Abstract
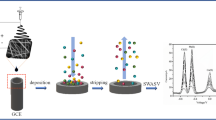
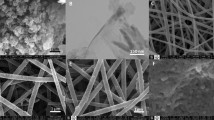
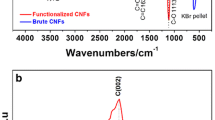
A novel method for selective and sensitive detection of chloride ion plays a vital role in environmental monitoring, industrial and healthcare sectors. Here, we spotlight the synthesis, characterization and electrochemical performance analysis of electrospun PVA-PANi-g-C3N4 nanofibers (NFs) over screen printed carbon electrode and engaged as a modified NF electrode for chloride ion determination. The resulting nanofibers morphological views, functional groups and elemental composition were captured and recorded by FESEM, FTIR and XPS. The electrochemical behaviour of PVA-PANi-g-C3N4 NFs was studied by cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and chronoamperometric techniques, as the results directed that the modified NF electrode reveals a significant electrochemical sensitivity, selectivity for Cl− ion with the value of linear regression co-efficient R2 = 0.99. The lowest limit of detection 0.2 µM with greater sensitivity (1.6082 µM µA/cm2) was succeeded. Owing to its synergistic interaction amid the PVA-PANi with g-C3N4 NF combinations an efficient electron transfer pathway was achieved which leads to an excellent ionic diffusion. Further, the outcomes from the real sample analysis creating them attractive and helping in profound study for electrochemical sensor towards practical applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q.S. Jiang, D. Mak, S. Devidas, E.M. Schwiebert, A. Bragin, Y.L. Zhang, W.R. Skach, W.B. Guggino, J.K. Foskett, J.F. Engelhardt, Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-associated ATP release is controlled by a chloride sensor. J. Cell Biol. 143, 645–657 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.143.3.645
C. Huber, T. Werner, C. Krause, I. Klimant, O.S. Wolfbeis, Energy transfer-based lifetime sensing of chloride using a luminescent transition metal complex. Anal. Chim. Acta 364, 143–151 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(98)00151-2
C. Huber, I. Klimant, C. Krause, T. Werner, T. Mayr, O.S. Wolfbeis, Optical sensor for seawater salinity. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 368, 196–202 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160000493
M.F. Montemor, J.H. Alves, A.M. Simoes, J.C.S. Fernandes, Z. Lourenco, A.J.S. Costa, A.J. Appleton, M.G.S. Ferreira, Multiprobe chloride sensor for in situ monitoring of reinforced concrete structures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 28, 233–236 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2006.01.005
L. Trnkova, V. Adam, J. Hubalek, P. Babula, R. Kizek, Amperometric sensor for detection of chloride ions. Sensors 8, 5619–5636 (2008). https://doi.org/10.3390/s8095619
I.H.A. Badr, M. Diaz, M.F. Hawthorne, L.G. Bachas, Mercuracarborand, anti-crown ether- based chloride sensitive liquid/polymeric membrane electrodes. Anal. Chem. 71, 1371–1377 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac980896e
J.N. Babu, V. Bhalla, M. Kumar, R.K. Mahajan, R.K. Puri, A chloride selective sensor based on a calix [4] arene possessing a urea moiety. Tetrahedron Lett. 49, 2772–2775 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.02.133
J. Junsomboon, J. Jakmunee, Determination of chloride in admixtures and aggregates for cement by a simple flow injection potentiometric system. Talanta 76, 365–368 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.03.006
S. Sebkova, Determination of chlorides on composite silver electrodes. Chem. Listy 97, 201–205 (2003)
F. Hahn, Novel valve for automatic calibration of a chloride sensor for river monitoring. Biosyst. Eng. 92, 275–284 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.07.008
R.H. Wu, X.G. Shao, Application of near-infrared spectra in the determination of water soluble chloride ion in plant samples. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 26, 617–619 (2006)
A.M. Pimenta, A.N. Araujo, M. Conceicao, B.S.M. Montenegro, C. Pasquini, J.J.R. Rohwedder, I.M. Raimundo, Chloride-selective membrane electrodes and optodes based on an indium(III) porphyrin for the determination of chloride in a sequential injection analysis system. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 36, 49–55 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2004.04.011
R.B.R. Mesquita, S.M.V. Fernandes, A. Rangel, Turbidimetric determination of chloride in different types of water using a single sequential injection analysis system. J. Environ. Monit. 4, 458–461 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1039/B200456A
M. Philippi, H.S. dos Santos, A.O. Martins, C.M.N. Azevedo, M. Pires, Alternative spectrophotometric method for standardization of chlorite aqueous solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 585, 361–365 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2006.12.053
H. Cao, H.W. Dong, Rapid and sensitive determination of trace chloride ion in drinks using resonance light scattering technique. J. Autom. Methods Manage. Chem. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/745636
V.G. Bonifacio, L.C. Figueiredo-Filho, L.H. Marcolino, O. Fatibello-Filho, An improved flow system for chloride determination in natural waters exploiting solid-phase reactor and long pathlength spectrophotometry. Talanta 72, 663–667 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2006.11.036
S. Krizkova, P. Ryant, O. Krystofova, V. Adam, M. Galiova, M. Beklova, P. Babula, J. Kaiser, K. Novotny, J. Novotny, M. Liska, R. Malina, J. Zehnalek, J. Hubalek, L. Havel, R. Kizek, Multi-instrumental analysis of tissues of sunflower plants treated with silver(I) ions—plants as bioindicators of environmental pollution. Sensors 8, 445–446 (2008). https://doi.org/10.3390/s8010445
H. Bai, G.Q. Shi, Gas sensors based on conducting polymers. Sensors 7, 267–307 (2007). https://doi.org/10.3390/s7030267
L. Ge, Y.S. Zhao, T. Mo, J.R. Li, P. Li, Immobilization of glucose oxidase in electrospun nanofibrous membranes for food preservation. Food Control 26, 188–193 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.01.022
H. Liu, J. Kameoka, D.A. Czaplewski, H.G. Craighead, Polymeric nanowire chemical sensor. Nano Lett. 4, 671–675 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl049826f
N.J. Pinto, A.T. Johnson Jr., A.G. MacDiarmid, C.H. Mueller, N. Theofylaktos, D.C. Robinson, F.A. Miranda, Electrospun polyaniline/polyethylene oxide nanofiber field-effect transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4244–4246 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1627484
M. Wei, J. Lee, B. Kang, J. Mead, Preparation of core-sheath nanofibers from conducting polymer blends. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 26, 1127–1132 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.200500212
G. Siné, C.C. Hui, A. Kuhn, P.J. Kulesza, K. Miecznikowski, M. Chojak, A. Paderewska, A. Lewera, Spatial control of polyaniline electrodeposition by patterned polyoxometalate monolayers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 150, C351 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1565139
L. Huang, Z. Wang, H. Wang, X. Cheng, A. Mitra, Y. Yan, Polyaniline nanowires by electropolymerization from liquid crystalline phases. J. Mater. Chem. 12, 388–391 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1039/B107499G
C. Bavatharani, E. Muthusankar, S.M. Wabaidur, Z.A. Alothman, K.M. Alsheetan, M.M. AL-Anazy, D. Ragupathy, Electrospinning technique for production of polyaniline nanocomposites/nanofibres for multi-functional applications: a review. Synth. Met. 271, 116609 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2020.116609
D. Zhang, Y. Wang, Synthesis and applications of one-dimensional nano-structured polyaniline: an overview. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 134, 9–19 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2006.07.037
M. Eswaran, S.M. Wabaidur, Z.A. Alothman, R. Dhanusuraman, V.K. Ponnusamy, Improved cyclic retention and high-performance supercapacitive behavior of poly (diphenylamine-co-aniline)/phosphotungstic acid nanohybrid electrode. Int. J. Energy Res. 45, 8180–8188 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5727
C. Bavatharani, E. Muthusankar, S.C. Lee, M.R. Johan, D. Ragupathy, Excellent cyclic retention and supercapacitive performance of electrochemically active nanocomposite electrode. Sens. Lett. 18, 395–400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2020.4233
E. Muthusankar, D. Ragupathy, Graphene/Poly (aniline-co-diphenylamine) nanohybrid for ultrasensitive electrochemical glucose sensor. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 20, 100390 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2019.100390
C. Bavatharani, E. Muthusankar, Z.A. Alothman, S.M. Wabaidur, V.K. Ponnusamy, D. Ragupathy, Ultra-high sensitive, selective, non-enzymatic dopamine sensor based on electrochemically active graphene decorated Polydiphenylamine-SiO2 nanohybrid composite. Ceram. Int. 46, 23276–23281 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.054
S.A. Travain, G.L. Ferreira, J.A. Giacometti, R.F. Bianchi, Electrical characterization of in situ polymerized polyaniline thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 143, 31–37 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2007.07.071
E. Muthusankar, V.K. Ponnusamy, D. Ragupathy, Electrochemically sandwiched poly (diphenylamine)/phosphotungstic acid/graphene nanohybrid as highly sensitive and selective urea biosensor. Synth. Met. 254, 134–140 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2019.06.012
C. Bavatharani, M. Eswaran, S.M. Wabaidur, Z.A. Alothman, P.C. Tsai, V.K. Ponnusamy, R. Dhanusuraman, Novel PDPA-SiO2 nanosphericals network decorated graphene nanosheets composite coated FTO electrode for efficient electro-oxidation of methanol. Fuel 279, 118439 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118439
G. Zhengyang, N. Song, H. Zhang, Z. Ma, Y. Wang, C. Chen, One-step electrofabrication of reduced graphene oxide/poly (N-methylthionine) composite film for high performance supercapacitors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 085501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ab8c82
B. Chokkiah, M. Eswaran, S.M. Wabaidur, M.R. Khan, V.K. Ponnusamy, D. Ragupathy, A novel electrodeposited poly (melamine)-palladium nanohybrid catalyst on GCE: prosperous multi-functional electrode towards methanol and ethanol oxidation. Fuel 300, 121005 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121005
L. Yinqiu, N. Song, Z. Ma, K. Zhou, Z. Gan, Y. Gao, S. Tang, C. Chen, Synthesis of a poly (N-methylthionine)/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for the detection of hydroquinone. Mater. Chem. Phys. 223, 548–556 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.11.045
E. Muthusankar, S.M. Wabaidur, Z.A. Alothman, M.R. Johan, V.K. Ponnusamy, D. Ragupathy, Fabrication of amperometric sensor for glucose detection based on phosphotungstic acid–assisted PDPA/ZnO nanohybrid composite. Ionics 26, 6341–6349 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03740-0
C. Chuanxiang, Z. Gan, K. Zhou, Z. Ma, Y. Liu, Y. Gao, Catalytic polymerization of N-methylthionine at electrochemically reduced graphene oxide electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 283, 1649–1659 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.051
M.S. Cho, S.Y. Park, J.Y. Hwang, H.J. Choi, Synthesis and electrical properties of polymer composites with polyaniline nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 24, 15–18 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2003.09.003
P.L.B. Araujo, E.S. Araujo, R.F.S. Santos, A.P.L. Pacheco, Synthesis and morphological characterization of PMMA/polyaniline nanofiber composites. Microelectron. J. 36, 1055–1057 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2005.04.024
A.R. Hopkins, D.D. Sawall, R.M. Villahermosa, R.A. Lipeles, Interfacial synthesis of electrically conducting polyaniline nanofiber composites. Thin Solid Films 469, 304–308 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2004.08.089
I.D. Norris, M.M. Shaker, F.K. Ko, A.G. MacDiarmid, Electrostatic fabrication of ultrafine conducting fibers: polyaniline/polyethylene oxide blends. Synth. Met. 114, 109–114 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0379-6779(00)00217-4
Z. Chen, Y. Jiang, B. Xin, S. Jiang, Y. Liu, L. Lin, Electrochemical analysis of conducting reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers as supercapacitor electrodes. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03204-1
A.M. Asiri, Electrospun polyaniline/polyvinyl alcohol/multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanofibers as promising bioanode material for biofuel cells. J. Electroanal. Chem. 789, 181–187 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.02.025
K. Jeyasubramanian, E. Muthusankar, G.S. Hikku, N. Selvakumar, Improved thermal and fire retardant behavior of polyvinyl alcohol matrix using nanocomposites. Int. J. Nanosci. 18, 1850025 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219581X18500254
Y. Hou, J. Li, Z. Wen, S. Cui, C. Yuan, J. Chen, N-doped graphene/porous g-C3N4 nanosheets supported layered-MoS2 hybrid as robust anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 8, 157–164 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.06.003
Y. Zheng, J. Liu, J. Liang, M. Jaroniec, S.Z. Qiao, Graphitic carbon nitride materials: controllable synthesis and applications in fuel cells and photocatalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 6717–6731 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2EE03479D
M. Eswaran, R. Dhanusuraman, P.C. Tsai, V.K. Ponnusamy, One-step preparation of graphitic carbon nitride/polyaniline/palladium nanoparticles based nanohybrid composite modified electrode for efficient methanol electro-oxidation. Fuel 251, 91–97 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.040
M. Rong, L. Lin, X. Song, Y. Wang, Y. Zhong, J. Yan, Y. Feng, X. Zeng, X. Chen, Fluorescence sensing of chromium (VI) and ascorbic acid using graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as a fluorescent “switch.” Biosens. Bioelectron. 68, 210–217 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.024
H. Ahmad, S.K. Kamarudin, L.J. Minggu, M. Kassim, Hydrogen from photo-catalytic water splitting process: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 43, 99–610 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.101
T. Sano, S. Tsutsui, K. Koike, T. Hirakawa, Y. Teramoto, N. Negishi, K. Takeuchi, Activation of graphitic carbon nitride (gC3N4) by alkaline hydrothermal treatment for photocatalytic NO oxidation in gas phase. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 6489–6496 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA10472A
Y. Wang, J. Yao, H. Li, D. Su, M. Antonietti, Highly selective hydrogenation of phenol and derivatives over a Pd@Carbon nitride catalyst in aqueous media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 2362–2365 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja109856y
G. Dong, Y. Zhang, Q. Pan, J.A. Qiu, A fantastic graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) material: electronic structure, photocatalytic and photoelectronic properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 20, 33–50 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2014.04.002
R.A. Medeiros, R. Matos, A. Benchikh, B. Saidani, C. Debiemme-Chouvy, C. Deslouis, R.C. Rocha-Filho, O. FatibelloFilho, Amorphous carbon nitride as an alternative electrode material in electroanalysis: simultaneous determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 797, 30–39 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.08.018
H. Zhang, Q. Huang, Y. Huang, F. Li, W. Zhang, C. Wei, J. Chen, P. Dai, L. Huang, Z. Huang, L. Kang, Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets doped graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Electrochim. Acta 142, 125–131 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.07.094
M. Amiri, H. Salehniya, A. Habibi-Yangjeh, Graphitic carbon nitride/chitosan composite for adsorption and electrochemical determination of mercury in real samples. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 8114–8122 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b01699
P. Frontera, C. Busacca, S. Trocino, P. Antonucci, M.L. Faro, E. Falletta, C.D. Pina, M. Rossi, Electrospinning of polyaniline: effect of different raw sources. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13, 4744–4751 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2013.7196
E. Muthusankar, S. Vignesh Kumar, N. Rajagopalan, D. Ragupathy, Synthesis and characterization of co-polymer nanocomposite film and its enhanced antimicrobial behaviour. BioNanoScience 8, 1008–1013 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0564-x
F. Lai, Z. Fang, L. Cao, W. Li, Z. Lin, P. Zhang, Self-healing flexible and strong hydrogel nanocomposites based on polyaniline for supercapacitors. Ionics (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03438-3
S.H. Patil, A.P. Gaikwad, S.D. Sathaye, K.R. Patil, To form layer by layer composite film in view of its application as supercapacitor electrode by exploiting the techniques of thin films formation just around the corner. Electrochim. Acta 265, 556–568 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.01.165
L. Tan, Xu. Jianhua, X. Zhang, Z. Hang, Y. Jia, S. Wang, Synthesis of g-C3N4/CeO2 nanocomposites with improved catalytic activity on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 356, 447–453 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.078
S. Pan, M. Jamal Deen, R. Ghosh, Low-cost graphite-based free chlorine sensor. Anal. Chem. 87, 10734–10737 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03164
M. Cuartero, G.A. Crespo, E. Bakker, Paper based thin-layer coulometric sensor for halide determination. Anal. Chem. 87, 1981–1990 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac504400w
M.M. Rahman, S.B. Khan, G. Gruner, M.S. Al-Ghamdi, M.A. Daous, A.M. Asiri, Chloride ion sensors based on low-dimensional α-MnO2–Co3O4 nanoparticles fabricated glassy carbon electrodes by simple I-V technique. Electrochim. Acta 103, 143–150 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.04.067
Q. Bin, M. Wang, L. Wang, Ag nanoparticles decorated into metal-organic framework (Ag NPs/ZIF-8) for electrochemical sensing of chloride ion. Nanotechnology 31, 125601 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab5cde
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Researchers Supporting Project No. (RSP-2021/1), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chokkiah, B., Eswaran, M., Wabaidur, S.M. et al. An efficient amperometric sensor for chloride ion detection through electroactive e-spun PVA-PANi-g-C3N4 nanofiber. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 9425–9437 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07378-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07378-0