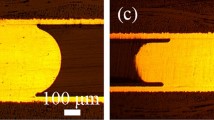
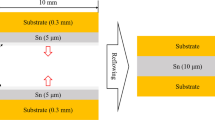
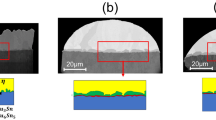
Abstract
A novel friction micro-welding (FMW) technology was used for copper column connection of column grid array (CGA) packaging. The investigation found that its temperature and strain fields could induce formations of diverse interface layers and new solder microstructures. This discontinuous scalloped Cu6Sn5 or Pb(Ag)-rich adsorption layer could form at the upper interface with insufficient hold-tight force. The thin Cu/Sn diffusion layer formed at middle and lower interfaces with greater hold-tight force. The lower position friction pair could be transferred from the solder/Cu column interface to the inside of solders in the later stage of welding, and the reliable join where solder adhered to the Cu/Sn diffusion layer could form. High-temperature visco-plastic solders were not fully extruded from joints and became a micro-zone named stir flow zone (SFZ). In SFZ and dynamic recrystallization zone (DRZ), the friction could induce annealing softening of solders, weak bonding between dispersed intermetallic compound (IMC) particles and β-Sn matrix and low microstructure compactness, but could provide atomic rapid diffusion channels conducive to solid-phase welding. However, above adverse effects disappeared after aging. The average pull-out loads of the SAC305/Cu column and Sn37Pb/Cu column FMW joints increased respectively from 39.6 N and 31.9 N to 76.5 N and 59.3 N. By atomic diffusion, aging self-healing of FMW joints benefited from regeneration of the interface IMC layer, healing of crystal defects caused by friction deformations, dispersion reinforcement of scattered IMC particles in SFZ after solid-phase wetting and the generation of reticulated segregation phases with high melting points at grain boundaries of DRZ.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
R. Ghaffarian, Microelectron. Reliab. 46(12), 2006–2024 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2006.07.094
J. Lau, W. Dauksher, J. Electron. Packag. 127, 96–105 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1846069
E. Suhir, R. Ghaffarian, J. Nicolics, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 570–579 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3790-9
S.B. Park, R. Joshi, Microelectron. Reliab. 48(5), 763–772 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2007.12.008
E. Suhir, R. Ghaffarian, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 11572–11582 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5288-5
X.W. Hu, T. Xu, L.M. Keer, Y.L. Li, X.X. Jiang, J. Alloys Compd. 690, 720–729 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.168
H. Nishikawa, N. Iwata, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 215, 6–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.08.007
B.L. Liu, Y.H. Tian, W. Liu, W.W. Wu, C.Q. Wang, Mater. Lett. 163, 254–257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.10.108
A.T. Tan, A.W. Tan, F. Yusof, Ultrason. Sonochem. 34, 616–625 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.06.039
H.J. Ji, Y.F. Qiao, M.Y. Li, Scr. Mater. 110, 19–23 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.07.036
A.T. Tan, A.W. Tan, F. Yusof, J. Alloys Compd. 705, 188–197 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.165
K.K. Zhang, X.J. Zhang, R.F. Qiu, H.X. Shi, Y.J. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 1681–1686 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-1783-8
M. Yang, S.H. Yang, H.J. Ji et al., J. Mater. Process. Technol. 236, 84–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.04.019
H.B. Xu, M.Y. Li, Y.G. Fu, Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 21, 45–54 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1108/09540910910989439
H.K. Yang, K. Cao, J. Lu, Y. Lu, Metal Mater. Trans. A 50A, 3013–3018 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05209-w
Y.Y. Long, F. Schneider, C. Li et al., Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-GT 6, 449–463 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-019-00061-0
D.C. Cox, R.D. Forrest, P.R. Smith, V. Stolojan, S.R.P. Silva, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 033102–033101 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1990268
C.X. Chen, L.J. Yan, E.S.-W. Kong, Y.F. Zhang, Nanotechnology. 17, 2192–2197 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/9/019
B. Zhao, G.H. Jiang, H.X. Qi, Ceram. Int. 42, 8098–8101 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.02.010
Q. Jia, G.S. Zou, W.G. Wang, H. Ren et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 16743–16752 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b20731
C.-H. Lee, E.-B. Choi, J.-H. Lee, Scr. Mater. 150, 7–12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.02.029
S.K. Bhogaraju, F. Conti, H.R. Kotadia, S. Keim, U. Tetzlaff, J. Alloys Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156043
Z.L. Zhao, L.R. Song, X. Liu, P. Wang, A rotary preheating friction micro-welding method. P.R.C. Patent. No.2017 -10763510.8, issued May 3, 2019
L. Anand, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 104, 12–17 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3225028
L. Xu, Z.B. Chen, W.J. Wang, Y.H. Fu, Y.P. Wu, J. Mater. Sci. 55, 10811–10823 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04689-1
J. Eckermann, S. Mehmood, H.M. Davies et al., Microelectron. Reliab. 54(6–7), 1235–1242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.02.017
J.-H. Cho, S.-H. Han, C.-G. Lee, Mater. Lett. 180, 157–161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.05.157
Y.S. Sato, Y. Nagahama, S. Mironov et al., Scr. Mater. 67, 241–244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.04.029
A. Heidarzadeh, A. Chabok, Y.T. Pei, Mater. Lett. 245, 94–97 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.02.108
M. Imam, V. Racherla, K. Biswas et al., Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 91, 1753–1769 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9865-9
J. Zhao, Y. Miyashita, Y. Mutoh, Int. J. Fatigue 23, 723–731 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-1123(01)00034-2
J. Han, S.H. TAN, F. Guo, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 124–132 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5864-3
B.T. Zhou, T.R. BIELER, T.-K. LEE, W.J. Liu, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 319–331 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-012-2307-z
A. Gerlich, G.A. Cingara, T.H. North, Metal Mater. Trans. A 37, 2773–2786 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02586110
M. Watanabe, K. Feng, Y. Nakamura et al., Mater. Trans. 52, 953–959 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.L-MZ201120
Z.B. Wang, J. Lu, K. Lu, Acta Mater. 53, 2081–2089 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2005.01.020
M. Abbasi, M. Dehghani, H.U. Guim et al., Acta Mater. 117, 262–269 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.06.064
S. Fukumoto, H. Tsubakino, K. Okita et al., Scr. Mater. 42, 807–812 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(00)00299-2
L. Wan, Y.X. Huang, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 99, 1781–1811 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2601-x
S.D. Ji, Z.W. Li, L.G. Zhang, Y. Wang, Mater. Lett. 188, 21–24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.10.032
J. Hu, Y.N. Shi, X. Sauvage, G. Sha, K. Lu, Science. 355, 1292–1296 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal5166
W. Xu, X.C. Liu, X.Y. Li, K. Lu, Acta Mater. 182, 207–214 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2019.10.036
Funding
This work was supported by (Grant Number [12531096]). Author Z.L. Zhao has received research support from the Scientific Research Foundation of Heilongjiang Province Education Department-China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by ZZ, KX, WQ, MH and JL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by ZZ, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Xiao, K., Quan, W. et al. Frictional metallurgy induced formation and evolution of solder/Cu column interconnect microstructure and properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 225 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09675-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09675-8