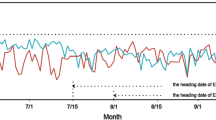
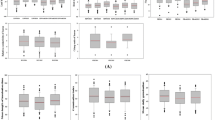
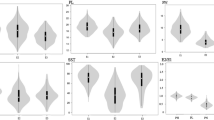
Abstract
Low temperature at the booting stage is a major abiotic stress-limiting rice production. In this study, Cold stress tolerance index of panicle traits of a recombinant inbred line was used to identify cold tolerance at booting stage for three consecutive years. The purpose was to locate the stable QTL linked to cold tolerance at booting stage. Combined with meta-analysis model, candidate genes for cold tolerance were mined. The results showed that a total of 17 cold resistant QTLs were detected, of which 5 were pleiotropic interval (CTB2-1, CTB6-2, CTB7-1, CTB7-2 and CTB7-4). However, only three traits obtained the same QTLs in different years, which indicated that cold tolerant QTL at the booting stage was greatly affected by environment. The six selected progenys with cold tolerance alleles can be used in cross combinations. A total of 47 cold tolerance meta-QTLs (MCqtl) were obtained from the meta-analysis, of which 8 reported cold response genes were found in 7 MCqtl regions, and 18 candidate genes conferring cold tolerance were identified, of which 10 candidate genes showed hits to ESTs expressed in the reproductive tissue. These results would lay a foundation for fine mapping of QTLs/genes related to cold tolerance in booting stage and marker-assisted selection for breeding in rice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi F, Onodera H, Toki S, Tanaka H, Komatsu S (2004) OsCDPK13, a calcium-dependent protein kinase gene from rice, is induced by cold and gibberellin in rice leaf sheath. Plant Mol Biol 55(4):541–552
Abe N, Kotaka S, Toriyama K, Kobayashi M (1989) Development of the Rice Norin-PL 8 with high tolerance to cool temperature at the booting stage. Plant Mol Biol 152:9–17
Andaya VC, Mackill DJ (2003) QTLs conferring cold tolerance at the booting stage of rice using recombinant inbred lines from a japonica × indica cross. Theor Appl Genet 106(6):1084–1090
Ballini E, Morel JB, Droc G, Price A, Courtois B, Notteghem JL, Tharreau D (2008) A genome-wide meta-analysis of rice blast resistance genes and quantitative trait loci provides new insights into partial and complete resistance. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21(7):859–868
Courtois B, Ahmadi N, Khowaja F, Price AH, Rami JF, Frouin J, Hamelin C, Ruiz M (2009) Rice root genetic architecture: meta-analysis from a drought QTL database. Rice 2(2–3):115–128
Cui D, Xu CY, Tang CF, Yang CG, Yu TQ, Xin-Xiang A, Cao GL, Xu FR, Zhang JG, Han LZ (2013) Genetic structure and association mapping of cold tolerance in improved japonica rice germplasm at the booting stage. Euphytica 193(3):369–382
Fujino K, Sekiguchi H, Matsuda Y, Sugimoto K, Ono K, Yano M (2008) Molecular identification of a major quantitative trait locus, qLTG3-1, controlling low-temperature germinability in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(34):12623–12628
Glass GV (1976) Primary, secondary, and meta-analysis of research. Educ Res 5(10):3–8
Goffinet B, Gerber S (2000) Quantitative trait loci: a meta-analysis. Genetics 155(1):463–473
Han LZ, Zhang YY, Qiao YL, Cao GL, Zhang SY, Kim JH, Koh HJ (2006) Genetic and QTL analysis for low-temperature vigor of germination in rice. J Genet Genomics 33(11):998–1006
Han L, Qiao Y, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Cao G, Kim J, Lee K, Koh H (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci for cold response of seedling vigor traits in rice. J Genet Genomics 34(3):239–246
Huang J, Yang X, Wang MM, Tang HJ, Ding LY, Shen Y, Zhang HS (2007) A novel rice C2H2-type zinc finger protein lacking DLN-box/EAR-motif plays a role in salt tolerance. BBA-Gene Struct Expr 1769(4):220–227
Huang J, Sun S, Xu D, Lan H, Sun H, Wang Z, Bao Y, Wang J, Tang H, Zhang H (2012) A TFIIIA-type zinc finger protein confers multiple abiotic stress tolerances in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 80(3):337–350
Ito Y, Katsura K, Maruyama K, Taji T, Kobayashi M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Functional analysis of rice DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors involved in cold-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol 47(1):141–153
Kanneganti V, Gupta A (2008) Overexpression of OsiSAP8, a member of stress associated protein (SAP) gene family of rice confers tolerance to salt, drought and cold stress in transgenic tobacco and rice. Plant Mol Biol 66(5):445–462
Khowaja FS, Norton GJ, Courtois B, Price AH (2009) Improved resolution in the position of drought-related QTLs in a single mapping population of rice by meta-analysis. BMC Genom 10(1):276
Kitomi Y, Ogawa A, Kitano H, Inukai Y (2008) CRL4 regulates crown root formation through auxin transport in rice. Plant Root 2(1):19–28
Konishi S, Izawa T, Lin SY, Ebana K, Fukuta Y, Sasaki T, Yano M (2006) An SNP caused loss of seed shattering during rice domestication. Science 312(5778):1392–1396
Kuroki M, Saito K, Matsuba S, Yokogami N, Shimizu H, Ando I, Sato Y (2007) A quantitative trait locus for cold tolerance at the booting stage on rice chromosome 8. Theor Appl Genet 115(5):593–600
Lai Y, Cheng J, He Y, Yang B, Wang Z, Zhang H (2016) Identification of QTLs with additive, epistatic, and QTL × seed maturity interaction effects for seed vigor in rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 239(2):1–12
Larsen RJ, Marx ML (1985) An introduction to probability and its applications, vol 85(2). Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp 2061–2071
Liao Y, Liu S, Jiang Y, Hu C, Zhang X, Cao X, Xu Z, Gao X, Li L, Zhu J (2017) Genome-wide analysis and environmental response profiling of dirigent family genes in rice (Oryza sativa). Genes Genom 39(1):47–62
Liu C, Wu Y, Wang X (2012) bZIP transcription factor OsbZIP52/RISBZ5: a potential negative regulator of cold and drought stress response in rice. Planta 235(6):1157–1169
Liu L, Lai Y, Cheng J, Wang L, Du W, Wang Z, Zhang H (2014) Dynamic quantitative trait locus analysis of seed vigor at three maturity stages in rice. Mol Breed 34(2):501–510
Lu G, Wu FQ, Wu W, Wang HJ, Zheng XM, Zhang Y, Chen X, Zhou K, Jin M, Cheng Z (2014) Rice LTG1 is involved in adaptive growth and fitness under low ambient temperature. Plant J 78(3):468–480
Ma Y, Dai X, Xu Y, Luo W, Zheng X, Zeng D, Pan Y, Lin X, Liu H, Zhang D (2015) COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell 160(6):1209–1221
Paterson AH, Lin Y-R, Li Z, Schertz KF (1995) Convergent domestication of cereal crops by independent mutations at corresponding genetic loci. Science 269(5231):1714–1718
Saito K, Miura K, Nagano K, Hayano-Saito Y, Araki H, Kato A (2001) Identification of two closely linked quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance on chromosome 4 of rice and their association with anther length. Theor Appl Genet 103(7):862–868
Saito K, Hayano-Saito Y, Maruyama-Funatsuki W, Sato Y, Kato A (2004) Physical mapping and putative candidate gene identification of a quantitative trait locus Ctb1 for cold tolerance at the booting stage of rice. Theor Appl Genet 109(3):515–522
Saito K, Hayanosaito Y, Kuroki M, Sato Y (2010) Map-based cloning of the rice cold tolerance gene Ctb1. Plant Sci 179(1):97–102
Shinada H, Iwata N, Sato T, Fujino K (2014) QTL pyramiding for improving of cold tolerance at fertilization stage in rice. Breed Sci 63(5):483–488
Shirasawa S, Endo T, Nakagomi K, Yamaguchi M, Nishio T (2012) Delimitation of a QTL region controlling cold tolerance at booting stage of a cultivar, ‘Lijiangxintuanheigu’, in rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 124(5):937–946
Sosnowski O, Charcosset A, Joets J (2012) BioMercator V3: an upgrade of genetic map compilation and quantitative trait loci meta-analysis algorithms. Bioinformatics 28(15):2082–2083
Su C, Wang Y, Hsieh T, Lu C, Tseng T, Yu S (2010) A novel MYBS3-dependent pathway confers cold tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol 153(1):145–158
Suh JP, Jeung JU, Lee JI, Choi YH, Yea JD, Virk PS, Mackill DJ, Jena KK (2010) Identification and analysis of QTLs controlling cold tolerance at the reproductive stage and validation of effective QTLs in cold-tolerant genotypes of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 120(5):985–995
Veyrieras J-B, Goffinet B, Charcosset A (2007) MetaQTL: a package of new computational methods for the meta-analysis of QTL mapping experiments. BMC Bioinform 8(1):49–64
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93(1):77–78
Wang CA, Ying S, Huang HJ, Li K, Wu P, Shou HX (2009) Involvement of OsSPX1 in phosphate homeostasis in rice. Plant J 57(5):895–904
Wang L, Cheng J, Lai Y, Du W, Huang X, Wang Z, Zhang H (2014) Identification of QTLs with additive, epistatic and QTL × development interaction effects for seed dormancy in rice. Planta 239(2):411–420
Wu Y, Ming H, Tao X, Tao G, Chen Z, Xiao W (2016) Quantitative trait loci identification and meta-analysis for rice panicle-related traits. Mol Genet Genomics 291(5):1927–1940
Xu LM, Lei Z, Zeng YW, Wang FM, Zhang HL, Shen SQ, Li ZC (2008) Identification and mapping of quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance at the booting stage in a japonica rice near-isogenic line. Plant Sci 174(3):340–347
Yamori W, Sakata N, Suzuki Y, Shikanai T, Makino A (2011) Cyclic electron flow around photosystem I via chloroplast NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (NDH) complex performs a significant physiological role during photosynthesis and plant growth at low temperature in rice. Plant J 68(6):966–976
Yang L, Wu K, Gao P, Liu X, Li G, Wu Z (2014) GsLRPK, a novel cold-activated leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase from Glycine soja, is a positive regulator to cold stress tolerance. Plant Sci 215–216(3):19–28
Yang LM, Liu HL, Lei L, Zhao HW, Wang JG, Li N, Sun J, Zheng HL, Zou DT (2018) Identification of QTLs controlling low-temperature germinability and cold tolerance at the seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 214(1):13
Ye C, Fukai S, Godwin I, Reinke R, Snell P, Schiller J, Basnayake J (2009) Cold tolerance in rice varieties at different growth stages. Crop Pasture Sci 60(4):328–338
Zeng Y, Li S, Pu X, Du J, Yang S, Liu K, Gui M, Zhang H (2006) Ecological difference and correlation among cold tolerance traits at the booting stage for core collection of rice landrace in Yunnan, China. Zhongguo Shuidao Kexue 20(3):265–271
Zeng Y, Yang S, Cui H, Yang X, Xu L, Du J, Pu X, Li Z, Cheng Z, Huang X (2009) QTLs of cold tolerance-related traits at the booting stage for NIL-RILs in rice revealed by SSR. Genes Genom 31(2):143–154
Zhang Z, Li J, Pan Y, Li J, Zhou L, Shi H, Zeng Y, Guo H, Yang S, Zheng W (2017) Natural variation in CTB4a enhances rice adaptation to cold habitats. Nat Commun 8:14788
Zhou L, Zeng Y, Zheng W, Tang B, Yang S, Zhang H, Li J, Li Z (2010) Fine mapping a QTL qCTB7 for cold tolerance at the booting stage on rice chromosome 7 using a near-isogenic line. Theor Appl Genet 121(5):895–905
Zhu Y, Chen K, Mi X, Chen T, Ali J, Ye G, Xu J, Li Z (2015) Identification and fine mapping of a stably expressed QTL for cold tolerance at the booting stage using an interconnected breeding population in rice. PLoS ONE 10(12):e0145704
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the national key R & D projects (2017YFD0100503-2, 2017YFD0300500, 2017YFD0300501-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L.M., Liu, H.L., Zhao, H.W. et al. Mapping quantitative trait loci and meta-analysis for cold tolerance in rice at booting stage. Euphytica 215, 89 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2410-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2410-9