Abstract
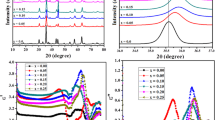
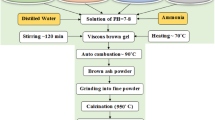
This research focuses on the formation and assessment of sol–gel auto-combustion-produced nanocrystalline Co0.40Ni0.6AlxFe2−xO4 (x = 0.00, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2) ferrites. The investigation explores the structural, morphological, electrical, dielectric, and magnetic characteristics of the spinel ferrites sintered at different temperatures (850 °C and 950 °C), with a specific emphasis on the impact of Al3+ substitution. A cubic single-phase spinel structure exhibiting excellent crystallinity and homogeneity is found across all samples, based on XRD evaluation. The nanoparticles had typical crystallite sizes between 40 and 48 nm and average particle sizes between 122 and 186 nm. Increasing Al3+ content resulted in increased nanoparticle porosity. According to infrared spectroscopy, the adsorption band v1 rose from 538 to 554 cm−1 whereas the v2 band dropped from 374 to 366 cm−1. With an increase in Al3+ content, the experimental magnetic moment (ηexp) and saturation magnetization (Ms) of the nanoparticles showed a notable upward trend. Furthermore, the samples sintered at 950 °C displayed higher AC resistivity, attributed to a reduction of the hopping electron within the grains. All of the ferrite nanoparticles under investigation also showed high coercivity values (1028.32–1222.76 Oe), designating them as ferrimagnetic materials and emphasizing the possibility for use in spintronics, high-frequency and microwave equipment like radar, antenna, and so on.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
H.M. Zaki, S. Al-Heniti, N.A. Shehri, New scheme for cation distribution and electrical characterization of nanocrystalline aluminum doped magnesium ferrite MgAlxFe2−xO4. Phys. B 436, 157 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2013.12.005
K.M. Muniba, A.D. Chandio, M.S. Akhtar, J.K. Khan, G. Mustafa, N.U. Channa, Z.A. Gilani, H.M. Asghar, Aluminum substitution in Ni-Co based spinel ferrite nanoparticles by sol-gel auto- combustion method. J. Electron. Mater. 50(6), 3302 (2021)
N. Hasan, S.S. Nishat, S. Sadman, M.M. Rahman, M.A. Hoque, M. Arifuzzaman, A. Kabir, Magnetic, optoelectronic, and rietveld refined structural properties of Al3+ substituted nanocrystalline Ni-Cu spinel ferrites: an experimental and DFT based study. Magn. Magn. Mater. 573, 170675 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2023.170675
Y. Slimani, M.A. Almessiere, A.D. Korkmaz, A. Baykal, H. Gungunes, M.G. Vakhitov, D.S. Klygach, S.V. Trukhanov, A.V. Trukhanov, The impact of indium ion on structural, magnetic, and electrodynamic traits of Co-Ni nanospinel ferrites. Magn. Magn. Mater. 562, 169782 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169782
K. Jalaiah, K.V. Babu, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of nickel doped Mn-Zn spinel ferrite synthesized by sol-gel method. Magn. Magn. Mater. 423, 275 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.09.114
A. Ditta, M.A. Khan, M. Junaid, R.M.A. Khalil, M.F. Warsi, Structural, magnetic and spectral properties of Gd and Dy co-doped dielectrically modified Co-Ni (Ni0.4Co0.6Fe2O4) ferrites. Phys. B 507, 27 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2016.11.030
F.A. Sheikh, H.M.N. Asghar, M. Khalid, Z.A. Gilani, S.M. Ali et al., Synthesis of Ce3+ substituted Ni-Co ferrites for high frequency and memory storage devices by sol-gel route. Alloys Compd. 938, 168637 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.168637
M.N. Islam, M. Harun-Or-Rashid, J. Islam, R. Parvin, A.K. Hossain, Improvement of microstructure and initial permeability of Mn0.5Ni0.1Zn0.4GdxFe2−xO4 with sintering temperature. Results Phys. 24, 104157 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104157
M.S. Samani, H. Sharifi, I. Sharifi, S.A.E. Mobarakeh, T. Isfahani, Effect of Cu doping on the structural and magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 129, 319 (2023)
M. Pardavi-Horvath, Microwave applications of soft ferrites. Magn. Magn. Mater 171, 215–216 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(00)00106-2
K. Raju, G. Venkataiah, D.H. Yoon, Effect of Zn substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Ni–Co ferrites. Ceram. Int. 40(7), 9337 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.157
P.B. Shetty, K.I. Maddani, K.S. MahaLaxmi, Ch.S. Lakshmi, Ch.S.L.N. Sridhar, Studies on lanthanum-doped nickel ferrites for improved structural, magnetic and optical properties. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 1246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10542-3
M. Hashim, A. Alimuddin, S.E. Shirsath, S.S. Meena, R.K. Kotnala, A. Parveen, A.S. Roy, S. Kumar, P. Bhatt, R. Kumar, Investigation of structural, dielectric, magnetic and antibacterial activity of Cu–Cd–Ni–FeO4 nanoparticles. Magn. Magn. Mater. 341, 148 (2013)
M.A. Islam, A.K.M.A. Hossain, M.Z. Ahsan, M.A.A. Bally, M.S. Ullah, S.M. Hoque, F.A. Khana, Structural characteristics, cation distribution, and elastic properties of Cr3+ substituted stoichiometric and non-stoichiometric cobalt ferrites. RSC Adv. 12, 8502 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA09090A
M.A.U. Nabi, M. Moin, M.S. Hasan, M.I. Arshad, A. Bibi, N. Amin, K. Mahmood, S.S. Ali, Study of electrical transport properties of cadmium-doped Zn-Mn soft ferrites by co-precipitation method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 34, 1813 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05588-x
P.B. Shetty, K.I. Maddani, K.S.M. Laxmi, C.S. Lakshmi, C.S.L.N. Sridhar, Studies on lanthanum-doped nickel ferrites for improved structural, magnetic and optical properties. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 1246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10542-3
S.U. Rather, O.M. Lemine, Effect of Al doping in zinc ferrite nanoparticles and their structural and magnetic properties. Alloys Compd. 812, 152058 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152058
T.C. Han, Z.Y. Tu, Y.T. Huang, Enhanced magnetic and magneto dielectric properties of Al-doped gallium ferrite nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 10, 015213 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5130051
L. Kumar, M. Kar, Influence of Al3+ ion concentration on the crystal structure and magnetic anisotropy of nanocrystalline spinel cobalt ferrite. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(15), 2042 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.03.010
M.M. Rahman, N. Hasan, M.A. Haque, M.B. Hossen, M. Arifuzzaman, Structural, dielectric and electrical transport properties of Al3+ substituted nanocrystalline Ni-Cu spinel ferrites prepared through sol gel route. Results Phys. 38, 105610 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2022.105610
B.K. Kuanr, S.R. Mishra, L. Wang, D. DelConte, D. Neupane, V. Veerakumar, Z. Celinski, Frequency and field dependent dynamic properties of CoFe2–x AlxO4 ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 76, 22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.11.033
M.M. Naik, H.S.B. Naik, G. Nagaraju, M. Vinuth, K. Vinu, S.K. Rashmi, Effect of aluminium doping on structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity on nickel ferrite nanoparticles by sol–gel auto combustion method. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 20395 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0174-y
A. Baykal, N. Kasapoğlu, Y. Köseoğlu, A.C. Başaran, H. Kavas, M.S. Toprak, Microwave-induced combustion synthesis and characterization of NixCo1−xFe2O4 nanocrystals (x = 0.0, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0). Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 6, 125–130 (2008)
V.A. Bharati, S.B. Somvanshi, A.V. Humbe, V.D. Murumkar, V.V. Sondur, K.M. Jadhav, Influence of trivalent Al–Cr co-substitution on the structural, morphological and Mossbauer ¨ properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. Alloys Compd. 821, 153501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153501
S.K. Ahmed, M.F. Mahmood, M. Arifuzzaman, M.B. Hossen, Enhancement of electrical and magnetic properties of Al3+ substituted CuZn nano ferrites with structural Rietveld refinement. Results Phys. 30, 104833 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104833
M. Naveed-Ul-Haq, S. Hussain, S. Webers, S. Salamon, I. Ahmad, T. Bibi, A. Hameed, H. Wende, On the structure–property relationships of (Al, Ga, In)-doped spinel cobalt ferrite compounds: a combined experimental and DFT study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 23, 18112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP02625A
S. Fayazzadeh, M. Khodaei, M. Arani, S.R. Mahdavi, T. Nizamov, A. Majouga, Magnetic properties and magnetic hyperthermia of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal method. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 2227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05490-6
M.N. Akhtar, A.A. Khan, M. Ahmad, M.A. Khan, Structural Rietveld refinement, morphological, and magnetic features of Cu doped Co-Ce nanocrystalline ferrites for high frequency applications. Phys. B 561, 121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.02.055
A. Ghafoor, M.A. Khan, M.U. Islam, Z.A. Gilani, A. Manzoor, H.M. Khan, I. Ali, M.F. Warsi, Structural and electromagnetic studies of Ni0.7Zn0.3Ho2xFe2–2xO4 ferrites. Ceram. Int. 42(12), 14252 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.054
S. Sharma, M.K. Verma, N.D. Sharma, N. Choudhary, S. Singh, D. Singh, Rare-earth doped Ni–Co ferrites synthesized by Pechini method: cation distribution and high temperature magnetic studies. Ceram. Int. 47, 17510 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.069
A.V. Raut, P.P. Khirade, A. Humbe, S.A. Jadhav, D.R. Shengule, Structural, electrical, dielectric and magnetic properties of Al3+ substituted Ni-Zn ferrite. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 29, 1331 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3421-6
M. Houshiar, L. Jamilpanah, Effect of Cu dopant on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Ni-Zn ferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 98, 213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.10.024
W. Anukool, R.A. El-Nabulsi, S. Dabagh, Effect of Al3+doping on dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticle for using in high frequency applications. Solgel Sci Technol. 105, 405 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-06029-y
P.N. Patil, S. Kumar, V.M. Jali, V.M. Sahoo, Low temperature and high magnetic field Mössbauer study of CuFe2O4 synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method. Mater. Today 89, 68–74 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.05.391
G. Chandra, R.C. Srivastava, V.R. Reddy, H.M. Agrawal, Effect of sintering temperature on magnetization and Mössbauer parameters of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 427, 225–229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.082
Md. Harun-Or-Rashid, Md.M. Rahman, M. Arifuzzaman, A.K.M.A. Hossain, Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of Ni0.38−xCu0.15+yZn0.47+x−yFe2O4 synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 13761–13776 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05953-z
L. Ji, G. Jiang, D. Wu, J. Chen, Study on the influence of ion doping on the crystal structure and magnetic properties of YFeO3. Mater Res. Express 7(6), 066103 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab9c5f
K.A. Aly, N.M. Khalil, Y. Algamal, Q.M. Saleem, Lattice strain estimation for CoAl2O4 nano particles using Williamson-Hall analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 676, 606–612 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.213
P. Solanki, S. Vasant, M. Joshi, Synthesis, crystal structure, spectroscopic and thermal analysis of strontium pyrophosphate dihydrate nanoparticles. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 11(4), 663–669 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.12227
L. Kumar, P. Kumar, A. Narayan, M. Kar, Rietveld analysis of XRD patterns of different sizes of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. Int. Nano Lett. 3(1), 8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-3-8
S. Ikram, J. Jacob, K. Mehboob, K. Mahmood, M.S. Nawaz, N. Amin, Relationship of various structural parameters with magnetic behavior of stoichiometric Tb3+ and Dy3+ co-substituted NiFe2O4 nanostructures. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 34(7), 1753–1758 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05687-9
E.H. El-Ghazzawy, M.A. Amer, Structural, elastic and magnetic studies of the as-synthesized Co1−xSrxFe2O4 nanoparticles. Alloys Compd. 690, 293 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.135
L. Kumar, P. Kumar, A. Narayan, M. Kar, Rietveld analysis of XRD patterns of different sizes of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. Int. Nano Lett. 3, 8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-3-8
K. Pubby, K.V. Babu, S.B. Narang, Magnetic, elastic, dielectric, microwave absorption and optical characterization of cobalt-substituted nickel spinel ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 255, 114513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114513
M. Arifuzzaman, M.B. Hossen, Md. Harun-Or-Rashid, M.L. Rahman, Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni0.7-xCuxCd0.3Fe2O4 prepared through sol-gel method. Mater Charact 171, 110810 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110810
M.N. Akhtar, A.A. Khan, M.N. Akhtar, M. Ahmad, M.A. Khan, Structural rietveld refinement, morphological and magnetic features of Cu doped Co Ce nanocrystalline ferrites for high frequency applications. Physica B 561, 121–131 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.02.055
I. Ali, M.U. Islam, M. Ishaque, H.M. Khan, M.N. Ashiq, M.U. Rana, Structural and magnetic properties of holmium substituted cobalt ferrites synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(22), 3773–3777 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.06.008
M.N. Akhtar et al., Evaluation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of CuZnNi (Cu Zn0.5−Ni0.5Fe2O4) nanocrystalline ferrites for core, switching and MLCI’s applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421, 260–268 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.08.035
S.U. Haque, K.K. Saikia, G. Murugesan, S. Kalainathan, A study on dielectric and magnetic properties of lanthanum substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 701, 612–618 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.309
T. Dabbebi et al., Investigations of microstructural and impedance spectroscopic properties of Mg0.5Co0.5Fe1.6Al0.4O4 ferrite prepared using sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. 32(9), 12521–12534 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05887-6
N. Channa et al., Structural, dielectric, impedance, and electric modulus properties of Cu2+-substituted CuxMn1-xFe2O4 spinel ferrites nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 32(3), 2832–2844 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05036-5
A.S. Priya, D. Geetha, N. Kavitha, Effect of Al substitution on the structural, electric and impedance behavior of cobalt ferrite. Vacuum 160, 453–460 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.12.004
W. Anukool, R.A. El-Nabulsi, S. Dabagh, Effect of Al3+ doping on dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticle for using in high frequency applications. J Solgel Sci Technol 105(2), 405–415 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-06029-y
Md. Harun-Or-Rashid, M.N. Islam, M. Arifuzzaman, A.K.M.A. Hossain, Effect of sintering temperature on the structural, morphological, electrical, and magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Zn and Ni–Cu–Zn–Sc ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(2), 2505–2523 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05018-7
A.K. Nikumbh et al., Structural, electrical, magnetic and dielectric properties of rare-earth substituted cobalt ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 355, 201–209 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.11.052
M.H. Rashid, A.K.M.A. Hossain, Structural, morphological and electromagnetic properties of Sc3+ doped Ni-Cu-Zn ferrites. Results Phys. 11, 888–895 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.10.050
M.V.S. Kumar, G.J. Shankarmurthy, E. Melagiriyappa, K.K. Nagaraja, H.S. Jayanna, M.P. Telenkov, Induced effects of Zn+2 on the transport and complex impedance properties of Gadolinium substituted nickel-zinc nano ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 478, 12–19 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.01.058
A. Rana, Study of anneal-tuned dielectric properties, AC conductivity, complex impedance, and modulus of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 45, 5444–5448 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.118
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Office of Research and Extension, Bangladesh University of Textiles, Dhaka, Bangladesh for the financial support extended during this research. The authors are also thankful to the Department of Physics, BUTEX and Institute of Fuel Research and Development, Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Dhaka 1205, Bangladesh, for allowing us to do this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.M. Rahman, M. Hedayet Ullah: Conceived and designed the experiments; Performed the experiments; Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents, materials, analysis tools or data; Wrote the paper. S. Tabassum, M.A. Hoque:Performed the experiments; Analyzed and interpreted the data; Wrote the paper. M. Harun-Or-Rashid: Analyzed and interpreted the data; wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.M., Ullah, M.H., Tabassum, S. et al. Rietveld refined structural and sintering temperature dependent electromagnetic properties of Al3+ substituted Ni–Co ferrites prepared through sol–gel auto combustion method for high-frequency and microwave devices. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 952 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12632-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12632-2