Abstract
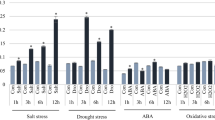
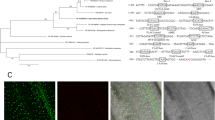
We describe here the isolation and characterization of OsiSAP8, a member of stress Associated protein (SAP) gene family from rice characterized by the presence of A20 and AN1 type Zinc finger domains. OsiSAP8 is a multiple stress inducible gene, induced by various stresses, namely heat, cold, salt, desiccation, submergence, wounding, heavy metals as well as stress hormone Abscisic acid. OsiSAP8 protein fused to GFP was localized towards the periphery of the cells in the epidermal cells of infiltrated Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Yeast two hybrid analysis revealed that A20 and AN1 type zinc-finger domains of OsiSAP8 interact with each other. Overexpression of the gene in both transgenic tobacco and rice conferred tolerance to salt, drought and cold stress at seed germination/seedling stage as reflected by percentage of germination and gain in fresh weight after stress recovery. Transgenic rice plants were tolerant to salt and drought during anthesis stage without any yield penalty as compared to unstressed transgenic plants.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi F, Onodera H, Toki S, Tanaka H, Komatsu S (2004) OsCDPK13, a calcium-dependent protein kinase gene from rice, is induced by cold and gibberellin in rice leaf sheath. Plant Mol Biol 55:541–552
Abe H, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao T, Iwasaki T, Hosokawa D, Shinozaki K (1997) Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought- and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 9:1859–1868
Abe H, Urao T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYCB (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 15:63–78
Altschul SF, Warren G, Webb M, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped blast and Psi-blast: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Anoop N, Gupta AK (2003) Transgenic indica rice cv IR-50 over-expressing Vigna aconitifolia delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylae synthetase cDNA shows tolerance to high salt. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 12:109–116
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1995) Current protocols in molecular biology, vol 1. Wiley, chap. 5
Boyer JS (1982) Plant productivity and environment. Science 218:443–448
Bray EA, Bailey-Serres J, Weretilnyk E (2000) Responses to abiotic stresses. In: Gruissem W, Buchannan B, Jones R (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, pp 1158–1249
Chen H, Nelson RS, Sherwood JL (1994) Enhanced recovery of transformants of Agrobacterium tumifaciens after freeze-thaw transformation and drug selection. Biotechniques 16:664–668
Cooper JT, Stroka DM, Brostjan C, Palmetshofer A, Bach FH, Ferran C (1996) A20 blocks endothelial cell activation through a NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 271:18068–18073
Dixit VM, Green S, Sarma V, Holzman LB, Wolf FW, O’Rourke K, Ward PA, Prochownik EV, Marks RM (1990) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induction of novel gene products in human endothelial cells including a macrophage-specific chemotaxin. J Biol Chem 265:2973–2978
Duan W, Sun B, Li TW, Tan BJ, Lee MK, Teo TS (2000) Cloning and characterization of AWP1, a novel protein that associates with serine/threonine kinase PRK1 in vivo. Gene 256:113–121
Evans PC, Ovaa H, Hamon M, Kilshaw PE, Hamm S, Bauer S, Ploegh HL, Smith TS (2004) Zinc-finger protein A20, a regulator of inflammation and cell survival, has de-ubiquitinating activity. Biochem J 378:727–734
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tagiri A, Tanaka H, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Tanaka Y (2004) Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:146–159
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
Hishiya A, Iemura S, Natsume T, Takayama S, Ikeda K, Watanabe K (2006) A novel ubiquitin-binding protein ZNF216 functioning in muscle atrophy. EMBO J 25:554–564
Hood EE, Gelvin SB, Melchers LS, Hoekema A (1993) New Agrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgenic Res 2:208–218
Hsieh TH, Lee JT, Charng YY, Chan MT (2002) Tomato plants ectopically expressing Arabidopsis CBF1 show enhanced resistance to water deficit stress. Plant Physiol 130:618–626
Huang J, Teng L, Li L, Liu T, Li L, Chen D, Xu LG, Zhai Z, Shu HB (2004) ZNF216 is an A20-like and IkappaB kinase gamma-interacting inhibitor of NFkappaB activation. J Biol Chem 279:16847–16853
Ito Y et al (2006) Functional analysis of rice DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors involved in cold-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol 47:141–153
Kasuga M, Liu Q, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1999) Improving plant drought, salt and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nature Biotechnol 17:287–291
Kathuria H, Giri J, Tyagi H, Tyagi AK (2007) Advances in transgenic Rice Biotechnology. Crit Rev Plant Sci 26:65–103
Kim S, Kang JY, Cho DI, Park JH, Kim SY (2004) ABF2, an ABRE-binding bZIP factor, is an essential component of glucose signaling and its overexpression affects multiple stress tolerance. Plant J 40:75–87
Kiyosue T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1994) Characterization and differential expression of DHN/LEA/RAB-like genes during cold-acclimation and drought stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 35:225–231
Kizis D, Lumbreras V, Pages M (2001) Role of AP2/EREBP transcription factors in gene regulation during abiotic stress. FEBS Lett 498:187–189
Lee S, Tsa YC, Mattera R, Smith WJ, Kostelansky MS, Weissman AM, Bonifacino JS, Hurley JH (2006) Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition and autoubiquitination by Rabex-5. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:264–271
Linnen JM, Bailey CP, Weeks DL (1993) Two related localized mRNAs from Xenopus laevis encode ubiquitin-like fusion proteins. Gene 128:81–188
Llave C, Kaschau KD, Carrington JC (2000) Virus encoded suppressor of post transcriptional gene silencing targets a maintenance step in the silencing pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13401–13406
Moons A, Keyser AD, Van Montagu M (1997) A group 3 LEA cDNA of rice, responsive to abscisic acid, but not to jasmonic acid, shows variety specific differences in salt stress response. Gene 191:197–204
Morita A, Umemura T, Kuroyanagi M, Futsuhara Y, Perata P, Yamaguchi J (1998) Functional dissection of a sugar-repressed alpha-amylase gene (Ramy1A) promoter in rice embryos. FEBS Lett 423:81–85
Mukhopadhyay A, Vij S, Tyagi AK (2004) Overexpression of a zinc-finger protein gene from rice confers tolerance to cold, dehydration, and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6309–6314
Oberschall A, Deak M, Torok K, Sass L, Vass I, Kovacs I, Feher A, Dudits D, Horvath GV (2000) A novel aldose/aldehyde reductase protects transgenic plants against lipid peroxidation under chemical and drought stress. Plant J 24:437–446
Oh SJ et al (2005) Arabidopsis CBF3/DREB1A and ABF3 in transgenic rice increased tolerance to abiotic stress without stunting growth. Plant Physiol 138:341–351
Opipari AW, Boguski MS, Dixit VM (1990) The A20 cDNA induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha encodes a novel type of zinc finger protein. J Biol Chem 265:14705–14708
Örvar BL, Sangwan V, Omann F, Dhindsa RS (2000) Early steps in cold sensing by plant cells: the role of actin cytoskeleton and membrane fluidity. Plant J 23:785–794
Penengo L, Mapelli M, Murachelli AG, Confalonieri S, Magri L, Musacchio A, Di Fiore PP, Polo S, Schneider TR (2006) Crystal structure of the ubiquitin binding domains of Rabex-5 reveals two modes of interactions with ubiquitin. Cell 124:1183–1195
Porra RJ (2002) The chequered history of the development and use of simultaneous equations for the accurate determination of chlorophylls a and b. Photosynth Res 73:149–156
Quevillon E, Silventoinen V, Pillai S, Harte N, Mulder N, Apweiler R, Lopez R (2005) InterProScan: protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res 33:116–120
Saijo Y, Hata S, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K, Izui K (2000) Over-expression of a single Ca2+-dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants. Plant J 23:319–327
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Scott DA, Greinwald JH Jr, Marietta JR, Drury S, Swiderski RE, Vinas A, DeAngelis MM, Carmi R, Ramesh A, Kraft ML, Elbedour K, Skworak AB, Friedman RA, Srikumari Srisailapathy CR, Verhoeven K, Van Camp G, Lovett M, Deininger P, Batzer MA, Morton CC, Keats BJ, Smith RJH, Sheffield VC (1998) Identification and mutation analysis of a cochlear-expressed, zinc finger protein gene at the DFNB7/11 and dn hearing-loss-loci on human chromosome 9q and mouse chromosome 19. Gene 215:461–469
Sharma YK, Hinojos CM, Mehdy MC (1992) cDNA cloning, structure and expression of a novel pathogenesis-related protein in bean. Mol Plant–Microbe Interact 5:89–95
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (1997) Gene expression and signal transduction in water-stress response. Plant Physiol 115:327–334
Shou HX, Bordallo P, Wang K (2004) Expression of the Nicotiana protein kinase (NPK1) enhanced drought tolerance in transgenic maize. J Exp Bot 55:1013–1019
Simpson SD, Nakashima K, Narusaka Y, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Two different novel cis-acting elements of erd1, a clpA homologous Arabidopsis gene function in induction by dehydration stress and dark induced senescence. Plant J 33:257–270
Sreenivasulu N, Sopory SK, Kavi Kishor PB (2007) Deciphering the regulatory mechanisms of abiotic stress tolerance in plants by genomic approaches. Gene 388:1–13
Strausberg RL et al (2002) Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16899–16903
Teige M et al (2004) The MKK2 pathway mediates cold and salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 15:141–152
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) ClustalW: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties, and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Urao T et al (1994) A transmembrane hybrid-type histidine kinase in Arabidopsis functions as an osmosensor. Plant Cell 11:1743–1754
Valliyodan B, Nguyen HT (2006) Understanding regulatory networks and engineering for enhanced drought tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biotech 9:189–195
Vij S, Tyagi AK (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the stress associated protein (SAP) gene family containing A20/AN1 zinger(s) in rice and their phylogenetic relationship with Arabidopsis. Mol Genet Genomics 276:565–575
Vinocur B, Altman A (2005) Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr Opin Biotech 16:123–132
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Welin BV, Olson A, Nylander M, Tapio Palva E (1994) Characterization of two cDNAs (ERD10 and ERD14) corresponding to genes that respond rapidly to dehydration stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 26:131–144
Wertz IE, O’Rourke KM, Zhou H, Eby M, Aravind L, Seshagiri S, Wu P, Wiesmann C, Baker R, Boone DL, Ma A, Koonin EV, Dixit VM (2004) De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-κB signaling. Nature 430:694–699
Xu K, Xu X, Fukao T, Canlas P, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Baile-Serres J, Ronald PC, Mackill DJ (2006) Sub1A is an ethylene-response-factor-like gene that confers submergence tolerance to rice. Nature 422:705–708
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1993) Arabidopsis DNA encoding two desiccation responsive rd29 genes. Plant Physiol 101:1119–1120
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1994) A novel cis acting element in an arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low temperature or high salt stress. Plant Cell 6:251–264
Yamamoto S, Nakano T, Suzuki K, Shinshi H (2004) Elicitor-induced activation of transcription via W-box related cis-acting elements from a basic chitinase gene by WRKY transcription factors in tobacco. Biochim Biophys Acta 1679:279–287
Yamanouchi U, Yano M, Lin H, Ashika M, Yamada K (2002) A rice spotted leaf gene, Spl7, encodes a heat stress transcription factor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7530–7535
Yi K, Wu Z, Zhou J, Du L, Guo L, Wu Y, Wu P (2005) OsPTF1, a novel transcription factor involved in tolerance to phosphate starvation in rice. Plant Physiol 138:2087–2096
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Akhilesh. K. Tyagi, Delhi University South campus, India for providing us the rice root cDNA library, Dr J. J. Finer, Ohio state university, USA for providing pHX4 vector and Dr Yedidya Gafni, Agricultural Research Organization, Israel for helping in sub-cellular localization studies. Special thanks go to Eddy (ARO, Israel) for technical assistance with confocal microscopy. AKG likes to acknowledge the financial support from Department of Biotechnology (DBT)-India, Centre for potential for genomic sciences-University grants commission (CPSGS-UGC) and UGC-SAP programmes. K.V is the recipient of a research fellowship from the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
OsiSAP8 is deposited in the Genbank with the Accession number AY345599.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanneganti, V., Gupta, A.K. Overexpression of OsiSAP8, a member of stress associated protein (SAP) gene family of rice confers tolerance to salt, drought and cold stress in transgenic tobacco and rice. Plant Mol Biol 66, 445–462 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9284-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9284-2