Abstract
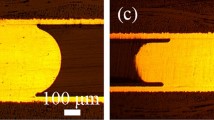
The shear performance and fracture behavior of microscale ball grid array structure Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder joints with different substrate surface finishes (Cu with organic solderability preservatives and electroless Ni/immersion Au) combinations under electro-thermo-mechanical (ETM) coupled loads with increasing current density (from 1.0 × 103 to 6.0 × 103 A/cm2) were systematically investigated by experimental characterization, theoretical analysis, and finite element simulation. The results reveal that the shear strength varies slightly with different surface finish combinations, initially increasing and then decreasing as the current density is increased. Moreover, the increase in current density shifts the fracture location from the solder matrix to the interface between solder and intermetallic compound (IMC) layer, resulting in a ductile-to-brittle transition. The interfacial fracture is triggered by electric current crowding at the groove of the IMC layer and driven by the mismatch strain at the solder/IMC layer interface.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The codes are not publicly available as they also form part of an ongoing study.
References
J.W. Nah, J.O. Suh, K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 013715 (2005)
K.N. Tu, Y.X. Liu, M.L. Li, Appl. Phys. Rev. 4, 011101 (2017)
W.Y. Li, H. Jin, W. Yue, M.Y. Tan, X.P. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 13022 (2016)
W.K. Le, J.Y. Zhou, C.B. Ke, M.B. Zhou, X.P. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 15575 (2020)
C. Kinney, T.K. Lee, K.C. Liu, J.W. Morris, J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2585 (2009)
C. Kinney, J.W. Morris Jr., T.K. Lee, K.C. Liu, J. Xue, D. Towne, J. Electron. Mater. 38, 221 (2009)
D.D. Maio, C. Murdoch, O. Thomas, C. Hunt, The degradation of solder joints under high current density and low-cycle fatigue. 11th International Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-Physics Simulation, and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems (EuroSimE), 1 (2010)
Y. Zuo, L.M. Ma, S.H. Liu, Y.T. Shu, F. Guo, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 597 (2015)
Y.F. Jiao, K. Jermsittiparsert, A.Y. Krasnopevtsev, Q.A. Yousif, M. Mater, Res. Express 6, 106302 (2019)
W.Y. Li, H.B. Qin, M.B. Zhou, X.P. Zhang, The influence of imposed electric current on the tensile fracture behavior of micro-scale Cu/Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu/Cu solder joints. 15th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT), 1030 (2014)
W.Y. Li, H.B. Qin, M.B. Zhou, X.P. Zhang, Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 52, 46 (2016)
X. M. Li, J. Gui, W.Y. Li, H. D. Yan, H.B. Qin, J.Q. Huang, D.G. Yang, Tensile performance of line-type microscale Cu/Sn–58Bi/Cu joints under electro-thermo-mechanical coupled loads. 21th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT), 1 (2020)
W.K. Le, X. Ning, C.B. Ke, M.B. Zhou, X.P. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 15184 (2019)
W.K. Le, X. Ning, J.Q. Huang, M.B. Zhou, X.P. Zhang, 19th IEEE International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT), 610 (2018)
W.K. Le, T. Sun, J.Y. Zhou, M.B. Zhou, X.P. Zhang, Effect of loading rate on the shear performance and fracture behavior of micro-scale BGA structure Cu/Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu/Cu joints under coupled electromechanical loads. 20th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT), 1 (2019)
H.Z. Wang, X.W. Hu, X.X. Jiang, Mater. Charact. 163, 110287 (2020)
H.Z. Wang, X.W. Hu, X.X. Jiang, Y.L. Li, J. Manuf. Process. 62, 291 (2021)
J. Shen, Z.M. Cao, D.J. Zhai, M.L. Zhao, P.P. He, Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 252 (2014)
S. Fuller, M. Sheikh, G. Baty, C.U. Kim, T.K. Lee, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 2853 (2021)
Y. Liu, F.L. Sun, H. Zhang, T. Xin, C.A. Yuan, G.Q. Zhang, Microelectron. Reliab. 55, 1234 (2015)
T. You, Y. Kim, W. Jung, J. Moon, H. Choe, J. Alloys Compd. 486, 242 (2009)
J.M. Kim, M.H. Jeong, S. Yoo, C.W. Lee, Y.B. Park, Microelectron. Eng. 89, 55 (2012)
W.Y. Li, X.P. Zhang, H.B. Qin, Y.-W. Mai, Microelectron. Reliab. 82, 224 (2018)
T. Siewert, S. Liu, D.R. Smith, J.C. Madeni, Database for solder properties with emphasis on new lead-free solders. NIST Spec. Publ. (2002)
T. An, F. Qin, J.G. Li, Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 1011 (2011)
H.B. Qin, X.P. Zhang, M.B. Zhou, J.B. Zeng, Y.-W. Mai, Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 617, 14 (2014)
K.S. Kim, S.H. Huh, K. Suganuma, Microelectron. Reliab. 43, 259 (2003)
R.Y. Tian, C.J. Hang, Y.H. Tian, J.Y. Feng, J. Alloys Compd. 777, 463 (2019)
V.M.F. Marques, C. Johnston, P.S. Grant, Acta Mater. 61, 2460 (2013)
C.L. Liang, K.L. Lin, Mater. Charact. 145, 545 (2018)
Y.H. Liao, C.L. Liang, K.L. Lin, A.T. Wu, AIP Adv. 5, 127210 (2015)
P.C. Liang, K.L. Lin, J. Alloys Compd. 722, 690 (2017)
H.C. Huang, K.L. Lin, A.T. Wu, J. Appl. Phys. 119, 115102 (2016)
J.R. Lloyd, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 32, R109 (1999)
S.W. Chen, C.M. Chen, W.C. Liu, J. Electron. Mater. 27, 1193 (1998)
L.H. Xu, J.H.L. Pang, K.N. Tu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 221909 (2006)
B. Chao, S.H. Chae, X.F. Zhang, K.H. Lu, J. Im, P.S. Ho, Acta Mater. 55, 2805 (2007)
G.I. Taylor, Proc. R. Soc. London 145, 362 (1934)
W.J. Poole, M.F. Ashby, N.A. Fleck, Scr. Mater. 34, 559 (1996)
P. Zhang, S.X. Li, Z.F. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 529, 62 (2011)
H.J. McQueen, W. Blum, Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 290, 95 (2000)
J.W. Elmer, E.D. Specht, J. Electron. Mater. 40, 201 (2011)
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51805103, Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province under Grant No. 2018GXNSFBA281065, Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangxi Province under Grant No. GuiKeAD18281021, Director Fund Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Manufacturing System and Advanced Manufacturing Technology No. 19-050-44-003Z, Self–Topic Fund of Engineering Research Center of Electronic Information Materials and Devices Nos. EIMD–AA202007 and EIMD–AB202005, and Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education Nos. YCBZ2021068 and JGY2021084.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BW contributed to methodology, data curation, formal analysis, and writing and preparation of the original draft. WL contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript, and funding acquisition. KP contributed to funding acquisition, conceptualization, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human tissues or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
This research is not related to human subjects.
Consent for publication
The author assigns non-exclusive publication rights to Springer and warrants that his contribution is unique and that he possesses all necessary authority to make this grant. The author assumes responsibility for the material’s release on behalf of all co-authors. This assignment of publication rights includes the non-exclusive right to reproduce and distribute the article in any format, including reprints, translations, photographic reproductions, microform, electronic form (offline, online), or other reproductions of a similar nature.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Li, W. & Pan, K. Shear performance of microscale ball grid array structure Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder joints with different surface finish combinations under electro-thermo-mechanical coupled loads. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 4924–4939 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07682-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07682-9