Abstract
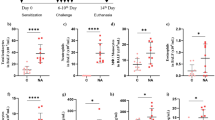
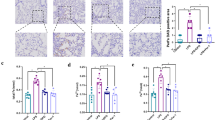
The present study was designed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effect of fluoxetine (Flu) against cigarette smoke (CS)-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in rats. Forty male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly assigned to five groups: control group, CS group, dexamethasone (2 mg/kg) group, and flu (2 mg/kg). H&E staining demonstrated that Flu inhibited CS-induced pathological injury. In addition, Flu could restore the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in serum. Flu also inhibited the levels of cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β). Furthermore, flu significantly inhibited the protein levels of TLR/NF-κB and apoptosis pathway in CS-induced rats. Our findings suggested that flu might effectively ameliorate the progression of COPD via inflammation and apoptosis pathway in rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, G., Y. Wang, Y. Zeng, G.F. Gao, X. Liang, M. Zhou, et al. 2013. Rapid health transition in China, 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of disease study 2010. The Lancet 381: 1987–2015.
Preobrazhenska, O., J.L. Wright, and A. Churg. 2012. Regional heterogeneity in murine lung fibroblasts from normal mice or mice exposed once to cigarette smoke. PloS One 7: e39761.
Zhu, L., T. Chen, X. Chang, R. Zhou, F. Luo, J. Liu, K. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Yang, H. Long, Y. Liu, T. Yan, and C. Ma. 2016. Salidroside ameliorates arthritis-induced brain cognition deficits by regulating Rho/ROCK/NF-κB pathway. Neuropharmacology 103: 134–142.
Wang, Y., Y.H. Gu, M. Liu, Y. Bai, and H.L. Wang. 2016. Fluoxetine protects against methamphetamine-induced lung inflammation by suppressing oxidative stress through the SERT/p38 MAPK/Nrf2 pathway in rats. Molecular Medicine Reports. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.6072.
Flouris, A.D., et al. 2010. Biologicalevidence for the acute health effects of secondhand smoke exposure. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 298 (1): L3–12.
Tuder, R.M., and J.H. Yun. 2008. It takes two to tango: cigarette smoke partners with viruses to promote emphysema. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 118: 2689–2693.
Jiang, W., F. Luo, Q. Lu, J. Liu, P. Li, X. Wang, et al. 2016. The protective effect of Trillin LPS-induced acute lung injury by the regulations of inflammation and oxidative state. Chemico-Biological Interactions 243: 127–134.
Chen, T., W. Jiang, H. Zhang, X. You, M. Liu, L. Wang, et al. 2016. Protective effect of trillin against ethanol-induced acute gastric lesions in an animal model. RSC Advances 6: 20081–20088.
Chen, T., R. Wang, W. Jiang, H. Wang, A. Xu, G. Lu, et al. 2016. Protective Effect of Astragaloside IV Against Paraquat-Induced Lung Injury in Mice by Suppressing Rho Signaling. Inflammation 39: 483–492.
Jiang, W., R. Zhou, P. Li, Y. Sun, Q. Lu, Y. Qiu, et al. 2016. Protective effect of chrysophanol on LPS/d-GalN-induced hepatic injury through the RIP140/NF-κB pathway. RSC Advances 6: 38192–38200.
Jing, W., M. Chunhua, and W. Shumin. 2015. Effects of acteoside on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury via regulation of NF-kappaB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 285: 128–135.
Chen, T., J. Gao, P. Xiang, Y. Chen, J. Ji, P. Xie, et al. 2015. Protective effect of platycodin D on liver injury in alloxan-induced diabetic mice via regulation of Treg/Th17 balance. International Immunopharmacology 26: 338–348.
Brusselle, G., K. Bracke, T. Maes, A. D’hulst, K. Moerloose, G. Joos, et al. 2006. Murine models of COPD. Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 19: 155–165.
Pauwels, R.A., K.F. Rabe, et al. 2004. The Lancet 364: 613–620.
Chen, T., Y. Mou, J. Tan, L. Wei, Y. Qiao, T. Wei, et al. 2015. The protective effect of CDDO-Me on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. International Immunopharmacology 25: 55–64.
Krommidas, G., K. Kostikas, G. Papatheodorou, A. Koutsokera, K.I. Gourgoulianis, C. Roussos, et al. 2010. Plasma leptin and adiponectin in COPD exacerbations: associations with inflammatory biomarkers. Respiratory Medicine 104: 40–46.
Jiang, Q., M. Yi, Q. Guo, C. Wang, H. Wang, S. Meng, et al. 2015. Protective effects of polydatin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through TLR4-MyD88-NF-kappaB pathway. International Immunopharmacology 29: 370–376.
Profita, M., G. Chiappara, F. Mirabella, R. Di Giorgi, L. Chimenti, G. Costanzo, et al. 2003. Effect of cilomilast (Ariflo) on TNF-α, IL-8, and GM-CSF release by airway cells of patients with COPD. Thorax 58: 573–579.
Chen, T., Q. Guo, H. Wang, H. Zhang, C. Wang, P. Zhang, et al. 2015. Effects of esculetin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury via regulation of RhoA/Rho Kinase/NF-small ka, CyrillicB pathways in vivo and in vitro. Free Radical Research 49: 1459–1468.
Zhang, K., J. Liu, X. You, P. Kong, Y. Song, L. Cao, et al. 2016. P2X7 as a new target for chrysophanol to treat lipopolysaccharide-induced depression in mice. Neuroscience Letters 613: 60–65.
Barton, G.M., and R. Medzhitov. 2003. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 300: 1524–1525.
Hertzog, P.J., L.A. O’Neill, and J.A. Hamilton. 2003. The interferon in TLR signaling: more than just antiviral. Trends in Immunology 24: 534–539.
Kopp, E., and R. Medzhitov. 2003. Recognition of microbial infection by Toll-like receptors. Current Opinion in Immunology 15: 396–401.
Yamamoto, M., S. Sato, H. Hennmi, K. Hoshino, T. Kaisho, et al. 2003. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 301: 640–643.
Meylan, E., K. Burnx, K. Hofmann, V. Blancheteau, F. Martinon, et al. 2004. RIP1 is an essential mediator of Toll-like receptor 3-induced NF-κB activation. Nature Immunology 5: 503–507.
Haw, T.J., M.R. Starkey, P.M. Nair, et al. 2016. A pathogenic role for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Mucosal Immunology 9 (4): 859–872.
Yang, M., P. Chen, H. Peng, et al. 2015. Cigarette smoke extract induces aberrant cytochrome-c oxidase subunit II methylation and apoptosis in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology 308 (5): C378–C384.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Z., Liu, J., Bian, H. et al. Fluoxetine, an Antidepressant Drug, Inhibited Cigarette Smoke-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Apoptosis in Rats. Inflammation 40, 1375–1381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0580-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0580-y