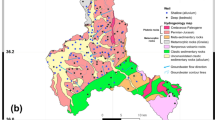
Abstract
Combining the results of base models to create a meta-model is one of the ensemble approaches known as stacking. In this study, stacking of five base learners, including eXtreme gradient boosting, random forest, feed-forward neural networks, generalized linear models with Lasso or Elastic Net regularization, and support vector machines, was used to study the spatial variation of Mn, Cd, Pb, and nitrate in Qom-Kahak Aquifers, Iran. The stacking strategy proved to be an effective substitute predictor for existing machine learning approaches due to its high accuracy and stability when compared to individual learners. Contrarily, there was not any best-performing base model for all of the involved parameters. For instance, in the case of cadmium, random forest produced the best results, with adjusted R2 and RMSE of 0.108 and 0.014, as opposed to 0.337 and 0.013 obtained by the stacking method. The Mn and Cd showed a tight link with phosphate by the redundancy analysis (RDA). This demonstrates the effect of phosphate fertilizers on agricultural operations. In order to analyze the causes of groundwater pollution, spatial methodologies can be used with multivariate analytic techniques, such as RDA, to help uncover hidden sources of contamination that would otherwise go undetected. Lead has a larger health risk than nitrate, according to the probabilistic health risk assessment, which found that 34.4% and 6.3% of the simulated values for children and adults, respectively, were higher than HQ = 1. Furthermore, cadmium exposure risk affected 84% of children and 47% of adults in the research area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaszadeh, M., Mirzaei, R., & Bakhtiari, A. (2020). Risk assessment and spatial modeling of heavy metals contamination in topsoil around Venarj Manganese Mine by artificial neural networks method. Journal of Environmental Health Enginering, 24–44. https://doi.org/10.29252/jehe.0.24
Aheto, J. M. K., Duah, H. O., Agbadi, P., & Nakua, E. K. (2021). A predictive model, and predictors of under-five child malaria prevalence in Ghana: How do LASSO, Ridge and Elastic net regression approaches compare? Preventive Medicine Reports, 23, 101475.
Ali, G., Birkel, C., Tetzlaff, D., Soulsby, C., McDonnell, J. J., & Tarolli, P. (2014). A comparison of wetness indices for the prediction of observed connected saturated areas under contrasting conditions. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 39(3), 399–413.
Almadani, M., & Kheimi, M. (2023). Stacking artificial intelligence models for predicting water quality parameters in rivers. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 24(2), 152–164.
Ayedun, H., Gbadebo, A. M., Idowu, O. A., & Arowolo, T. A. (2015). Toxic elements in groundwater of Lagos and Ogun States, Southwest, Nigeria and their human health risk assessment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 1–17.
Barreras, A., de la Rosa, J. A., Mayorga, R., Cuenca, R., Moreno, C., Godinez, C., et al. (2022). Spatial predictions of tree density and tree height across Mexico´ s forests using ensemble learning and forest inventory data (2009–2014). Authorea Preprints. https://doi.org/10.22541/au.166512787.73882380/v1
Barzegar, R., Asghari Moghaddam, A., Adamowski, J., & Nazemi, A. H. (2019). Assessing the potential origins and human health risks of trace elements in groundwater: A case study in the Khoy plain, Iran. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41, 981–1002.
Belkhiri, L., Mouni, L., Narany, T. S., & Tiri, A. (2017). Evaluation of potential health risk of heavy metals in groundwater using the integration of indicator kriging and multivariate statistical methods. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 4, 12–22.
Beven, K. J., & Kirkby, M. J. (1979). A physically based, variable contributing area model of basin hydrology/Un modèle à base physique de zone d’appel variable de l’hydrologie du bassin versant. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 24(1), 43–69.
Bose, E., Maganti, S., Bowles, K. H., Brueshoff, B. L., & Monsen, K. A. (2019). Machine learning methods for identifying critical data elements in nursing documentation. Nursing Research, 68(1), 65–72.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random Forests. Machine Learning, 45, 5–32.
Bui, X. N., Nguyen, H., Tran, Q. H., Bui, H. B., Nguyen, Q. L., Nguyen, D. A., et al. (2019). A lasso and elastic-net regularized generalized linear model for predicting blast-induced air over-pressure in open-pit mines. Journal of the Polish Mineral Engineering Society. https://doi.org/10.29227/IM-2019-02-52
Chakrabortty, R., Roy, P., Chowdhuri, I., & Pal, S. C. (2021). Groundwater vulnerability assessment using random forest approach in a water‐stressed paddy cultivated region of West Bengal, India. Groundwater Geochemistry: Pollution and Remediation Methods, 392–410. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119709732.ch20
Chen, G., & Balakrishnan, N. (1995). A general purpose approximate goodness-of-fit test. Journal of Quality Technology, 27(2), 154–161.
Chen, W., Li, H., Hou, E., Wang, S., Wang, G., Panahi, M., et al. (2018). GIS-based groundwater potential analysis using novel ensemble weights-of-evidence with logistic regression and functional tree models. Science of the Total Environment, 634, 853–867.
Das, R., & Saha, S. (2022). Spatial mapping of groundwater potentiality applying ensemble of computational intelligence and machine learning approaches. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 18, 100778.
Din, I. U., Muhammad, S., Faisal, S., & Ali, W. (2023). Heavy metal (loid) s contamination and potential risk assessment via groundwater consumption in the district of Hangu. Pakistan. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(12), 33808–33818.
Du, P., Bai, X., Tan, K., Xue, Z., Samat, A., Xia, J., et al. (2020). Advances of four machine learning methods for spatial data handling: A review. Journal of Geovisualization and Spatial Analysis, 4, 1–25.
Duggal, V., Rani, A., Mehra, R., & Balaram, V. (2017). Risk assessment of metals from groundwater in northeast Rajasthan. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 90, 77–84.
Elbeltagi, A., Salam, R., Pal, S. C., Zerouali, B., Shahid, S., Mallick, J., et al. (2022). Groundwater level estimation in northern region of Bangladesh using hybrid locally weighted linear regression and Gaussian process regression modeling. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 149(1–2), 131–151.
Falah, F., & Zeinivand, H. (2019). Gis-based groundwater potential mapping in khorramabad in lorestan, Iran, using frequency ratio (fr) and weights of evidence (woe) models. Water Resources, 46, 679–692.
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2010). Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. Journal of Statistical Software, 33(1), 1–22.
Ganaie, M. A., Hu, M., Malik, A. K., Tanveer, M., & Suganthan, P. N. (2022). Ensemble deep learning: A review. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 115, 105151.
Ghanbari, S. S., & Mahmoudi, A. H. (2022). An improvement in data interpretation to estimate residual stresses and mechanical properties using instrumented indentation: A comparison between machine learning and Kriging model. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 114, 105186.
Giri, S., & Singh, A. K. (2015). Human health risk assessment via drinking water pathway due to metal contamination in the groundwater of Subarnarekha River Basin, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(3), 63.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., Black, W. C., & Anderson, R. E. (2019). Multivariate data analysis (Eighth). Cengage Learning EMEA.
Han, J. H., Zhang, Z. H., & Wang, Z. H. (2022). Responses of acrocarpous moss communities to heavy metal (Fe, Mn, Cd) and sulfur pollution in the Changgou carbonate manganese ore, SW China. Journal of Mountain Science, 19(5), 1292–1306.
Harel, O. (2009). The estimation of R2 and adjusted R2 in incomplete data sets using multiple imputation. Journal of Applied Statistics, 36(10), 1109–1118.
Hateffard, F., Balog, K., Tóth, T., Mészáros, J., Árvai, M., Kovács, Z. A., et al. (2022). High-resolution mapping and assessment of salt-affectedness on arable lands by the combination of ensemble learning and multivariate geostatistics. Agronomy, 12(8), 1858.
Helsel, D. R. (2011). Statistics for censored environmental data using Minitab and R (Vol. 77). Wiley.
Hengl, T., Nussbaum, M., Wright, M. N., Heuvelink, G. B., & Gräler, B. (2018). Random forest as a generic framework for predictive modeling of spatial and spatio-temporal variables. PeerJ, 6, e5518.
Hengl, T., Miller, M. A., Križan, J., Shepherd, K. D., Sila, A., Kilibarda, M., ... & Crouch, J. (2021). African soil properties and nutrients mapped at 30 m spatial resolution using two-scale ensemble machine learning. Scientific reports, 11(1), 6130.
Hengl, T., Parente, L., & Bonannella, C. (2022). Spatial and spatiotemporal interpolation/prediction using ensemble machine learning. https://opengeohub.github.io/spatial-prediction-eml/. Accessed on 1 January 2023
Hoareau, C. E., Hadibarata, T., & Yılmaz, M. (2022). Occurrence of cadmium in groundwater in China: A review. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 15(17), 1455.
Hodson, T. O. (2022). Root-mean-square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): When to use them or not. Geoscientific Model Development, 15(14), 5481–5487.
Hosseini, F. S., Choubin, B., Bagheri-Gavkosh, M., Karimi, O., Taromideh, F., & Mako, C. (2022). susceptibility assessment of groundwater nitrate contamination using an ensemble machine learning approach. Groundwater. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.13258
Hosseini, M., & Kerachian, R. (2023). Optimal redesign of coastal groundwater quality monitoring networks under uncertainty: Application of the theory of belief functions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(21), 59701–59718.
Hu, J., Zhu, C., Long, Y., Yang, Q., Zhou, S., Wu, P., et al. (2021). Interaction analysis of hydrochemical factors and dissolved heavy metals in the karst Caohai Wetland based on PHREEQC, cooccurrence network and redundancy analyses. Science of the Total Environment, 770, 145361.
Ibe, F. C., Opara, A. I., & Ibe, B. O. (2020). Application of pollution risk evaluation models in groundwater systems in the vicinity of automobile scrap markets in Owerri municipal and environs, southeastern Nigeria. Scientific African, 8, e00450.
Jiang, Z., Yang, S., Liu, Z., Xu, Y., Shen, T., Qi, S., et al. (2022). Can ensemble machine learning be used to predict the groundwater level dynamics of farmland under future climate: a 10-year study on Huaibei Plain. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(29), 44653–44667.
Kaur, L., Rishi, M. S., & Siddiqui, A. U. (2020). Deterministic and probabilistic health risk assessment techniques to evaluate non-carcinogenic human health risk (NHHR) due to fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of Panipat, Haryana. India. Environmental Pollution, 259, 113711.
Kavcar, P., Sofuoglu, A., & Sofuoglu, S. C. (2009). A health risk assessment for exposure to trace metals via drinking water ingestion pathway. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 212(2), 216–227.
Kazemi, G. A. (2011). Impacts of urbanization on the groundwater resources in Shahrood, Northeastern Iran: Comparison with other Iranian and Asian cities. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 36(5–6), 150–159.
Knoll, L., Breuer, L., & Bach, M. (2019). Large scale prediction of groundwater nitrate concentrations from spatial data using machine learning. Science of the Total Environment, 668, 1317–1327.
Kumar Mallick, S., Maity, B., Das, P., & Rudra, S. (2023). GIS-based groundwater recharge potentiality analysis using frequency ratio and weights of evidence models. In Case studies in geospatial applications to groundwater resources (pp. 91–108). Elsevier.
Larsen, S. (1967). Soil Phosphorus. Advances in Agronomy, 19, 151–210.
Li, F., Zhang, Y., Fan, Z., & Oh, K. (2015). Accumulation of de-icing salts and its short-term effect on metal mobility in urban roadside soils. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 94, 525–531.
Li, Z., Zhang, C., Liu, H., Zhang, C., Zhao, M., Gong, Q., & Fu, G. (2022). Developing stacking ensemble models for multivariate contamination detection in water distribution systems. Science of the Total Environment, 828, 154284.
Liu, M., & Lu, J. (2014). Support vector machine-an alternative to artificial neuron network for water quality forecasting in an agricultural nonpoint source polluted river? Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 11036–11053.
Liu, R., Liu, F., & Shang, Z. S. (2011). Release characteristics of heavy metals of different manganese slags under the conditions of release and its effect on plant growth of seedlings. Environmental Science Survey, 30(1), 5–9.
Lu, H., & Ma, X. (2020). Hybrid decision tree-based machine learning models for short-term water quality prediction. Chemosphere, 249, 126169.
Madadi, R., Mohamadi, S., Rastegari, M., Karbassi, A., Rakib, M. R. J., Khandaker, M. U., et al. (2022). Health risk assessment and source apportionment of potentially toxic metal (loid) s in windowsill dust of a rapidly growing urban settlement, Iran. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 19736.
Mahajan, M., Gupta, P. K., Singh, A., Vaish, B., Singh, P., Kothari, R., & Singh, R. P. (2022). A comprehensive study on aquatic chemistry, health risk and remediation techniques of cadmium in groundwater. Science of the Total Environment, 818, 151784.
Mallick, J., Talukdar, S., & Ahmed, M. (2022). Combining high resolution input and stacking ensemble machine learning algorithms for developing robust groundwater potentiality models in Bisha watershed. Saudi Arabia. Applied Water Science, 12(4), 77.
McMahon, P. B., Belitz, K., Reddy, J. E., & Johnson, T. D. (2018). Elevated manganese concentrations in United States groundwater, role of land surface–soil–aquifer connections. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(1), 29–38.
Millard, S. P. (2013). EnvStats: An R package for environmental statistics. Springer.
Misi, A., Gumindoga, W., & Hoko, Z. (2018). An assessment of groundwater potential and vulnerability in the Upper Manyame Sub-Catchment of Zimbabwe. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 105, 72–83.
Mitchell, R. J., Babcock, R. S., Gelinas, S., Nanus, L., & Stasney, D. E. (2003). Nitrate distributions and source identification in the Abbotsford-Sumas aquifer, northwestern Washington State. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32(3), 789–800.
Moeini, M., Shojaeizadeh, A., & Geza, M. (2022). Supervised stacking ensemble machine learning approach for enhancing prediction of total suspended solids concentration in Urban watersheds. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 148(6), 04022026.
Mohammadpour, R., Shaharuddin, S., Chang, C. K., Zakaria, N. A., Ghani, A. A., & Chan, N. W. (2015). Prediction of water quality index in constructed wetlands using support vector machine. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 6208–6219.
Moller, A. B., Beucher, A. M., Pouladi, N., & Greve, M. H. (2020). Oblique geographic coordinates as covariates for digital soil mapping. The Soil, 6(2), 269–289.
Morris, B. L., Lawrence, A. R., Chilton, P. J. C., Adams, B., Calow, R. C., & Klinck, B. A. (2003). Groundwater and its susceptibility to degradation: a global assessment of the problem and options for management. United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi, Kenya.
Nasir, Y., & Durlofsky, L. J. (2022). Deep reinforcement learning for optimal well control in subsurface systems with uncertain geology. Journal of Computational Physics. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.13375.
Nguyen, D. H., Le, X. H., Heo, J. Y., & Bae, D. H. (2021). Development of an extreme gradient boosting model integrated with evolutionary algorithms for hourly water level prediction. IEEE Access, 9, 125853–125867.
Nozariamini, S., Ata, S. M., & Amal, B. K. (2020). Assessment the water supply system of Qom City based on the water safety plan. Britain International of Exact Sciences (BIoEx) Journal, 2(3), 690–696.
Olea, R. A. (2018). A practical primer on geostatistics (No. 2009–1103). US Geological Survey.
Parween, S., Siddique, N. A., Diganta, M. T. M., Olbert, A. I., & Uddin, M. G. (2022). Assessment of urban river water quality using modified NSF water quality index model at Siliguri city, West Bengal, India. Environmental and Sustainability Indicators, 16, 100202.
Pereira, G. W., Valente, D. S. M., Queiroz, D. M. D., Coelho, A. L. D. F., Costa, M. M., & Grift, T. (2022). Smart-map: An open-source QGIS plugin for digital mapping using machine learning techniques and ordinary kriging. Agronomy, 12(6), 1350.
Pilehvar, A. A. (2022). Investigating the relationship between informal economy and competitiveness in Iran’s metropolises. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-022-00965-4
Puga, A. P., Melo, L. C. A., de Abreu, C. A., Coscione, A. R., & Paz-Ferreiro, J. (2016). Leaching and fractionation of heavy metals in mining soils amended with biochar. Soil and Tillage Research, 164, 25–33.
Qasemi, M., Shams, M., Sajjadi, S. A., Farhang, M., Erfanpoor, S., Yousefi, M., et al. (2019). Cadmium in groundwater consumed in the rural areas of Gonabad and Bajestan, Iran: occurrence and health risk assessment. Biological Trace Element Research, 192, 106–115.
Rahimi, M. H., Kalantari, N., Sharifdoost, M., & Gashtasebi, A. (2018). Groundwater pollution assessment in urban areas of Qom City. International Journal of Human Capital in Urban Management, 3(2), 97–110.
Rahmati, O., Choubin, B., Fathabadi, A., Coulon, F., Soltani, E., Shahabi, H., et al. (2019). Predicting uncertainty of machine learning models for modelling nitrate pollution of groundwater using quantile regression and UNEEC methods. Science of the Total Environment, 688, 855–866.
Ranjbar, A., & Mahjouri, N. (2018). Development of an efficient surrogate model based on aquifer dimensions to prevent seawater intrusion in anisotropic coastal aquifers, case study: The Qom aquifer in Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77, 1–15.
Ranjbar, A., & Mahjouri, N. (2020). Multi-objective freshwater management in coastal aquifers under uncertainty in hydraulic parameters. Natural Resources Research, 29, 2347–2368.
Ranjbar, A., Mahjouri, N., & Cherubini, C. (2020). Development of an efficient conjunctive meta-model-based decision-making framework for saltwater intrusion management in coastal aquifers. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research, 29, 45–58.
Royston, P. (1993). A toolkit for testing for non-normality in complete and censored samples. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series D (The Statistician), 42(1), 37–43.
Ruidas, D., Pal, S. C., Towfiqul Islam, A. R. M., & Saha, A. (2023). Hydrogeochemical evaluation of groundwater aquifers and associated health hazard risk mapping using ensemble data driven model in a water scares plateau region of eastern India. Exposure and Health, 15(1), 113–131.
Sadeghi, A. R., & Hosseini, S. M. (2023). Assessment and delineation of potential groundwater recharge zones in areas prone to saltwater intrusion hazard: A case from Central Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1), 203.
Sadri Moghaddam, S., & Mesghali, H. (2023). A new hybrid ensemble approach for the prediction of effluent total nitrogen from a full-scale wastewater treatment plant using a combined trickling filter-activated sludge system. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(1), 1622–1639.
Sakizadeh, M., & Milewski, A. (2023). Quantifying LULC changes in Urmia Lake Basin using machine learning techniques, intensity analysis and a combined method of cellular automata (CA) and artificial neural networks (ANN)(CA-ANN). Modeling Earth Systems and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-023-01895-z
Sarkar, S., Mukherjee, A., Gupta, S. D., Bhanja, S. N., & Bhattacharya, A. (2022). Predicting regional-scale elevated groundwater nitrate contamination risk using machine learning on natural and human-induced factors. ACS ES&T Engineering, 2(4), 689–702.
Shen, Z., Hou, X., Li, W., Aini, G., Chen, L., & Gong, Y. (2015). Impact of landscape pattern at multiple spatial scales on water quality: A case study in a typical urbanised watershed in China. Ecological Indicators, 48, 417–427.
Shrestha, N. (2020). Detecting multicollinearity in regression analysis. American Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 8(2), 39–42.
Singh, K. P., Basant, N., & Gupta, S. (2011). Support vector machines in water quality management. Analytica Chimica Acta, 703(2), 152–162.
Singha, S., Pasupuleti, S., Singha, S. S., Singh, R., & Kumar, S. (2021). Prediction of groundwater quality using efficient machine learning technique. Chemosphere, 276, 130265.
Strahler, A. N. (1964). Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basin and channel networks. Handbook of applied hydrology (pp. 439–476). McGraw-Hill.
Sylvain, J. D., Anctil, F., & Thiffault, É. (2021). Using bias correction and ensemble modelling for predictive mapping and related uncertainty: A case study in digital soil mapping. Geoderma, 403, 115153.
Su, Y. S., Ni, C. F., Li, W. C., Lee, I. H., & Lin, C. P. (2020). Applying deep learning algorithms to enhance simulations of large-scale groundwater flow in IoTs. Applied Soft Computing, 92, 106298.
Talukdar, S., Ahmed, S., Naikoo, M. W., Rahman, A., Mallik, S., Ningthoujam, S., et al. (2023). Predicting lake water quality index with sensitivity-uncertainty analysis using deep learning algorithms. Journal of Cleaner Production, 406, 136885.
Tanwer, N., Deswal, M., Khyalia, P., Laura, J. S., & Khosla, B. (2023). Assessment of groundwater potability and health risk due to fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of Churu District of Rajasthan, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45, 1–23.
USEPA (1991). Risk assessment guidance for superfund: volume I: Human health evaluation manual (Part B, development of risk-based preliminary remediation goals). Interim Final.
USEPA (2012). Integrated risk information system. United States Environmental Protection Agency. https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/search/index.cfm
Wang, G., & Zhou, L. (2017). Application of green manure and pig manure to Cd-contaminated paddy soil increases the risk of Cd uptake by rice and Cd downward migration into groundwater: Field micro-plot trials. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228, 1–15.
Wang, L., Zhu, Z., Sassoubre, L., Yu, G., Liao, C., Hu, Q., & Wang, Y. (2021). Improving the robustness of beach water quality modeling using an ensemble machine learning approach. Science of the Total Environment, 765, 142760.
Wang, S., Peng, H., & Liang, S. (2022). Prediction of estuarine water quality using interpretable machine learning approach. Journal of Hydrology, 605, 127320.
Yun, S. W., Kang, D. H., Ji, W. H., Jung, M. H., & Yu, C. (2020). distinct dispersion of as, cd, Pb, and Zn in farmland soils near abandoned mine tailings: Field observation results in South Korea. Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 1–13.
Zhang, D., Wang, P., Cui, R., Yang, H., Li, G., Chen, A., & Wang, H. (2022). Electrical conductivity and dissolved oxygen as predictors of nitrate concentrations in shallow groundwater in Erhai Lake region. Science of the Total Environment, 802, 149879.
Zhang, Y., Xu, B., Guo, Z., Han, J., Li, H., Jin, L., et al. (2019). Human health risk assessment of groundwater arsenic contamination in Jinghui irrigation district, China. Journal of Environmental Management, 237, 163–169.
Zhao, C., Zhang, X., Fang, X., Zhang, N., Xu, X., Li, L., et al. (2022). Characterization of drinking groundwater quality in rural areas of Inner Mongolia and assessment of human health risks. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 234, 113360.
Zhao, X., Dong, D., Hua, X., & Dong, S. (2009). Investigation of the transport and fate of Pb, Cd, Cr (VI) and As (V) in soil zones derived from moderately contaminated farmland in Northeast. China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(2–3), 570–577.
Zounemat-Kermani, M., Batelaan, O., Fadaee, M., & Hinkelmann, R. (2021). Ensemble machine learning paradigms in hydrology: A review. Journal of Hydrology, 598, 126266.
Acknowledgements
The authors of this paper would like to express their gratitude to Iranian Department of Environment and the Qom Province Water Authority for providing the data applied in the current research. Additionally, we would like to thank the USGS for providing the freely available products employed for LULC classification.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Mohamad Sakizadeh makes the main contribution in writing this paper. Prof.Chaosheng Zhang provides research ideas for revision of the initial version of the paper and Prof. Adam Milewski read and revised the paper to improve its quality before final submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors wish to declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Data availability
Data are available on request from the authors.
Consent to participate
All co-authors have agreed.
Consent for publication
All co-authors have agreed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sakizadeh, M., Zhang, C. & Milewski, A. Spatial distribution pattern and health risk of groundwater contamination by cadmium, manganese, lead and nitrate in groundwater of an arid area. Environ Geochem Health 46, 80 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01845-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01845-9