J., Chan, T.H.: Development of a vibration based method to update axial shortening of vertical load bearing elements in reinforced concrete buildings. Eng. Struct. 46, 49–61 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.07.010
Toksoy, T., Aktan, A.: Bridge-condition assessment by modal flexibility. Exp. Mech. 34, 271–278 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02319765
Stubbs, N., Kim, J.-T., Farrar, C., eds.: Field verification of a nondestructive damage localization and severity estimation algorithm. Proceedings-SPIE the international society for optical engineering; 1995: SPIE International Society for Optical.
Shi, Z., Law, S., Zhang, L.: Structural damage localization from modal strain energy change. Sound Vib. 218(5), 825–844 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1006/jsvi.1998.1878
Law, S., Shi, Z., Zhang, L.: Structural damage detection from incomplete and noisy modal test data. J. Eng. Mech. 124(11), 1280–1288 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1998)124:11(1280)
Ko, J., Sun, Z., Ni, Y.: Multi-stage identification scheme for detecting damage in cable-stayed Kap Shui Mun Bridge. Eng. Struct. 24(7), 857–868 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0296(02)00024-X
Xu, H., Humar, J.: Damage detection in a girder bridge by artificial neural network technique. Comput-Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng. 21(6), 450–464 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8667.2006.00449.x
Nick, H., Ashrafpoor, A., Aziminejad, A., eds.: Damage identification in steel frames using dual-criteria vibration-based damage detection method and artificial neural network. Structures. Elsevier (2023)
Cha, Y.-J., Mostafavi, A., Benipal, S.S.: DNoiseNet: deep learning-based feedback active noise control in various noisy environments. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 121, 105971 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.105971
Mostafavi, A., Cha, Y.-J.: Deep learning-based active noise control on construction sites. Autom. Constr. 151, 104885 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2023.104885
Diao, Y., Lv, J., Wang, Q., Li, X., Xu, J.: Structural damage identification based on variational mode decomposition–Hilbert transform and CNN. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13349-023-00715-3
Jing, L., Zhao, M., Li, P., Xu, X.: A convolutional neural network based feature learning and fault diagnosis method for the condition monitoring of gearbox. Measurement 111, 1–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.07.017
Dubey, S.R., Chakraborty, S., Roy, S.K., Mukherjee, S., Singh, S.K., Chaudhuri, B.B.: diffGrad: an optimization method for convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(11), 4500–4511 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2955777
Stubbs, N., Garcia, G.: Application of pattern recognition to damage localization. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 11(6), 395–409 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8667.1996.tb00352.x
Farrar, C.R., Jauregui, D.A.: Comparative study of damage identification algorithms applied to a bridge: I. Experiment. Smart Mater. Struct. 7(5), 704 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/7/5/013
Farrar, C.R., Jauregui, D.A.: Comparative study of damage identification algorithms applied to a bridge: II. Numerical study. Smart Mater. Struct. 7(5), 720 (1998)
Farrar, C., Jauregui, D.: Damage detection algorithms applied to experimental modal data from the I-40 bridge. Los Alamos National Lab.(LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States) (1996)
Farrar, C.R., Baker, W., Bell, T., Cone, K., Darling, T., Duffey, T., et al.: Dynamic characterization and damage detection in the I-40 bridge over the Rio Grande. Los Alamos National Lab., NM (United States) (1994)
ABAQUS. 6-14-4 ed: SIMULIA; 2014.
Tan, Z.X., Thambiratnam, D., Chan, T., Razak, H.A.: Detecting damage in steel beams using modal strain energy based damage index and Artificial Neural Network. Eng. Fail. Anal. 79, 253–262 (2017)
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ is the main author and AA is the corresponding author. Other authors act as supervisors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zalaghi, S., Aziminejad, A., Rahami, H. et al. Damage Identification in Steel Girders of Highway Bridges Utilizing Vibration Based Methods and Convolution Neural Network in the Presence of Noise. J Nondestruct Eval 43, 39 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-024-01057-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-024-01057-w