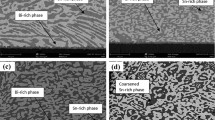
Abstract
Miniaturization of electronic devices causes reliability issues in solder joints such as a reduction in mechanical, structural, and electrical properties. This work focuses on studying the effects of cobalt nanoparticle (NP) addition on the structural and mechanical properties of the Sn-58Bi solder joint. 0, 0.5, 1, and 2% Co NP added samples were prepared. The reflow process was done at 180 °C for 1 min. After the reflow process, all samples were aged at 70 °C for different periods of 0 h, 126 h, and 504 h. After the tensile test, the fractography was done using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The result showed that after the addition of Co-nanoparticles, the grain size of Sn-58Bi was refined and significantly reduced for as reflowed samples. After thermal aging, the grain size was increased for all types of samples, while the increment in Sn-58Bi-0.5Co/1Co/2Co was controlled as compared to the Sn-58Bi solder joint.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This manuscript has no associated data.
References
R.R. Tummala, E.J. Rymaszewski, A.G. Klopfenstein, Microelectronics Packaging Handbook: Technology Drivers Part I (Springer Science & Business Media, 2012)
C.A. Mack, Fifty years of Moore’s law. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 24(2), 202–207 (2011)
W. Arden et al., More-than-Moore white paper. Version 2, 14 (2010)
S.K. Kang, A.K. Sarkhel, Lead (Pb)-free solders for electronic packaging. J. Electron. Mater. 23(8), 701–707 (1994)
S. Menon et al., High lead solder (over 85%) solder in the electronics industry: RoHS exemptions and alternatives. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(6), 4021–4030 (2015)
E. Ringgaard, T. Wurlitzer, Lead-free piezoceramics based on alkali niobates. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25(12), 2701–2706 (2005)
L.-H. Su et al., Interfacial reactions in molten Sn/Cu and molten In/Cu couples. Metall. and Mater. Trans. B. 28(5), 927–934 (1997)
H.R. Kotadia, P.D. Howes, S.H. Mannan, A review: on the development of low melting temperature Pb-free solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(6–7), 1253–1273 (2014)
N.C. Lee, Getting ready for lead-free solders. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. (1997). https://doi.org/10.1108/09540919710800656
M.N. Bashir et al., Effects of tin particles addition on structural and mechanical properties of eutectic Sn–58Bi solder joint. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09028-5
G. Ren, I.J. Wilding, M.N. Collins, Alloying influences on low melt temperature SnZn and SnBi solder alloys for electronic interconnections. J. Alloy. Compd. 665, 251–260 (2016)
Z. Mei, J. Morris, Characterization of eutectic Sn-Bi solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 21(6), 599–607 (1992)
C. Wu et al., Properties of lead-free solder alloys with rare earth element additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 44(1), 1–44 (2004)
Z. Huang, P.P. Conway, R. Qin, Modeling of interfacial intermetallic compounds in the application of very fine lead-free solder interconnections. Microsyst. Technol. 15(1), 101–107 (2009)
J. Shen et al., Microstructure and mechanical properties of gas metal arc welded CoCrFeMnNi joints using a 308 stainless steel filler metal. Scripta Mater. 222, 115053 (2023)
J. Shen et al., Gas tungsten arc welding of as-cast AlCoCrFeNi2. 1 eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 223, 111176 (2022)
J. Oliveira et al., Improving the ductility in laser welded joints of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy to 316 stainless steel. Mater. Des. 219, 110717 (2022)
F. Wang et al., Recent progress on the development of Sn–Bi based low-temperature Pb-free solders. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(4), 3222–3243 (2019)
X. Li et al., Effects of nanoscale Cu6Sn5 particles addition on microstructure and properties of SnBi solder alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 684, 328–334 (2017)
M.-L. Li et al., Materials modification of the lead-free solders incorporated with micro/nano-sized particles: a review. Mater. Des. 197, 109224 (2021)
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, Transient liquid phase bonding of Sn–Bi solder with added Cu particles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(5), 4232–4244 (2016)
G. Xu et al., Retarding the electromigration effects to the eutectic SnBi solder joints by micro-sized Ni-particles reinforcement approach. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(3), 878–884 (2011)
K.D. Min et al., Microstructures and mechanical properties of Sn-58 wt% Bi solder with Ag-decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes under 85° C/85% relative humidity environmental conditions. J. Electron. Mater. 49(2), 1527–1533 (2020)
L. Yang et al., Improved microstructure and mechanical properties for Sn58Bi solder alloy by addition of Ni-coated carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 642, 7–15 (2015)
F. Khodabakhshi, M. Zareghomsheh, G. Khatibi, Nanoindentation creep properties of lead-free nanocomposite solders reinforced by modified carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 797, 140203 (2020)
S.-J. Zhong et al., Development of lead-free interconnection materials in electronic industry during the past decades: structure and properties. Mater. Des. 215, 110439 (2022)
Y. Li, Y. Chan, Effect of silver (Ag) nanoparticle size on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn58Bi–Ag composite solders. J. Alloy. Compd. 645, 566–576 (2015)
N. Jiang et al., Influences of doping Ti nanoparticles on microstructure and properties of Sn58Bi solder. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(19), 17583–17590 (2019)
S.H. Rajendran, H. Kang, J.P. Jung, Ultrasonic-assisted dispersion of ZnO nanoparticles to Sn-Bi solder: a study on microstructure, spreading, and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30(5), 3167–3172 (2021)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, Growth mechanism of intermetallic compound and mechanical properties of nickel (Ni) nanoparticle doped low melting temperature tin–bismuth (Sn–Bi) solder. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(1), 781–794 (2016)
M. Nasir Bashir et al., Effect of cobalt nanoparticles on mechanical properties of Sn–58Bi solder joint. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33, 22573–22579 (2022)
C. Chen et al., Mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of Cu/Sn58Bi/Cu solder joint reinforced by B4C nanoparticles. J. Market. Res. 23, 1225–1238 (2023)
M.N. Bashir et al., Effect of cobalt doping on the microstructure and tensile properties of lead free solder joint subjected to electromigration. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32(11), 1129–1136 (2016)
M.N. Bashir et al., Effects of cobalt nanoparticle on microstructure of Sn58Bi solder joint. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 34(4), 248 (2023)
X. Chen et al., Mechanical deformation behavior and mechanism of Sn-58Bi solder alloys under different temperatures and strain rates. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 662, 251–257 (2016)
Y. Zhang et al., Alloying Effects on the phase stability and mechanical properties of doped Cu-Sn IMCs: a first-principle study. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 4018–4027 (2016)
M.N. Bashir et al., Effect of Ni and Co nanoparticle-doped flux on microstructure of SAC305 solder matrix. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08827-0
M.N. Bashir, A. Haseeb, Grain size stability of interfacial intermetallic compound in Ni and Co nanoparticle-doped SAC305 solder joints under electromigration. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08352-0
M.N. Bashir et al., Role of crystallographic orientation of β-Sn grain on electromigration failures in lead-free solder joint: an overview. Coatings 12(11), 1752 (2022)
F. Gao, T. Takemoto, H. Nishikawa, Effects of Co and Ni addition on reactive diffusion between Sn–3.5 Ag solder and Cu during soldering and annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 420(1), 39–46 (2006)
G. Sujan et al., Interfacial reaction, ball shear strength and fracture surface analysis of lead-free solder joints prepared using cobalt nanoparticle doped flux. J. Alloy. Compd. 695, 981–990 (2017)
G. Sujan, A. Haseeb, A. Afifi, Effects of metallic nanoparticle doped flux on the interfacial intermetallic compounds between lead-free solder ball and copper substrate. Mater. Charact. 97, 199–209 (2014)
R. Kane, B. Giessen, N. Grant, New metastable phases in binary tin alloy systems. Acta Metall. 14(5), 605–609 (1966)
L. Yang et al., Effects of Ni addition on mechanical properties of Sn58Bi solder alloy during solid-state aging. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 667, 368–375 (2016)
C. Ma, R. Swalin, A study of solute diffusion in liquid tin. Acta Metall. 8(6), 388–395 (1960)
G. Careri, A. Paoletti, Self-diffusion in liquid indium and tin. Il Nuovo Cimento. 2(3), 574–591 (1955)
R. Tian et al., Effects of nanoparticle addition on the reliability of Sn-based Pb-free solder joints under various conditions: a review. NANO 18(01), 2330001 (2023)
A. Haseeb, T.S. Leng, Effects of Co nanoparticle addition to Sn–3.8 Ag–0.7 Cu solder on interfacial structure after reflow and ageing. Intermetallics 19(5), 707–712 (2011)
S. Tay et al., Influence of Ni nanoparticle on the morphology and growth of interfacial intermetallic compounds between Sn–3.8 Ag–0.7 Cu lead-free solder and copper substrate. Intermetallics 33, 8–15 (2013)
J. Bobet et al., Study of Mg-M (M= Co, Ni and Fe) mixture elaborated by reactive mechanical alloying—hydrogen sorption properties. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 25(10), 987–996 (2000)
J.-L. Bobet, E. Akiba, B. Darriet, Study of Mg-M (M= Co, Ni and Fe) mixture elaborated by reactive mechanical alloying: hydrogen sorption properties. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 26(5), 493–501 (2001)
H. Yano et al., Oxygen reduction activity of carbon-supported Pt− M (M= V, Ni, Cr Co, and Fe) alloys prepared by nanocapsule method. Langmuir 23(11), 6438–6445 (2007)
M. Jiang et al., A thermodynamic assessment of the Co–Sn system. Calphad 28(2), 213–220 (2004)
S.-W. Chen et al., Interfacial reactions in Sn-Ag/Co couples. J. Electron. Mater. 43(2), 636–639 (2014)
A. Yakymovych et al., Effect of nano Co reinforcements on the structure of the Sn-3.0 Ag-0.5 Cu solder in liquid and after reflow solid states. Mater. Chem. Phys. 181, 470–475 (2016)
Z. Ma, S. Belyakov, C. Gourlay, Effects of cobalt on the nucleation and grain refinement of Sn-3Ag-0.5 Cu solders. J. Alloys Compds. 682, 326–337 (2016)
M.G. Cho et al., Enhancement of heterogeneous nucleation of β-Sn phases in Sn-rich solders by adding minor alloying elements with hexagonal closed packed structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(2), 021905 (2009)
D.H. Kim et al., Effects of Co addition on bulk properties of Sn-3.5 Ag solder and interfacial reactions with Ni-P UBM. J. Electron. Mater. 38(1), 39–45 (2009)
J.-M. Song, C.-F. Huang, H.-Y. Chuang, Microstructural characteristics and vibration fracture properties of Sn–Ag–Cu–TM (TM= Co, Ni, and Zn) alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 35(12), 2154–2163 (2006)
F. Cheng, H. Nishikawa, T. Takemoto, Microstructural and mechanical properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solders with minor addition of Ni and/or Co. J. Mater. Sci. 43(10), 3643–3648 (2008)
A. El-Daly et al., Microstructure, mechanical properties, and deformation behavior of Sn–10 Ag–05 Cu solder after Ni and Sb additions. Mater. Des. 43, 40–49 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the research support provided by the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Funding
This research received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saad, H.M., Bashir, M.N. Fractography analysis of Sn-58Bi solder joint after addition of cobalt nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2235 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11647-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11647-5