Abstract
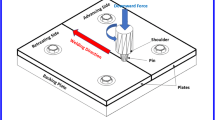
A fully coupled thermo-mechanical finite element model was used to study the friction stir welding process of AA2024-T3 in different thicknesses. The computational results show that the material flows on the retreating and the front sides are higher. So, the slipping rates on the retreating and the front sides are lower than the ones on the trailing and advancing sides. This is the reason that the heat fluxes on the trailing and the advancing sides are higher, which leads to the fact that the temperatures are higher in this region for both thin and thick plates. The energy entering the welding plate accounts for over 50% in the total energy and about 85% in the energy comes from the frictional heat in FSW of AA2024-T3 and the balance from the mechanical effects. The stirring effect of the welding tool becomes weaker in FSW of thick plates. With consideration of the material deformations and the energy conversions, FSW of thin plates shows advantages.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhadeshia HKDH, DebRoy T (2009) Sci Technol Weld Join 14:193
Cavaliere P, Squillace A, Panella F (2008) J Mater Process Technol 200:364
Lorrain O, Serri J, Favier V, Zahrouni H, Hadrouz ME (2009) J Mech Mater Struct 4:351
Ma ZY (2008) Metall Mater Trans A 39:642
Mahmoud ERI, Takahashi M, Shibayanagi T, Ikeuchi K (2009) Sci Technol Weld Join 14:413
Mishra RS, Ma ZY (2005) Mater Sci Eng R 50:1
Nandan R, DebRoy T, Bhadeshia HKDH (2008) Prog Mater Sci 53:980
Zhou L, Liu HJ (2010) Int J Hydro Energy 35:8733
Buffa G, Fratini L, Shivpuri R (2007) J Mater Process Technol 191:356
Genevois C, Fabr`egue D, Deschamps A, Poole WJ (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 441:39
Simar A, Bre′chet Y, de Meester B, Denquin A, Pardoen T (2007) Acta Mater 55:6133
Zhang Z, Zhang HW (2009) Mater Des 30:900
Zhang Z, Zhang HW (2009) J Mater Process Technol 209:241
Zhang Z, Zhang HW (2007) Sci Technol Weld Join 12:226
Zhang Z, Liu YL, Chen JT (2009) Int J Adv Manuf Technol 45:889
Hamilton C, Dymek S, Sommers A (2008) Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48:1120
Khandkar MZH, Khan JA, Reynolds AP (2003) Sci Technol Weld Join 8:165
Schmidt H, Hattel J (2005) Model Simul Mater Sci Eng 13:77
Qin X, Michaleris P (2009) Sci Technol Weld Join 14:640
Arora A, Nandan R, Reynolds AP, DebRoy T (2009) Scr Mater 60:13
Assidi M, Fourment L, Guerdoux S, Nelson T (2010) Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50:143
Zhang Z (2008) J Mater Sci 43:5867. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2865-x
Zhang Z, Chen JT (2008) J Mater Sci 43:222. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2129-1
Zhang HW, Zhang Z, Chen JT (2007) J Mater Process Technol 183:62
Colligan K (1999) Weld J 78:229
Guerra M, Schmidt C, McClure JC, Murr LE, Nunes AC (2003) Mater Charact 49:95
Li Y, Murr LE, McClure JC (1999) Scr Mater 40:1041
Zhang HW, Zhang Z, Chen JT (2005) Sci Eng A 403:340
Zhang Z, Zhang HW (2008) Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37:279
Cavaliere P, Campanile G, Panella F, Squillace A (2006) J Mater Process Technol 180:263
Dixit V, Mishra RS, Lederich RJ, Talwar R (2009) Sci Technol Weld Join 14:346
Peel M, Steuwer A, Preuss M, Withers PJ (2003) Acta Mater 51:4791
Lombard H, Hattingh DG, Steuwer A, James MN (2009) Mater Sci Eng A 501:119
Lombard H, Hattingh DG, Steuwer A, James MN (2008) Eng Fract Mech 75:341
Yan JH, Sutton MA, Reynolds AP (2005) Sci Technol Weld Join 10:725
Nandan R, Roy GG, Lienert TJ, DebRoy T (2007) Acta Mater 55:883
Chen CM, Kovacevic R (2003) Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:1319
Zhang Z, Zhang HW (2007) Sci Technol Weld Join 12:436
Belystchko T, Liu WK, Moran B (2000) Nonlinear finite elements for continua and structures. Wiley, New York, p 393
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 10802017) and the National Key Basic Research Special Foundation of China (2010CB832704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Chen, J.T., Zhang, Z.W. et al. Coupled thermo-mechanical model based comparison of friction stir welding processes of AA2024-T3 in different thicknesses. J Mater Sci 46, 5815–5821 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5537-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5537-1