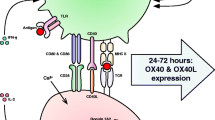
Recent studies have demonstrated that mast cells not only mediate inflammatory reactions in type I allergy but also play an important role in adaptive immunity. In the present study, we investigated the effects of interferon-α, which shares the same receptor as IFN-β, on human cord blood-derived mast cells. Mast cells produced TNF-α, and IL-10, and expressed OX40 ligand upon activation by crosslinking of FcɛRI. When treated with interferon-α, TNF-α production was decreased while IL-10 and TGF-β productions were increased. Furthermore, flow cytometric analysis revealed that interferon-α downregulated expression OX40 ligand on mast cells which is crucial for mast cell-T cell interaction. We confirmed that the viability of mast cells was not affected by interferon-α treatment. Accordingly, interferon-α-treated mast cells induced lower levels of CD4+ T cell proliferation compared with those without interferon-α treatment. These results suggest that type I interferons suppress T cell immune responses through their regulatory effects on mast cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Galli SJ: Mast cells and basophils. Curr Opin Hematol 7:32–39, 2000
Kawakami T, Galli SJ: Regulation of mast-cell and basophil function and survival by IgE. Nat Rev Immunol 2:773–786, 2002
McLachlan JB, Hart JP, Pizzo SV, Shelburne CP, Staats HF, Gunn MD, Abraham SN: Mast cell-derived tumor necrosis factor induces hypertrophy of draining lymph nodes during infection. Nat Immunol 4:1199–1205, 2003
Nakae S, Suto H, Kakurai M, Sedgwick JD, Tsai M, Galli SJ: Mast cells enhance T cell activation: Importance of mast cell-derived TNF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:6467–6472, 2005
Frandji P, Mourad W, Tkaczyk C, Singer M, David B, Colle JH, et al.: IL-4 mRNA transcription is induced in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells through an MHC class II-dependent signaling pathway. Eur J Immunol 28:844–854, 1998
Frandji P, Oskeritzian C, Cacaraci F, Lapeyre J, Peronet R, David B, et al.: Antigen-dependent stimulation by bone marrow-derived mast cells of MHC class II-restricted T cell hybridoma. J Immunol 151:6318–6328, 1993
Skokos D, Le Panse S, Villa I, Rousselle JC, Peronet R, David B, et al.: Mast cell-dependent B and T lymphocyte activation is mediated by the secretion of immunologically active exosomes. J Immunol 166:868–876, 2001
Kashiwakura J, Yokoi H, Saito H, Okayama Y: T cell proliferation by direct cross-talk between OX40 ligand on human mast cells and OX40 on human T cells: Comparison of gene expression profiles between human tonsillar and lung-cultured mast cells. J Immunol 173:5247–5257, 2004
Nakae S, Suto H, Iikura M, Kakurai M, Sedgwick JD, Tsai M, et al.: Mast cells enhance T cell activation: importance of mast cell costimulatory molecules and secreted TNF. J Immunol 176:2238–2248, 2006
Pawankar R: Mast cells in allergic airway disease and chronic rhinosinusitis. Chem Immunol Allergy 87:111–129, 2005
Araki Y, Andoh A, Fujiyama Y, Bamba T: Development of dextran sulphate sodium-induced experimental colitis is suppressed in genetically mast cell-deficient Ws/Ws rats. Clin Exp Immunol 119:264–269, 2000
Skaper SD, Facci L, Romanello S, Leon A: Mast cell activation causes delayed neurodegeneration in mixed hippocampal cultures via the nitric oxide pathway. J Neurochem 66:1157–1166, 1996
Secor VH, Secor WE, Gutekunst CA, Brown MA: Mast cells are essential for early onset and severe disease in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 191:813–822, 2000
Olsson Y: Mast cells in plaques of multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 50:611–618, 1974
Tuomisto L, Kilpelainen H, Riekkinen P: Histamine and histamine-N-methyltransferase in the CSF of patients with multiple sclerosis. Agents Actions 13:255–257, 1983
Rozniecki JJ, Hauser SL, Stein M, Lincoln R, Theoharides TC: Elevated mast cell tryptase in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. Ann Neurol 37:63–66, 1995
Virley DJ: Developing therapeutics for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. NeuroRx 2:638–649, 2005
Berghella AM, Totaro R, Pellegrini P, Contasta I, Russo T, Carolei A, et al.: Immunological study of IFNbeta-1a-treated and untreated multiple sclerosis patients: clarifying IFNbeta mechanisms and establishing specific dendritic cell immunotherapy. Neuroimmunomodulation 12:29–44, 2005
Imura A, Hori T, Imada K, Ishikawa T, Tanaka Y, Maeda M, et al.: The human OX40/gp34 system directly mediates adhesion of activated T cells to vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med 183:2185–2195, 1996
Royer B, Varadaradjalou S, Saas P, Gabiot AC, Kantelip B, Feger F, et al.: Autocrine regulation of cord blood-derived human mast cell activation by IL-10. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108:80–86, 2001
Carre PC, Mortenson RL, King TE, Jr., Noble PW, Sable CL, Riches DW: Increased expression of the interleukin-8 gene by alveolar macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. A potential mechanism for the recruitment and activation of neutrophils in lung fibrosis. J Clin Invest 88:1802–1810, 1991
Li DQ, Luo L, Chen Z, Kim HS, Song XJ, Pflugfelder SC: JNK and ERK MAP kinases mediate induction of IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and IL-8 following hyperosmolar stress in human limbal epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res 82:588–596, 2006
de Saint-Vis B, Fugier-Vivier I, Massacrier C, Gaillard C, Vanbervliet B, Ait-Yahia S, et al.: The cytokine profile expressed by human dendritic cells is dependent on cell subtype and mode of activation. J Immunol 160:1666–1676, 1998
Diamond MP, El-Hammady E, Wang R, Saed G: Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta, type III collagen, and fibronectin by dichloroacetic acid in human fibroblasts from normal peritoneum and adhesions. Fertil Steril 79:1161–1167, 2003
Kirshenbaum AS, Worobec AS, Davis TA, Goff JP, Semere T, Metcalfe DD: Inhibition of human mast cell growth and differentiation by interferon gamma-1b. Exp Hematol 26:245–251, 1998
Ndhlovu LC, Ishii N, Murata K, Sato T, Sugamura K: Critical involvement of OX40 ligand signals in the T cell priming events during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 167:2991–2999, 2001
Bissonnette EY, Chin B, Befus AD: Interferons differentially regulate histamine and TNF-alpha in rat intestinal mucosal mast cells. Immunology 86:12–17, 1995
Riccardi-Arbi R, Bacci S, Romagnoli P, Rucci L: Interferon-alpha affects the tumour necrosis factor-alpha content of mast cells in human nasal mucosa. A pilot study in allergic patients. Ital J Anat Embryol 109:115–122, 2004
Akdis M, Blaser K, Akdis CA: T regulatory cells in allergy. Chem Immunol Allergy 91:159–173, 2006
Carboni S, Aboul-Enein F, Waltzinger C, Killeen N, Lassmann H, Pena-Rossi C: CD134 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of EAE and is upregulated in the CNS of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 145:1–11, 2003
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was partly supported by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, T., Kambe, N., Uchiyama, T. et al. Type I Interferons Attenuate T Cell Activating Functions of Human Mast Cells by Decreasing TNF-α Production and OX40 Ligand Expression While Increasing IL-10 Production. J Clin Immunol 26, 512–518 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9043-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9043-1