Abstract
Purpose
Even though butein can be a promising candidate for anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic activities, it is poorly soluble limiting its availability for product development. Size reduction and solid dispersion (SD) were adopted independently to evaluate their feasibility for enhancement in solubility as well as bioavailability.
Methods
To reduce the particle size, milling method was carried out under dry and wet conditions. For solid dispersion preparation, simple solvent evaporation method was used with hydrophilic excipients including PVP K-30 and Poloxamer 407. Physicochemical properties such as crystallinity, size, and kinetic solubility of prepared formulations were assessed using dynamic light scattering, X-ray powder diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, and solubility. In vivo pharmacokinetic study was also conducted with selected samples.
Results
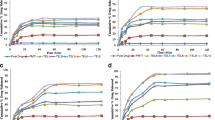
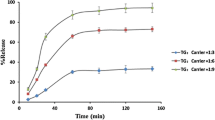
Butein is weakly basic with its pKa 6.76 and log P 3.81 based on the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. High temperature and basic pH were degradative stresses as significant color change in solution. Milling decreased the size distribution down to 4.2 μm without dramatic change in the solubility. However, the solubility of solid dispersion increased from 3.15 up to 114.57 μg/mL, suggesting amorphous state increased solubility significantly. Its amorphous state was confirmed by DSC and PXRD. In addition, oral absorption of SD in vivo confirmed its enhanced pharmacokinetic parameters; faster Tmax, higher Cmax and AUC.
Conclusions
Solid dispersion exhibited enhancement in pharmacokinetic parameters compared to size reduction, suggesting its feasibility for solid dispersion formulation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branham ML, Moyo T, Govender T (2012) Preparation and solid-state characterization of ball milled saquinavir mesylate for solubility enhancement. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 80:194–202
Chaumeil J (1998) Micronization: a method of improving the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Method Find Exp Clin 20:211–216
Chu KR, Lee E, Jeong SH, Park E-S (2012) Effect of particle size on the dissolution behaviors of poorly water-soluble drugs. Arch Pharm Res 35:1187–1195
Dangprasirt P, Ritthidej G (1995) Development of diclofenac sodium controlled release solid dispersions by spray drying using optimization strategy I. Powder formulation. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 21:2323–2337
Eloy JO, Marchetti JM (2014) Solid dispersions containing ursolic acid in Poloxamer 407 and PEG 6000: a comparative study of fusion and solvent methods. Powder Technol 253:98–106
Frizon F, De Oliveira EJ, Donaduzzi CM, Mitsui ML, Marchetti JM (2013) Dissolution rate enhancement of loratadine in polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 solid dispersions by solvent methods. Powder Technol 235:532–539
Jung J-Y, Yoo SD, Lee S-H, Kim K-H, Yoon D-S, Lee K-H (1999) Enhanced solubility and dissolution rate of itraconazole by a solid dispersion technique. Int J Pharm 187:209–218
Khadka P, Ro J, Kim H, Kim I, Kim JT, Kim H, Cho JM, Yun G, Lee J (2014) Pharmaceutical particle technologies: an approach to improve drug solubility, dissolution and bioavailability. Asian J Pharm Sci 9:304–316
Kim K-T, Lee J-Y, Lee M-Y, Song C-K, Choi J-H, Kim D-D (2011) Solid dispersions as a drug delivery system. J Pharm Invest 41:125–142
Leuner C, Dressman J (2000) Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:47–60
Lloyd G, Craig D, Smith A (1999) A calorimetric investigation into the interaction between paracetamol and polyethlene glycol 4000 in physical mixes and solid dispersions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 48:59–65
Ning X, Sun J, Han X, Wu Y, Yan Z, Han J, He Z (2011) Strategies to improve dissolution and oral absorption of glimepiride tablets: solid dispersion versus micronization techniques. Drug Dev Inv Pharm 37:727–736
Padmavathi G, Roy NK, Bordoloi D, Arfuso F, Mishra S, Sethi G, Bishayee A, Kunnumakkara AB (2017) Butein in health and disease: a comprehensive review. Phytomedicine 25:118–127
Pokharkar VB, Mandpe LP, Padamwar MN, Ambike AA, Mahadik KR, Paradkar A (2006) Development, characterization and stabilization of amorphous form of a low T g drug. Powder Technol 167:20–25
Qian F, Huang J, Hussain MA (2010) Drug–polymer solubility and miscibility: stability consideration and practical challenges in amorphous solid dispersion development. J Pharm Sci 99:2941–2947
Rashid R, Kim DW, Ud Din F, Mustapha O, Yousaf AM, Park JH, Kim JO, Yong CS, Choi H-G (2015) Effect of hydroxypropylcellulose and Tween 80 on physicochemical properties and bioavailability of ezetimibe-loaded solid dispersion. Carbohyd Polym 130:26–31
Saffoon N, Uddin R, Huda NH, Sutradhar KB (2011) Enhancement of oral bioavailability and solid dispersion: a review. J Appl Pharm Sci 1:13–20
Samoszuk M, Tan J, Chorn G (2005) The chalcone butein from Rhus verniciflua stokes inhibits clonogenic growth of human breast cancer cells co-cultured with fibroblasts. BMC Complement Altern M 5:5
Schultheiss N, Newman A (2009) Pharmaceutical cocrystals and their physicochemical properties. Cryst Growth Des 9:2950–2967
Serajuddin A (1999) Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J Pharm Sci 88:1058–1066
Sethia S, Squillante E (2004) Solid dispersion of carbamazepine in PVP K30 by conventional solvent evaporation and supercritical methods. Int J Pharm 272:1–10
Vasconcelos T, Sarmento B, Costa P (2007) Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov Today 12:1068–1075
Vyas V, Sancheti P, Karekar P, Shah M, Pore Y (2009) Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersion systems of tadalafil with poloxamer 407. Acta Pharm 59:453–461
Weuts I, Kempen D, Decorte A, Verreck G, Peeters J, Brewster M, Van Den Mooter G (2005) Physical stability of the amorphous state of loperamide and two fragment molecules in solid dispersions with the polymers PVP-K30 and PVP-VA64. Eur J Pharm Sci 25:313–320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, N.A., Oh, H.K., Lee, J.C. et al. Comparison of solubility enhancement by solid dispersion and micronized butein and its correlation with in vivo study. J. Pharm. Investig. 51, 53–60 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-020-00486-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-020-00486-9