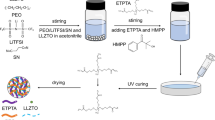
Abstract
Lithium aluminate (LAO) is known to be an effective filler for improving the conductivity of polyethylene–LiX (PEO–LiX) solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs), while succinonitrile (SN) is an excellent solid plasticizer with plastic crystalline organic molecules. In this work, LAO micro-rods are prepared via a simple hydrothermal method, and a novel PEO-based composite polymer electrolyte is developed by the addition of SN and LAO. The resulting optimal composite PEO:LiTFSI:SN(15%):LAO(10%) (PEOL-SPE) has a maximized ionic conductivity of 1.36 × 10−5 S·cm−1at 30 °C, and the membrane has a wide electrochemical window of 5.2 V. The fabricated cell with LiFePO4 as the cathode, metallic lithium as the anode and PEOL-SPE as the electrolyte membrane delivers an impressive initial charge/discharge capacity of 153.1/141.3 mAh g−1 at 60 °C. The addition of 10 wt% of the LAO micro-rods results in a favorable increase in the ionic conductivity, and no apparent blocking effect is observed to impede the electrochemical performance. These results bring to light the potential of micro-sized additives for use in lithium battery applications.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Zhang JJ, Zhao JH, Yue LP, Wang QF, Chai JC, Liu ZH, Zhou XH, Li H, Guo YG, Cui GL, Chen LQ (2015) Safety-reinforced poly(propylene carbonate)-based all-solid-state polymer electrolyte for ambient-temperature solid polymer lithium batteries. Adv Energy Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201501082
Zhou YF, Xie S, Chen CH (2006) In-situ thermal polymerization of rechargeable lithium batteries with poly(methyl methacrylate) based gel-polymer electrolyte. J Mater Sci 41:7492–7497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0803-3
Prasanth R, Aravindan V, Srinivasan M (2012) Novel polymer electrolyte based on cob-web electrospun multi component polymer blend of polyacrylonitrile/poly(methylmethacrylate)/polystyrene for lithium ion batteries—preparation and electrochemical characterization. J Power Sour 202:299–307
Ramesh S, Ng HM (2011) An investigation on PAN–PVC–LiTFSI based polymer electrolytes system. Solid State Ionics 192:2–5
Cui WW, Tang DY, Gong ZL, Guo YD (2012) Performance enhancement induced by electrospinning of polymer electrolytes based on poly(methyl methacrylate-co-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid lithium). J Mater Sci 47:6276–6285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6547-3
Yue LP, Ma J, Zhang JJ, Zhao JY, Dong SM, Liu ZH, Cui GL, Chen LQ (2016) All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater 5:139–164
Karthik K, Murugan R (2018) Lithium garnet based free-standing solid polymer composite membrane for rechargeable lithium battery. J Solid State Electrochem 22:2989–2998
Srivastava S, Schaefer JL, Yang Z, Tu Z, Archer LA (2014) 25th anniversary article: polymer–particle composites: phase stability and applications in electrochemical energy storage. Adv Mater 26:201–234
Ramesh S, Arof AK (2009) A study incorporating nano-sized silica into PVC-blend-based polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. J Mater Sci 44:6404–6407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3883-z
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 394:456–458
Kim JW, Ji KS, Lee JP, Park JW (2003) Electrochemical characteristics of two types of PEO-based composite electrolyte with functional SiO2. J Power Sour 119–121:415–421
Wang ZX, Huang XJ, Chen LQ (2003) Understanding of effects of nano-Al2O3 particles on ionic conductivity of composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochem Solid State Lett 6:E40–E44
Xiong HM, Zhao KK, Zhao X, Wang YW, Chen JS (2003) Elucidating the conductivity enhancement effect of nano-sized SnO2 fillers in the hybrid polymer electrolyte PEO–SnO2–LiClO4. Solid State Ionics 159:89–95
Chenyang YW, Chen SY, Yuan CY, Tsai CH, Yan DP (2005) Preparation and characterization of composite polymer electrolytes based on UV-curable Vinylic ether-containing cyclotriphosphazene, LiClO4, and α-Al2O3. Macromolecules 38:2710–2715
Ishida H, Campbell S, Blackwell J (2000) General Approach to Nanocomposite Preparation. Chem Mater 12:1260–1267
Gilman JW, Jackson CL, Morgan AB, Harris R (2000) Flammability properties of polymer–layered-silicate nanocomposites. Polypropylene and polystyrene nanocomposites. Chem Mater 12:1866–1873
Suski L, Tarniowy M (2001) The phase stability of solid LiAlO2 used for the electrolyte matrix of molten carbonate fuel cells. J Mater Sci 36:5119–5124. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012425324262
Croce F, Scrosati B, Mariotto G (2002) Electrochemical and spectroscopic study of the transport properties of composite polymer electrolytes. Chem Mater 4:1134–1136
Wang G, Roos J, Brinkmann D, Capuano F, Croce F, Scrosati B (1992) Comparison of NMR and conductivity in (PEP) 8LiClO4 + γ-LiAlO2. Solid State Ionics 53–56:1102–1105
Hu LF, Tang ZL, Zhang ZT (2007) New composite polymer electrolyte comprising mesoporous lithium aluminate nanosheets and PEO/LiClO4. J Power Sour 166:226–232
Kumar B, Nellutla S, Thokchom JS, Chen C (2006) Ionic conduction through heterogeneous solids: delineation of the blocking and space charge effects. J Power Sour 160:1329–1335
Karatas Y, Banhatti RD, Kaskhedikar N, Burjanadze M, Funke K, Wiemhofer HD (2009) Synthesis and modeling of polysiloxane-based salt-in-polymer electrolytes with various additives. J Phys Chem B 113:15473–15484
Alarco PJ, Abu-Lebdeh Y, Abouimrane A, Armand M (2004) The plastic-crystalline phase of succinonitrile as a universal matrix for solid-state ionic conductors. Nat Mater 3:476–481
Fan LZ, Hu YS, Bhattacharyya AJ, Maier J (2007) Succinonitrile as a versatile additive for polymer electrolytes. Adv Funct Mater 17:2800–2807
Fan LZ, Wang XL, Long F, Wang X (2008) Enhanced ionic conductivities in composite polymer electrolytes by using succinonitrile as a plasticizer. Solid State Ionics 179:1772–1775
Joshi UA, Chung SH, Lee JS (2005) Surfactant-free hydrothermal synthesis of lithium aluminate microbricks and nanorods from aluminium oxide nanoparticles. Chem Commun 35–36:4471–4473
Xi JY, Qiu XP, Ma XM, Cui MZ, Yang J, Tang XZ, Zhu WT, Chen LQ (2005) Composite polymer electrolyte doped with mesoporous silica SBA-15 for lithium polymer battery. Solid State Ionics 176:1249–1260
Chen B, Huang Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, Xu Q, Long P, Chen S, Xu X (2016) A new composite solid electrolyte PEO/Li10GeP2S12/SN for all-solid-state lithium battery. Electrochim Acta 210:905–914
Morales E (1998) Morphological properties of composite solid polymer electrolytes based on polyethylene oxide. J Appl Polym Sci 69:2435–2440
Han HB, Liu K, Feng SW, Zhou SS, Feng WF, Nie J, Li H, Huang XJ, Matsumoto H, Armand M (2010) Ionic liquid electrolytes based on multimethoxyethyl substituted ammoniums and perfluorinated sulfonimides: preparation, characterization, and properties. Electrochim Acta 55:7134–7144
Kumar B, Scanlon LG, Spry RJ (2001) On the origin of conductivity enhancement in polymer-ceramic composite electrolytes. J Power Sour 96:337–342
Zhang JX, Zhao N, Zhang M, Li YQ, Chu PK, Guo XX, Di ZF, Wang X, Li H (2016) Flexible and ion-conducting membrane electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: dispersion of garnet nanoparticles in insulating polyethylene oxide. Nano Energy 28:447–454
Chen SJ, Wang JY, Zhang ZH, Wu LB, Yao LL, Wei ZY, Deng YH, Xie DJ, Yao XY, Xu XX (2018) In-situ preparation of poly(ethylene oxide)/Li3PS4 hybrid polymer electrolyte with good nanofiller distribution for rechargeable solid-state lithium batteries. J Power Sour 387:72–80
Fan LZ, Maier J (2006) Composite effects in poly(ethylene oxide)–succinonitrile based all-solid electrolytes. Electrochem Commun 8:1753–1756
Liu S, Imanishi N, Zhang T, Hirano A, Takeda Y, Yamamoto O, Yang J (2010) Effect of nano-silica filler in polymer electrolyte on Li dendrite formation in Li/poly(ethylene oxide)–Li(CF3SO2)2N/Li. J Power Sour 195:6847–6853
Maier J (1994) Defect chemistry at interfaces. Solid State Ionics 70–71:43–51
Kumar B (2004) From colloidal to composite electrolytes: properties, peculiarities, and possibilities. J Power Sour 135:215–231
Lee H, Choi S, Choi S, Kim HJ, Choi Y, Yoon S, Cho JJ (2007) SEI layer-forming additives for LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/graphite 5 V Li-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 9:801–806
Ju JW, Wang YT, Chen BB, Ma J, Dong SM, Chai JC, Qu HT, Cui LF, Wu XX, Cui GL (2018) Integrated interface strategy toward room temperature solid-state lithium batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:13588–13597
Li ZH, Zhang DM, Yang FX (2009) Developments of lithium-ion batteries and challenges of LiFePO4 as one promising cathode material. J Mater Sci 44:2435–2443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3316-z
Nagaraju DH, Kuezma M, Suresh GS (2015) LiFePO4 wrapped reduced graphene oxide for high performance Li-ion battery electrode. J Mater Sci 50:4244–4249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8976-2
Xu D, He YB, Chu X et al (2015) Synthesis of lithium iron phosphate/carbon microspheres by using polyacrylic acid coated iron phosphate nanoparticles derived from iron(III) acrylate. Chemsuschem 8:1009–1016
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 21473128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., He, J., Han, W. et al. Composite solid electrolyte PEO/SN/LiAlO2 for a solid-state lithium battery. J Mater Sci 54, 9603–9612 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03535-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03535-3