Abstract
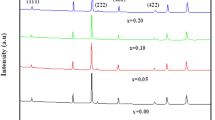
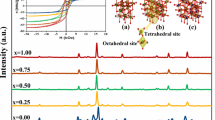
Nanocrystalline chromium substituted Ni–Zn nanoferrites with composition Ni0.5Zn0.5CrxFe2−xO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.25, in steps of 0.05) have been synthesized using citrate-gel auto-combustion method. The as synthesized powder of the starting composition has been characterized by using TG–DTA in air atmosphere for the temperature up to 800 °C and X-ray diffraction for its structure. Upon confirming the spinel phase for the starting composition, the chromium substituted Ni–Zn ferrite nano powders were synthesized by the similar procedure. The as synthesized powders were pressed into pellets and toroids under uniaxial pressure followed with sintering in air atmosphere for 4 h at 1100 °C for electrical and magnetic characterizations. The X-ray diffraction studies revealed a decrease of the lattice constant and considerable modification in the structure of Ni–Zn ferrite with the substitution of Cr3+ for Fe3+ ions. The room temperature FT-IR spectra displayed three significant IR absorption bands in the wave number range of 350–600 cm−1 which is a characteristic of the spinel structure. The band positions and intensities were found to vary with chromium substitution in Ni–Zn ferrite. The room temperature DC electrical resistivity and activation energy for conduction in the Ni–Zn–Cr ferrite samples were measured by using the two-probe method while the AC resistivity studies were carried out in the frequency range of 1 kHz to 13 MHz and the all the observations have been discussed in the light of existing understanding.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Manikandan, A. Vanitha, E. Ranjith kumar, S. Kavita, Influence of sintering temperature on structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Li substituted CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 11–17 (2017)
T. Yunoki, Y. Kimura, A. Fujimori, Maintenance properties of enzyme molecule stereostructure at high temperature by adsorption on organo-modified magnetic nanoparticle layer template. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 92, 1662–1671 (2019)
Z. Zhou, L. Yang, J. Gao, X. Chen, Structure–relaxivity relationships of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. Adv. Mater. 31, 1804567 (2019)
M.-N. Chen, L.-P. Mo, Z.-S. Cui, Z.-H. Zhang, Magnetic nanocatalysts: synthesis and application in multicomponent reactions. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 15, 27–37 (2019)
M. George, A.M. John, S.S. Nair, P.A. Joy, M.R. Anantharaman, Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 190–195 (2006)
L. Gama, E.P. Hernandez, D.R. Cornejo, A.A. Costa, S.M. Rezende, R.H.G.A. Kiminami, A.C.F.M. Costa, Magnetic and structural properties of nanosize Ni–Zn–Cr ferrite particles synthesized by combustion reaction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 317, 29–33 (2007)
M. Siva Ram Prasad, B.B.V.S.V. Prasad, B. Rajesh Babu, Magnetic, structural and DC electrical resistivity studies on the divalent cobalt substituted Ni–Zn ferrite system. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 29, 1550067 (2015)
X. Li, G. Wang, Low-temperature synthesis and growth of superparamagnetic Zn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 nanosized particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 1276–1279 (2009)
A. Sutka, G. Mezinskis, Sol–gel auto-combustion synthesis of spinel-type ferrite nanomaterials. Front. Mater. Sci. 6, 128–141 (2012)
M. Siva Ram Prasad, B. Rajesh Babu, K.V. Ramesh, K. Trinath, Structural and magnetic studies on chromium substituted Ni–Zn nano ferrite synthesized by citrate gel auto combustion method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 2735–2745 (2014)
M. Siva Ram Prasad, B. Rajesh Babu, K.V. Ramesh, K. Trinath, DC electrical resistivity studies and structure of Ni0.5Zn0.5CrxFe2−xO4 nanoferrites. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 29, 1550101 (2015)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 2nd edn. (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Boston, 1978)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751–767 (1976)
V.K. Lakhani, T.K. Pathak, N.H. Vasoya, K.B. Modi, Structural parameters and X-ray Debye temperature determination study on copper-ferrite-aluminates. Solid State Sci. 13(3), 539–547 (2011)
J.K. Burdett, G.D. Price, S.L. Price, Role of the crystal-field theory in determining the structures of spinels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104, 92–95 (1982)
M.J. Buerger, Crystal Structure Analysis (Wiley, New York, 1960)
B.B.V.S. Vara Prasad, B. Rajesh Babu, M. Sivaram Prasad, Structural and dielectric studies of Mg2+ substituted Ni–Zn ferrite. Mater. Sci. Pol. 33(4), 806–815 (2015)
V.K. Lakhani, K.B. Modi, Effect of Al2+ substitution on the transport properties of copper ferrite. J. Phys. D 44, 245403 (2011)
S. Amiri, H. Shokrollahi, Magnetic and structural properties of RE doped Co-ferrite (RE = Nd, Eu, and Gd) nano-particles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 345, 18 (2013)
S.S. Bhatu, V.K. Lakhani, A.R. Tanna, N.H. Vasoya, J.U. Buch, P.U. Sharma, U.N. Trivedi, H.H. Joshi, K.B. Modi, Effect of nickel substitution on structural, infrared and elastic properties of lithium ferrite. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 45, 596–608 (2007)
A.A. Birajdar, S.E. Shirsath, R.H. Kadam, S.M. Patnge, D.R. Mane, A.R. Shitre, Frequency and temperature dependent electrical properties of Ni0.7Zn0.3CrxFe2−xO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5). Ceram. Int. 38, 2963–2970 (2012)
L. Néel, Aimantation à saturation des ferrites mixtes de Nickel et de Zinc. C. R. Hebd. Seances L Acad. Sci. 230(4), 375–377 (1950)
J.W. Verwey, J.H. de Boer, Cation arrangement in a few oxides with crystal structures of the spinel type. Recl Trav. Chim. Phys. Bas. 55, 531 (1936)
M. Sivaram Prasad, B.B.V.S.V. Prasad, B.B. Rajesh, K.H. Rao, K.V. Ramesh, Magnetic properties and DC electrical resistivity studies on cadmium substituted nickel–zinc ferrite system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(16), 2115–2121 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivaram Prasad, M., Vara Prasad, B.B.V.S., Ramesh, K.V. et al. Structural, Magnetic and DC Electrical Resistivity Studies of Ni–Zn–Cr Ferrites Prepared by the Citrate-Gel Auto-Combustion Method. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 1163–1175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01719-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01719-y