Abstract
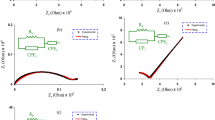
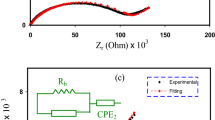
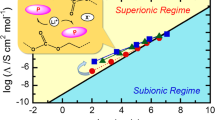
In this study, biopolymer-based solid polymer blend electrolyte (SPBE) films were created from chitosan (CS), poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (POZ), potassium iodide (KI), and glycerol (GL) using solvent casting. The effect of GL as a plasticizer on the electrical properties of materials was investigated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. GL significantly increased dopant salt dissociation, increasing mobile charge density and decreasing bulk resistance (\({{\text{R}}}_{{\text{b}}}\)). This increased ionic conductivity and ion transport in the polymer electrolyte (PE) system, with the samples containing the most GL exhibiting the highest conductivity (3.96 × 10–4 S/cm). Electrochemical impedance plots revealed distinct conductivity characteristics at electrode interfaces due to double-layer capacitances. Electrical Equivalent Circuit (EEC) analysis was utilized to interpret impedance measurements, revealing improved ion transport after EEC fitting. The theoretical and practical significance of transport parameters derived from the impedance plots was demonstrated. The dielectric properties of PE films were analyzed to gain insight into electrolyte ion conduction and polarization. GL increased dielectric constant (\({\varepsilon }{\prime}\)) and dielectric loss (\({\varepsilon }^{{\prime}{\prime}}\)) values at low frequencies, thereby enhancing dielectric properties and conductivity through an increase in the number of mobile ions. However, excessive GL diminished dielectric properties due to ion aggregation. Increased loss tangent (\({\text{tan}}\delta\)) peaks in PE films revealed the impact of GL on charge carrier mobility and resistivity. PE films exhibited negligible real electrical modulus (\({M}{\prime}\)) at low frequencies in the absence of electrode polarization (EP), while imaginary part of the electrical modulus (\({M}^{{\prime}{\prime}}\)) demonstrated a loss peak indicating substantial relaxation. GL incorporation altered relaxation dynamics, which may have implications for particular applications. The study also cast light on the dynamics of material relaxation, which may be pertinent to various applications particularly in flexible electronics.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the necessary Data are available within the main text.
References
J.L. Ndeugueu, M. Aniya, Structural characterization of the ac conductivity in Ag ion conducting glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 2483–2488 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3318-x
W. Li, M. Yuan, M. Yang, Dual-phase polymer electrolyte with enhanced phase compatibility based on Poly(MMA-g-PVC)/PMMA. Eur. Polym. J. 42, 1396–1402 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2005.12.015
A. Bhide, K. Hariharan, Ionic transport studies on (PEO)6:NaPO3 polymer electrolyte plasticized with PEG400. Eur. Polym. J. 43, 4253–4270 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2007.07.038
J.H. Kim, J. Won, Y.S. Kang, Olefin-induced dissolution of silver salts physically dispersed in inert polymers and their application to olefin/paraffin separation. J. Membr. Sci. 241, 403–407 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2004.05.027
C.M. Nyuk, M.I.N. Mohd Isa, Solid biopolymer electrolytes based on carboxymethyl cellulose for use in coin cell proton batteries. J Sustain Sci Manag 2017.
M.Y. Chong, Development of biodegradable solid polymer electrolytes incorporating different nanoparticles for electric double layer capacitor. University of Malaya, 2017.
N.S. Salleh, S.B. Aziz, Z. Aspanut, M.F.Z. Kadir, Electrical impedance and conduction mechanism analysis of biopolymer electrolytes based on methyl cellulose doped with ammonium iodide. Ionics (Kiel) 22, 2157–2167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1731-0
M.F.F. Shukur, R. Ithnin, M.F.Z.F.Z. Kadir, Electrical characterization of corn starch-LiOAc electrolytes and application in electrochemical double layer capacitor. Electrochim. Acta 136, 2014–6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.05.075
L. Sampathkumar, P. Christopher Selvin, S. Selvasekarapandian, P. Perumal, R. Chitra, M. Muthukrishnan, Synthesis and characterization of biopolymer electrolyte based on tamarind seed polysaccharide, lithium perchlorate and ethylene carbonate for electrochemical applications. Ionics (Kiel) 25, 1067–1082 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02857-1
V. Moniha, M. Alagar, S. Selvasekarapandian, B. Sundaresan, R. Hemalatha, G. Boopathi, Synthesis and characterization of bio-polymer electrolyte based on iota-carrageenan with ammonium thiocyanate and its applications. J. Solid State Electrochem. 22, 3209–3223 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-4028-6
B.-W. Du, S.-Y. Hu, R. Singh, T.-T. Tsai, C.-C. Lin, F.-H. Ko, Eco-friendly and biodegradable biopolymer chitosan/Y2O3 composite materials in flexible organic thin-film transistors. Mater (Basel, Switzerland) 10, 1026 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091026
R. Hirase, Y. Higashiyama, M. Mori, Y. Takahara, C. Yamane, Hydrated salts as both solvent and plasticizer for chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 80, 993–996 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.01.001
T.S. Trung, W.W. Thein-Han, N.T. Qui, C.H. Ng, W.F. Stevens, Functional characteristics of shrimp chitosan and its membranes as affected by the degree of deacetylation. Bioresour. Technol. 97, 659–663 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.03.023
P. Bai, F. Cao, X. Lan, F. Zhao, Y. Ma, C. Zhao, Chitosan gel beads immobilized Cu (II) for selective adsorption of amino acids. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 70, 903–908 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2008.01.001
G. Lu, L. Kong, B. Sheng, G. Wang, Y. Gong, X. Zhang, Degradation of covalently cross-linked carboxymethyl chitosan and its potential application for peripheral nerve regeneration. Eur. Polym. J. 43, 3807–3818 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2007.06.016
Y. He, B. Zhu, Y. Inoue, Hydrogen bonds in polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 29, 1021–1051 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2004.07.002
H.B. Tahir, R.M. Abdullah, S.B. Aziz, The H+ ion transport study in polymer blends incorporated with ammonium nitrate: XRD, FTIR, and electrical characteristics. Results Phys 42, 105960 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2022.105960
D. Knorr, Use of chitinous polymers in food. Food Technol. 38, 85–97 (1984)
J.H. Kim, S.M. Park, J. Won, Y.S. Kang, Dependence of facilitated olefin transport on the thickness of silver polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 236, 209–212 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2004.02.019
S.U. Hong, J.Y. Kim, Y.S. Kang, Effect of water on the facilitated transport of olefins through solid polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 181, 289–293 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)00628-1
S.W. Kang, J.H. Kim, K. Char, J. Won, Y.S. Kang, Nanocomposite silver polymer electrolytes as facilitated olefin transport membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 285, 102–107 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.08.005
R.W. Moreadith, T.X. Viegas, M.D. Bentley, J.M. Harris, Z. Fang, K. Yoon et al., Clinical development of a poly(2-oxazoline) (POZ) polymer therapeutic for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease—proof of concept of POZ as a versatile polymer platform for drug development in multiple therapeutic indications. Eur. Polym. J. 88, 524–552 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.09.052
L. Ruiz-Rubio, M.L. Alonso, L. Pérez-Álvarez, R.M. Alonso, J.L. Vilas, V.V. Khutoryanskiy, Formulation of Carbopol®/Poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) s mucoadhesive tablets for buccal delivery of hydrocortisone. Polymers (Basel) 10, 175 (2018)
Hu Y, Yoshida K, Vajeeston P, Kim S, Sørby MH, Orimo S, et al. Lithium ionic conduction in composites of Li (BH4) 0.75 I0. 25 and amorphous 0.75 Li2S· 0.25 P2S5 for battery applications. Electrochim Acta 2018;278:332–9.
S.B. Aziz, M.H. Hamsan, R.M. Abdullah, M.F.Z. Kadir, A promising polymer blend electrolytes based on chitosan: Methyl cellulose for EDLC application with high specific capacitance and energy density. Molecules 24, 2503 (2019)
S.B. Aziz, M.H. Hamsan, W.O. Karim, M.F.Z. Kadir, M.A. Brza, O.G. Abdullah, High proton conducting polymer blend electrolytes based on chitosan: dextran with constant specific capacitance and energy density. Biomolecules 9, 267 (2019)
S.B. Aziz, M.H. Hamsan, M.F.Z. Kadir, W.O. Karim, R.M. Abdullah, Development of polymer blend electrolyte membranes based on chitosan: dextran with high ion transport properties for EDLC application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 3369 (2019)
P. Tamilselvi, M. Hema, Conductivity studies of LiCF3SO3 doped PVA: PVdF blend polymer electrolyte. Physica B 437, 53–57 (2014)
Y.M. Yusof, M.F. Shukur, H.A. Illias, M.F.Z. Kadir, Conductivity and electrical properties of corn starch–chitosan blend biopolymer electrolyte incorporated with ammonium iodide. Phys. Scr. 89, 35701 (2014)
Meaurio E, Hernandez-Montero N, Zuza E, Sarasua J-R. Miscible Blends Based on Biodegradable Polymers. Charact. Polym. Blends, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2014, p. 7–92. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527645602.ch02.
Adam AA, Soleimani H, Dennis JO, Aldaghri OA, Alsadig A, Ibnaouf KH, et al. Insight into the Effect of Glycerol on Dielectric Relaxation and Transport Properties of Potassium-Ion-Conducting Solid Biopolymer Electrolytes for Application in Solid-State Electrochemical Double-Layer Capacitor. Molecules 2023;28. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083461.
Asnawi ASFM, B. Aziz S, M. Nofal M, Hamsan MH, Brza MA, Yusof YM, et al. Glycerolized Li+ ion conducting chitosan-based polymer electrolyte for energy storage EDLC device applications with relatively high energy density. Polymers (Basel) 2020;12:1433.
Aziz SB, Asnawi ASFM, Kadir MF, Alshehri SM, Ahamad T, Yusof YM, et al. Structural, Electrical and Electrochemical Properties of Glycerolized Biopolymers Based on Chitosan (CS): Methylcellulose (MC) for Energy Storage Application. Polymers (Basel) 2021;13. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081183.
S.L. Agrawal, M. Singh, M. Tripathi, M.M. Dwivedi, K. Pandey, Dielectric relaxation studies on [PEO–SiO2]:NH4SCN nanocomposite polymer electrolyte films. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 6060–6068 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3833-9
S.B. Aziz, Z.H.Z. Abidin, Ion-transport study in nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes based on chitosan: electrical and dielectric analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132, 41774 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41774
S.B. Aziz, B.S. Aziz, Role of dielectric constant on ion transport: reformulated Arrhenius equation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2527013
S.B. Aziz, Z.H.Z. Abidin, Electrical and morphological analysis of chitosan:AgTf solid electrolyte. Mater. Chem. Phys. 144, 280–286 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.12.029
S.B. Aziz, R.M. Abdullah, M.A. Rasheed, H.M. Ahmed, Role of ion dissociation on DC conductivity and silver nanoparticle formation in PVA:AgNt based polymer electrolytes: deep insights to ion transport mechanism. Polymers (Basel) 9, 338 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080338
Y. Zhang, X. Xu, Modeling oxygen ionic conductivities of ABO3 perovskites through machine learning. Chem. Phys. 558, 111511 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2022.111511
Y. Zhang, X. Xu, Machine learning glass transition temperature of polyacrylamides using quantum chemical descriptors. Polym. Chem. 12, 843–851 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01581D
Y. Zhang, X. Xu, Machine Learning Properties of Electrolyte Additives: A Focus on Redox Potentials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 60, 343–354 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c05055
D.K. Pradhan, R.N.P. Choudhary, B.K. Samantaray, Studies of dielectric relaxation and AC conductivity behavior of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 3, 597–608 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.01.008
C.V. Subba Reddy, A.-P. Jin, Q.-Y. Zhu, L.-Q. Mai, W. Chen, Preparation and characterization of (PVP+ NaClO 4) electrolytes for battery applications. Eur. Phys. J. E 19, 471–476 (2006)
Y.C. Lee, M.H. Buraidah, H.J. Woo, L.P. Teo, Electrical and optical properties of poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) based polymer electrolytes containing water-soluble potassium iodide salt. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/15421406.2023.2166135
Sangwan B, Kumar S, Singh A, Pandey SP, Singh PK, Singh RC, et al. Modified Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Based Polymer Electrolyte for Dye Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs). Macromol. Symp., vol. 407, Wiley Online Library; 2023, p. 2100462.
S.B. Aziz, T.J. Woo, M.F.Z. Kadir, H.M. Ahmed, A conceptual review on polymer electrolytes and ion transport models. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 3, 1–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSAMD.2018.01.002
Aziz SB, Woo TJ, Kadir MFZ, Ahmed HM, B Aziz S, S Marf A, et al. Impedance, Electrical Equivalent Circuit (EEC) Modeling, Structural (FTIR and XRD), Dielectric, and Electric Modulus Study of MC-Based Ion-Conducting Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Materials (Basel) 2022;15:1–17. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010170.
S. B. Aziz, A. Marf, E.M.A. Dannoun, M.A. Brza, R.M. Abdullah, The study of the degree of crystallinity, electrical equivalent circuit, and dielectric properties of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-based biopolymer electrolytes. Polymers (Basel) 12, 2184 (2020)
J. M. Hadi, S. B. Aziz, M. M. Nofal, S.A. Hussein, M.H. Hafiz, M.A. Brza et al., Electrical, dielectric property and electrochemical performances of plasticized silver ion-conducting chitosan-based polymer nanocomposites. Membranes (Basel) (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070151
M.A. Brza, S.B. Aziz, H. Anuar, S.M. Alshehri, F. Ali, T. Ahamad et al., Characteristics of a plasticized PVA-based polymer electrolyte membrane and H+ conductor for an electrical double-layer capacitor: structural, morphological, and ion transport properties. Membranes (Basel) (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040296
S. Rajendran, R. Babu, P. Sivakumar, Investigations on PVC/PAN composite polymer electrolytes. J. Membr. Sci. 315, 67–73 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.02.007
B. Chatterjee, N. Kulshrestha, P.N. Gupta, Electrical properties of starch-PVA biodegradable polymer blend. Phys. Scr. 90, 25805 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/90/2/025805
H.T. Ahmed, V.J. Jalal, D.A. Tahir, A.H. Mohamad, O.G. Abdullah, Effect of PEG as a plasticizer on the electrical and optical properties of polymer blend electrolyte MC-CH-LiBF4 based films. Results Phys 15, 102735 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102735
M.H. Hamsan, M.M. Nofal, S.B. Aziz, M.A. Brza, E.M.A. Dannoun, A.R. Murad et al., Plasticized polymer blend electrolyte based on chitosan for energy storage application: structural, circuit modeling, morphological and electrochemical properties. Polymers (Basel) (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081233
D.K. Das-Gupta, Molecular processes in polymer electrets. J. Electrostat. 51–52, 159–166 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3886(01)00090-0
S.B. Aziz, M.H. Hamsan, M.A. Brza, M.F.Z. Kadir, S.K. Muzakir, R.T. Abdulwahid, Effect of glycerol on EDLC characteristics of chitosan:methylcellulose polymer blend electrolytes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 8355–8366 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.05.114
M.M.E. Jacob, S.R.S. Prabaharan, S. Radhakrishna, Effect of PEO addition on the electrolytic and thermal properties of PVDF-LiClO4 polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 104, 267–276 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(97)00422-0
C.P. Fonseca, F. Cavalcante, F.A. Amaral, C.A.Z. Souza, S. Neves, Thermal and conduction properties of a PCL-biodegradable gel polymer electrolyte with LiClO4, LiF3CSO3, and LiBF4 salts. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2, 52 (2007)
S.B. Aziz, R.M. Abdullah, M.F.Z. Kadir, H.M. Ahmed, Non suitability of silver ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on chitosan mediated by barium titanate (BaTiO3) for electrochemical device applications. Electrochim. Acta 296, 494–507 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.11.081
S.B. Aziz, R.M. Abdullah, Crystalline and amorphous phase identification from the tanδ relaxation peaks and impedance plots in polymer blend electrolytes based on [CS:AgNt]x:PEO(x–1) (10 ≤ x ≤ 50). Electrochim. Acta 285, 30–46 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.233
M.A. Brza, S.B. Aziz, H. Anuar, F. Ali, R.T. Abdulwahid, J.M. Hadi, Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as a novel approach to investigate the influence of metal complexes on electrical properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)(PVA) composites. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 16, 210542 (2021)
E.M.A. Dannoun, S.B. Aziz, M.A. Brza, M. Nofal, A.S.M. Asnawi, Y.M. Yusof et al., The study of plasticized solid polymer blend electrolytes based on natural polymers and their application for energy storage EDLC devices. Polymers (Basel) 12, 2531 (2020)
Hadi JM, Aziz SB, R. Saeed S, Brza MA, Abdulwahid RT, Hamsan MH, et al. Investigation of ion transport parameters and electrochemical performance of plasticized biocompatible chitosan-based proton conducting polymer composite electrolytes. Membranes (Basel) 2020;10:363.
E.M.A. Dannoun, S.B. Aziz, R.T. Abdulwahid, S.I. Al-Saeedi, M.M. Nofal, N.M. Sadiq et al., Study of MC: DN-based biopolymer blend electrolytes with inserted Zn-metal complex for energy storage devices with improved electrochemical performance. Membranes (Basel) 12, 769 (2022)
L.P. Teo, M.H. Buraidah, A.F. Nor, S.R. Majid, Conductivity and dielectric studies of Li2SnO3. Ionics (Kiel) 18, 655–65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-012-0667-2
A.K. Arof, S. Amirudin, S.Z. Yusof, I.M. Noor, A method based on impedance spectroscopy to determine transport properties of polymer electrolytes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 1856–1867 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp53830c
S.B. Aziz, Occurrence of electrical percolation threshold and observation of phase transition in chitosan(1–x):AgIx (0.05 ≤ x ≤ 0.2)-based ion-conducting solid polymer composites. Appl. Phys. A 122, 706 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0235-0
M. Marzantowicz, J.R. Dygas, F. Krok, Impedance of interface between PEO: LiTFSI polymer electrolyte and blocking electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 53, 7417–7425 (2008)
J. Yang, Hopping conduction and low-frequency dielectric relaxation in 5 mol % Mn doped ( Pb, Sr ) TiO3 films Hopping conduction and low-frequency dielectric relaxation in 5mol % Mn doped ( Pb, Sr ) TiO3 films. J. Appl. Phys. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3021447
M.D. Migahed, M. Ishra, T. Fahmy, A. Barakat, Electric modulus and AC conductivity studies in conducting PPy composite films at low temperature. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 65, 1121–1125 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2003.11.039
S. Bhadra, N.K. Singha, D. Khastgir, Dielectric properties and EMI shielding efficiency of polyaniline and ethylene 1-octene based semi-conducting composites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 396–403 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2008.03.009
R. Mishra, N. Baskaran, P.A. Ramakrishnan, K.J. Rao, Lithium ion conduction in extreme polymer in salt regime 112, 261–273 (1998)
N. Kamarulzaman, Z. Osman, M.R. Muhamad, Z.A. Ibrahim, A.K. Arof, N.S. Mohamed, Performance characteristics of LiMn2O4/polymer/carbon electrochemical cells. J. Power. Sources 97–98, 722–725 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(01)00647-4
L.V.S. Lopes, D.C. Dragunski, A. Pawlicka, J.P. Donoso, Nuclear magnetic resonance and conductivity study of starch based polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 48, 2021–2027 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(03)00181-6
Y.N. Sudhakar, M. Selvakumar, D.K. Bhat, LiClO4-doped plasticized chitosan and poly(ethylene glycol) blend as biodegradable polymer electrolyte for supercapacitors. Ionics (Kiel) 19, 277–285 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-012-0745-5
M.F.F. Shukur, R. Ithnin, M.F.Z.F.Z.Z. Kadir, S.B.B.S.B. Aziz, R.M. Abdullah, Z.H.Z. Abidin et al., LiClO4-doped plasticized chitosan and poly(ethylene glycol) blend as biodegradable polymer electrolyte for supercapacitors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 13, 2021–2027 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(03)00181-6
N.K. Zainuddin, N.M.J. Rasali, A.S. Samsudin, Study on the effect of PEG in ionic transport for CMC-NH4Br-based solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics (Kiel) 24, 3039–3052 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2505-7
H.J. Woo, S.R. Majid, A.K. Arof, Dielectric properties and morphology of polymer electrolyte based on poly(ɛ-caprolactone) and ammonium thiocyanate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 134, 755–761 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.03.064
S.B. Aziz, Li+ ion conduction mechanism in poly (ε-caprolactone)-based polymer electrolyte. Iran Polym J 22, 877–83 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-013-0186-7
A. Abdullah, S.Z. Abdullah, A.M.M. Ali, T. Winie, M.Z.A. Yahya, R.H.Y. Subban, Electrical properties of PEO–LiCF3SO3–SiO2 nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Mater. Res. Innov. 13, 255–258 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1179/143307509X440451
S. Selvasekarapandian, Devi R. Chithra, Dielectric studies on a solid electrolyte AgI-PbBr2-Ag2OB2O3. Mater. Chem. Phys. (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(98)00256-9
R.T. Abdulwahid, S.B. Aziz, M.F.Z. Kadir, Environmentally friendly plasticized electrolyte based on chitosan (CS): potato starch (PS) polymers for EDLC application: Steps toward the greener energy storage devices derived from biopolymers. J Energy Storage 67, 107636 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2023.107636
S.B. Aziz, M.H. Hamsan, M.F.Z. Kadir, H.J. Woo, Design of polymer blends based on Chitosan:POZ with improved dielectric constant for application in polymer electrolytes and flexible electronics. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 8586136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8586136
M.A. Brza, S.B. Aziz, H. Anuar, F. Ali, Structural, ion transport parameter and electrochemical properties of plasticized polymer composite electrolyte based on PVA: a novel approach to fabricate high performance EDLC devices. Polym. Test. 91, 106813 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106813
R.T. Abdulwahid, S.B. Aziz, M.F.Z. Kadir, Insights into ion transport in biodegradable solid polymer blend electrolyte based on FTIR analysis and circuit design. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 167, 110774 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2022.110774
T. Eschen, J. Kösters, M. Schönhoff, N.A. Stolwijk, Ionic transport in polymer electrolytes based on PEO and the PMImI ionic liquid: effects of salt concentration and iodine addition. J. Phys. Chem. B 116, 8290–8298 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp303579b
Maurya KK, Hashimi SA. Evidence of Ion Association in Polymer Electrolyte by Direct Mobility Measurements in Solid State Ionics: Materials and Applications, ed. by BVR Chowdari, S. Chandra, S. Singh and PC Srivastava 1992.
T. Winie, S. Ramesh, A.K. Arof, Studies on the structure and transport properties of hexanoyl chitosan-based polymer electrolytes. Physica B 404, 4308–4311 (2009)
R. Singh, P.K. Singh, V. Singh, B. Bhattacharya, Quantitative analysis of ion transport mechanism in biopolymer electrolyte. Opt. Laser Technol. 113, 303–309 (2019)
A. Chandra, R.C. Agrawal, Y.K. Mahipal, Ion transport property studies on PEO-PVP blended solid polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Phys. D 42, 135107 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/42/13/135107
S.B. Aziz, The mixed contribution of ionic and electronic carriers to conductivity in chitosan based solid electrolytes mediated by CuNt salt. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28, 1942–1952 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0862-3
C.S. Ramya, S. Selvasekarapandian, G. Hirankumar, T. Savitha, P.C. Angelo, Investigation on dielectric relaxations of PVP-NH4SCN polymer electrolyte. J. Non Cryst. Solids 354, 1494–1502 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.08.038
Acknowledgements
The author gratefully acknowledges the financial support for University of Sulaimani.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdullah, R.M. Investigation of ion transport in plasticized polymer electrolytes using electrical equivalent circuit (EEC) modeling. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 777 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12564-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12564-x