Abstract
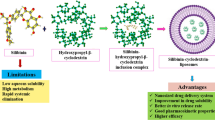
Cyclosporine A (CP) inclusion complex using cyclodextrin (binary) and cyclodextrin with TPGS (ternary) was prepared by the freeze-drying method. The phase solubility study was performed to calculate the solubility parameters. The prepared formulations were evaluated for saturation solubility and drug release studies. The spectroscopy and molecular docking studies were performed to confirm the formation of inclusion complex. The phase solubility results revealed a high stability constant for both binary and ternary samples. A significant enhancement in saturation solubility and dissolution was found in the prepared inclusion complexes. The spectroscopy studies revealed no interaction between the drug and carrier. The molecular docking study displayed the formation of a stable complex with a good docking score. The diffraction pattern showed the conversion of crystalline CP into an amorphous form after the formation of the inclusion complex. The findings were also supported by the saturation solubility study, which showed a significant enhancement in solubility. From the results, it can be concluded that Cyclosporine A inclusion complex using HP βCD with TPGS is an excellent delivery system. Therefore, the prepared delivery systems may be an alternative to the conventional delivery system for enhanced solubility of highly lipophilic drugs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaur, K., Exploring, J.R.: RSM-CCD-optimized chitosan-/gelatin-based hybrid polymer network containing CPM–β-CD inclusion complexes as controlled drug delivery systems. Polym. Bull. 76, 3569–3592 (2019)
Cheirsilp, B., Rakmai, J.: Inclusion complex formation of cyclodextrin with its guest and their applications. Biol. Eng. Med. 2, 1–6 (2017)
Schonbeck, C., Holm, R., Westh, P., Gunther, H., Peters: Extending the hydrophobic cavity of β-cyclodextrin results in more negative heat capacity changes but reduced binding affinities. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 78, 351–361 (2014)
Przybyla, M.A., Yilmaz, G., Becer, R.: Natural cyclodextrins and their derivatives for polymer synthesis. Polym. Chem. 11(48), 7582–7602 (2020)
Das, S., Nath, S., Singh, T.S., Chattopadhyay, N.: Cavity size dependent stoichiometry of probe–cyclodextrin complexation: Experimental and molecular docking demonstration. J. Photochem. Photobiol A: Chem. 388, 112158 (2020)
Saha, S., Roy, A., Roy, K., Roy, M.N.: Study to explore the mechanism to form inclusion complexes of β-cyclodextrin with vitamin molecules. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–12 (2016)
Cid-Samamed, A., Rakmai, J., Mejuto, J.C., Simal-Gandara, J., Astray, G.: Cyclodextrins inclusion complex: Preparation methods, analytical techniques and food industry applications. Food Chem. 384, 132467 (2022)
Liu, J.Y., Zhang, X., Tian, B.R.: Selective modifications at the different positions of cyclodextrins: A review of strategies. Turkish J. Chem. 44(2), 261–278 (2020)
Jun, S.W., Kim, M.S., Kim, J.S., Park, H.J., Lee, S., Woo, J.S., Hwang, S.J.: Preparation and characterization of simvastatin/ hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 66, 413 (2007)
Zoeller, T., Dressman, J.B., Klein, S.: Application of a ternary HP-β- CD-complex approach to improve the dissolution performance of a poorly soluble weak acid under biorelevant conditions. Int. J. Pharm. 430, 176–183 (2012)
Ding, X., Zheng, M., Lu, J., Zhu, X.: Preparation and evaluation of binary and ternary inclusion complexes of fenofibrate/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phen Macr Chem. 91, 17–24 (2018)
Srivalli, K.M.R., Mishra, B.: Improved aqueous solubility and antihypercholesterolemic activity of ezetimibe on formulating with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin and hydrophilic auxiliary substances. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 17(2), 272–283 (2016)
Bera, H., Chekuri, S., Sarkar, S., Kumar, S., Muvva, N.B., Mothe, S., Nadimpalli, J.: Novel pimozide-β-cyclodextrin-polyvinylpyrrolidone inclusion complexes for Tourette syndrome treatment. J. Mol. Liquid. 215, 135–143 (2016)
Kurkov, S.V., Loftsson, T., Cyclodextrins: Int. J. Pharm. 453, 167–180 (2013)
Zhang, Y., Zhou, Q., Jia, S., Lin, K., Fan, G., Yuan, J., Yu, S., Shi, J.: Specific modification with tpgs and drug loading of cyclodextrin polyrotaxanes and the enhanced antitumor activity study in vitro and in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(50), 46427–46436 (2019)
Yang, C., Qin, Y., Tu, K., Xu, C., Li, Z., Zhang, Z.: Star-shaped polymer of β–cyclodextrin-g-vitamin E TPGS for doxorubicin delivery and multidrug resistance inhibition. Colloids Surf. B: Biointer. 169, 10–19 (2018)
Beauchesne, P.R., Chung, N.S., Wasan, K.M., Cyclosporine, A.: A review of current oral and intravenous delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 33, 211–220 (2007)
Onoue, S., Sato, H., Kawabata, Y., Mizumoto, T., Hashimoto, N., Yamada, S.: In vitro and in vivo characterization on amorphous solid dispersion of cyclosporine A for inhalation therapy. J. Cont. Rel. 138, 16–23 (2009)
Ismailos, G., Reppas, C., Dressman, J.B., Macheras, P.: Unusual solubility behaviour of cyclosporin A in aqueous media. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 43, 287–289 (1991)
Onoue, S., Suzuki, H., Kojo, Y., Matsunaga, S., Sato, H., Mizumoto, T., Yuminoki, K., Hashimoto, N., Yamada, S.: Self-micellizing solid dispersion of cyclosporine A with improved dissolution and oral bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 62, 16–22 (2014)
Boukhris, T., Skiba, M.L., Skiba, M.: Novel oral formulation of cyclosporine-spray-dried dispersion using cyclodextrin copolymers. Digest J. Nanomat Biostr. 7(1), 143–154 (2012)
Suzuki, H., Moritani, T., Morinaga, T., Seto, Y., Sato, H., Onoue, S.: Amorphous solid dispersion of cyclosporine A prepared with fine droplet drying process: Physicochemical and pharmacokinetic characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 519(1–2), 213–219 (2017)
Suzuki, H., Ueno, K., Mizumoto, T., Seto, Y., Sato, H., Onoue, S.: Self-micellizing solid dispersion of cyclosporine A with improved dissolution and oral bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 96(1), 107–114 (2017)
Guada, M., Lasa-Saracíbar, B., Lana, H., Dios-Vieitez, M.C., Prieto, M.J.B.: Lipid nanoparticles enhance the absorption of cyclosporine A through the gastrointestinal barrier: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 500(1–2), 154–161 (2016)
Guada, M., Lana, H., Gil, A.G., Dios-Vieitez Mdel, C., Blanco-Prieto, M.J.: Cyclosporine a lipid nanoparticles for oral administration: Pharmacodynamics and safety evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 101, 112–118 (2016)
Yu, H., Xia, D., Zhu, Q., Zhu, C., Chen, D., Gan, Y.: Supersaturated polymeric micelles for oral cyclosporine a delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 85(3), 1325–1336 (2013)
Binkhathlan, Z., Ali, R., Qamar, W., Lavasanifar, A.: Pharmacokinetics of orally administered poly(Ethylene Oxide)-block-Poly(ε-Caprolactone) micelles of cyclosporine A in rats: Comparison with Neoral®. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 21, 177s–191s (2018)
Binkhathlan, Z., Ali, R., Qamar, W., Lavasanifar, A.: Pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution of orally administered cyclosporine A-loaded poly(ethylene oxide)-block-Poly(ε-caprolactone) micelles versus Sandimmune® in rats. Pharm. Res. 38, 51–65 (2021)
Lahiani-Skiba, M., Hallouard, F., Bounoure, F., Milon, N., Karrout, Y., Skiba, M.: Enhanced dissolution and oral bioavailability of Cyclosporine A: Microspheres based on αβ-Cyclodextrins polymers. Pharmaceutics. 10(4), 285 (2018)
Huynh, N.A.K., Do, T.H.T., Le, X.L., Huynh, T.T.N., Nguyen, D.H., Tran, N.K., Tran, C.T.H.L., Nguyen, D.H., Truong, C.T.: Development of softgel capsules containing cyclosporine a encapsulated pine essential oil based self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. J. Drug Del. Sci. Tech. 68, 103115 (2022)
Chaudhari, P., Birangal, S., Mavlankar, N., Pal, A., Mallela, L.S., Roy, S., Kodoth, A.K., Ghate, V., Nampoothiri, M., Lewis, S.A.: Oil-free eye drops containing cyclosporine A / cyclodextrin/PVA supramolecular complex as a treatment modality for dry eye disease. Carbohyd Pol. 297, 120007 (2022)
Malaekeh-Nikouei, B., Nassirli, H., Davies, N.: Enhancement of cyclosporine aqueous solubility using α- and hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin mixtures. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 59, 245–250 (2007)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 4, 117–212 (1965)
Brewster, Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv Rev. 59, 645–666 (2007)
Suvarna, V., Thorat, S., Nayak, U., Sherje, A., Murahari, M.: Host-guest interaction study of Efavirenz with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and L-arginine by computational simulation studies: Preparation and characterization of supramolecular complexes. J. Mol. Liq. 259, 55–64 (2018)
Wang, D., Chen, G., Ren, L.: Preparation and characterization of the Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin inclusion complex of Amiodarone Hydrochloride with enhanced oral bioavailability in fasted state. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 18(5), 1526–1535 (2017)
Mayank, P., Rajashree, H.: Multicomponent cyclodextrin system for improvement of solubility and dissolution rate of poorly water soluble drug. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 14(1), 104–115 (2019)
Shah, R.B., Tawakkul, M.A., Khan, M.A.: Comparative evaluation of flow for pharmaceutical powders and granules. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 9(1), 250–258 (2008)
Goh, H.P., Heng, P.W.S., Liew, C.L.: Comparative evaluation of powder flow parameters with reference to particle size and shape. Int. J. Pharm. 547(1–2), 133–141 (2018)
Eid, E.E.M., Almaiman, A.A., Alshehade, S.A., Alsalemi, W., Kamran, S., Suliman, F.O.: Alshawsh. M. A. characterization of thymoquinone-Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin inclusion complex for Anticancer Applications. Molecules. 28(10), 4096 (2023)
Marques, C.S.F., Barreto, N.S., Oliveira, S.S., Cd., Santos, A.L.S., Branquinha, M.H., Sousa, D., Pd., Castro, M., Andrade, L.N., Pereira, M.M., Silva, C.: Fd. β-Cyclodextrin/Isopentyl caffeate inclusion complex: Synthesis, characterization and antileishmanial activity. Molecules. 25(18), 4181 (2020)
de Freitas, M.R., Rolim, L.A., Soares, M.F., Rolim-Neto, P.J., de Albuquerque, M.M., Soares-Sobrinho, J.L.: Inclusion complex of methyl-β-cyclodextrin and olanzapine as potential drug delivery system for schizophrenia. Carbohydr. Polym. 89, 1095–1100 (2012)
Bajracharya, R., Song, J.G., Lee, S.H., Jeong, S.H., Han, H.K.: Enhanced oral bioavailability of mt-102, a new anti-inflammatory agent, via a ternary solid dispersion formulation. Pharmaceutics. 14, 1510 (2022)
Vasconcelos, T., Prezotti, F., Araujo, F., Lopes, C., Loureiro, A., Marques, S., Sarmento, B.: Third-generation solid dispersion combining soluplus and poloxamer 407 enhances the oral bioavailability of resveratrol. Int. J. Pharm. 595, 120245 (2021)
Bajracharya, R., Lee, S.H., Song, J.G., Kim, M., Lee, K., Han, H.K.: Development of a ternary solid dispersion formulation of LW6 to improve the in vivo activity as a BCRP inhibitor: Preparation and in vitro/in vivo characterization. Pharmaceutics. 11, 206 (2019)
Kim, N.A., Oh, H.K., Lee, J.C., Choi, Y.H., Jeong, S.H.: Comparison of solubility enhancement by solid dispersion and micronized butein and its correlation with in vivo study. J. Pharm. Investig. 51, 53–60 (2021)
Hirlekar, R.S., Sonawane, S.N., Kadam, V.J.: Studies on the effect of water-soluble polymers on drug-cyclodextrin complex solubility. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 10(3), 858–863 (2009)
Lakshman, J.P., Cao, Y., Kowalski, J., Serajuddin, A.T.: Application of melt extrusion in the development of a physically and chemically stable high-energy amorphous solid dispersion of a poorly water-soluble drug. Mol. Pharm. 5(6), 994–1002 (2008)
Furqan, A., Maulvi, Sonali, J., Dalwadi, Vaishali, T., Thakkar, T.G., Soni, M.C., Gohel, T.R., Gandhi: Improvement of dissolution rate of aceclofenac by solid dispersion technique. Powder Technol. 207(1–3), 47–54 (2011)
Lebrun, P., Krier, F., Mantanus, J.: Design space approach in the optimization of the spray-drying process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 80(1), 226–234 (2012)
Fesik, S.W., Gampe, R.T.J., Eaton, H.L., Gemmecker, G., Olejniczak, E.T., Neri, P., Holzman, T.F., Egan, D.A., Edalji, R., Simmer, R., et al.: NMR studies of [U-13 C] cyclosporin A bound to cyclophilin: Bound conformation and portions of cyclosporin involved in binding. Biochemistry. 30(26), 6574–6583 (1991)
Rolt, R., O’Neill, P.M., Liangc, T.J., Stachulsk, A.V.: Synthesis of MeBmt and related derivatives via syn selective ATH-DKR†. RSC Adv. 9, 40336–40339 (2019)
Duttagupta, I., Ghosh, K.C., Sinha, S.: Synthetic studies toward nonribosomal peptides. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 48, 29–64 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This research project was supported by the Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2023R108), Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sadaf Jamal Gilani: Conceptualization, Funding, Resources. Syed Sarim Imam: Experimental, Data curation. Raisuddin Ali: Characterization, Data curation, Writing of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gilani, S.J., Imam, S.S. & Ali, R. Formulation and evaluation of multicomponent inclusion complex of cyclosporine A. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-024-01225-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-024-01225-5