Abstract
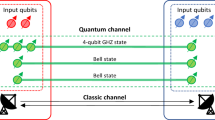
Possibility of using non-maximally entangled states in quantum bidirectional direct communication has been shown recently by Srikanth A and Balakrishnan (Quantum Inf. Process. 19:133, 2020) [1]. The effect of noise in this protocol is analyzed by considering amplitude and phase damping models. Suitable combinations of messages and initial states are identified to minimize the effect of noise in the protocol. Further, we have shown the possibility of demarking the effects due to noise and the intruder.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Srikanth, A., Balakrishnan, S.: Controller-independent quantum bidirectional communication using non-maximally entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(4), 1–11 (2020)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 560, 7–11 (2014)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Mermin, N.D.: Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(5), 557 (1992)
Cabello, A.: Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(26), 5635–5638 (2000)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A. 65(3), 032302 (2002)
Nurhadi, A. I. and Syambas, N. R.: Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) Protocols: A Survey, IEEE 4th International Conference on Wireless and Telematics (ICWT) 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICWT.2018.8527822 (2018)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two step quantum direct communication protocol using Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen block. Phys. Rev. A. 68(04), 042317 (2003)
Boström, K., Felbinger, T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89(18), 187902 (2002)
Cai, Q.Y., Li, B.W.: Improving the capacity of the Bostrom and Felbinger protocol. Phys. Rev. A. 69(5), 054301 (2004)
Chen, X.B., Wang, T.Y., Du, J.Z., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Controlled quantum secure direct communication with quantum encryption. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 6(03), 543–551 (2008)
Chen, X.B., Wen, Q.Y., Guo, F.Z., Sun, Y., Xu, G., Zhu, F.C.: Controlled quantum secure direct communication with W state. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 6(04), 899–906 (2008)
Nguyen, B.A.: Quantum dialogue. Phys. Lett. A. 328(1), 6–10 (2004)
Man, Z.X., Zhang, Z.J., Li, Y.: Quantum dialogue revisited. Chin. Phys. Lett. 22(1), 22–24 (2005)
Ji, X., Zhang, S.: Secure quantum dialogue based on single-photon. Chinese. Phys. 15(7), 1418–1420 (2006)
Man, Z.X., Xia, Y.J., Zhang, Z.J.: Secure deterministic bidirectional communication without entanglement. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 4(4), 739–746 (2006)
Dong, L., Xiu, X.M., Gao, Y.J., Chi, F.: A controlled quantum dialogue protocol in the network using entanglement swapping. Opt. Commun. 281(24), 6135–6138 (2008)
Ye, T.Y., Jiang, L.Z.: Improvement of controlled bidirectional quantum direct communication using a GHZ state. Chin. Phys. Lett. 30(4), 040305 (2013)
Ye, T.Y., Jiang, L.Z.: Quantum dialogue without information leakage based on the entanglement swapping between any two bell states and the shared secret bell state. Phys. Scr. 89(1), 015103 (2013)
Ye, T.Y.: Robust quantum dialogue based on the entanglement swapping between any two logical bell states and the shared auxiliary logical bell state. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(4), 1469–1486 (2015)
Gao, G.: Two quantum dialogue protocols without information leakage. Opt. Commun. 283(10), 2288–2293 (2010)
Wang, H., Zhang, Y.Q., Liu, X.F., Hu, Y.P.: Efficient quantum dialogue using entangled states and entanglement swapping without information leakage. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(6), 2593–2603 (2016)
Ye, T.Y.: Large payload bidirectional quantum secure direct communication without information leakage. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 11(05), 1350051 (2013)
Shi, G.F.: Bidirectional quantum secure communication scheme based on bell states and auxiliary particles. Opt. Commun. 283(24), 5275–5278 (2010)
Ye, T.Y.: Quantum secure dialogue with quantum encryption. Commun. Theor. Phys. 62(3), 338–342 (2014)
Shi, G.F., Tian, X.L.: Quantum secure dialogue based on single photons and controlled-not operations. J. Mod. Opt. 57(20), 2027–2030 (2010)
Gao, G., Fang, M., Wang, Y., Zang, D.J.: A ping-pong quantum dialogue scheme using genuine four-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50(10), 3089–3095 (2011)
Ye, T.Y.: Quantum dialogue without information leakage using a single quantum entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(11), 3719–3727 (2014)
Kao, S.H., Hwang, T.: Controlled quantum dialogue robust against conspiring users. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(10), 4313–4324 (2016)
Zarmehi, F., Houshmand, M.: Controlled bidirectional quantum secure direct communication network using classical XOR operation and quantum entanglement. IEEE Commun. Lett. 20(10), 2071–2074 (2016)
Li, W., Zha, X.W., Yu, Y.: Secure quantum dialogue protocol based on four-qubit cluster state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(2), 371–380 (2018)
Ye, T.Y., Ye, C.Q.: Semi-quantum dialogue based on single photons. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(5), 1440–1454 (2018)
Ye, T.: Information leakage resistant quantum dialogue against collective noise. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57(12), 2266–2275 (2014)
Ye, T.: Fault tolerant channel-encrypting quantum dialogue against collective noise. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58(4), 1–10 (2015)
Zhang, M.H., Cao, Z.W., Peng, J.Y., Chai, G.: Fault tolerant quantum dialogue protocol over a collective noise channel. Eur. Phys. J. D. 73(3), 1–8 (2019)
Chang, C.H., Luo, Y.P., Yang, C.W., Hwang, T.: Intercept-and-resend attack on controlled bidirectional quantum direct communication and its improvement. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(9), 3515–3522 (2015)
Mohapatra, A.K., Balakrishnan, S.: Controller-independent bidirectional quantum direct communication. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(6), 147 (2017)
Nielsen, M. A. and Chuang, I. L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information, (Cambridge University Press), Cambridge (2000)
Sharma, V., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A., Banerjee, S.: A comparative study of protocols for secure quantum communication under noisy environment: single-qubit-based protocols versus entangled-state-based protocols. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(11), 4681–4710 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramachandran, M., Balakrishnan, S. Effect of Noise in the Quantum Bidirectional Direct Communication Protocol Using Non- maximally Entangled States. Int J Theor Phys 61, 127 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05115-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05115-9