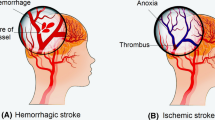
Abstract
Ischemic damage to the central nervous system (CNS) is a catastrophic postoperative complication of aortic occlusion subsequent to cardiovascular surgery that can cause brain impairment and sometimes even paraplegia. Over recent years, numerous studies have investigated techniques for protecting and revascularizing the nervous system during intraoperative ischemia; however, owing to a lack of knowledge of the physiological distinctions between the brain and spinal cord, as well as the limited availability of testing techniques and treatments for ischemia–reperfusion injury, the cause of brain and spinal cord ischemia–reperfusion injury remains poorly understood, and no adequate response steps are currently available in the clinic. Given the limited ability of the CNS to repair itself, it is of great clinical value to make full use of the proliferative and differentiation potential of stem cells to repair nerves in degenerated and necrotic regions by stem cell transplantation or mobilization, thereby introducing a novel concept for the treatment of severe CNS ischemia–reperfusion injury. This review summarizes the most recent advances in stem cell therapy for ischemia–reperfusion injury in the brain and spinal cord, aiming to advance basic research and the clinical use of stem cell therapy as a promising treatment for this condition.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abe K (2000) Therapeutic potential of neurotrophic factors and neural stem cells against ischemic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:1393–1408. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004647-200010000-00001
Alessandrini M, Preynat-Seauve O, De Bruin K, Pepper MS (2019) Stem cell therapy for neurological disorders. S Afr Med J 109:70–77. https://doi.org/10.7196/SAMJ.2019.v109i8b.14009
Alim I, Caulfield JT, Chen Y, Swarup V, Geschwind DH, Ivanova E et al (2019) Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell 177:1262-1279.e25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.032
Altenhöfer S, Kleikers PW, Radermacher KA, Scheurer P, Rob Hermans JJ, Schiffers P et al (2012) The NOX toolbox: validating the role of NADPH oxidases in physiology and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:2327–2343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1010-9
Andres RH, Horie N, Slikker W, Keren-Gill H, Zhan K, Sun G et al (2011) Human neural stem cells enhance structural plasticity and axonal transport in the ischaemic brain. Brain 134:1777–1789. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr094
Bacigaluppi M, Russo GL, Peruzzotti-Jametti L, Rossi S, Sandrone S, Butti E et al (2016) Neural stem cell transplantation induces stroke recovery by upregulating glutamate transporter GLT-1 in astrocytes. J Neurosci 36:10529–10544. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1643-16.2016
Barnabé-Heider F, Göritz C, Sabelström H, Takebayashi H, Pfrieger FW, Meletis K et al (2010) Origin of new glial cells in intact and injured adult spinal cord. Cell Stem Cell 7:470–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2010.07.014
Beers DR, Henkel JS, Zhao W, Wang J, Appel SH (2008) CD4+ T cells support glial neuroprotection, slow disease progression, and modify glial morphology in an animal model of inherited ALS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:15558–63. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0807419105
Bell MT, Puskas F, Agoston VA, Cleveland JC Jr, Freeman KA, Gamboni F et al (2013) Toll-like receptor 4-dependent microglial activation mediates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. Circulation 128:S152–S156. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.112.000024
Ben-Hur T, Ben-Menachem O, Furer V, Einstein O, Mizrachi-Kol R, Grigoriadis N (2003) Effects of proinflammatory cytokines on the growth, fate, and motility of multipotential neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:623–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1044-7431(03)00218-5
Ben-Mordechai T, Holbova R, Landa-Rouben N, Harel-Adar T, Feinberg MS, Abd EI et al (2013) Macrophage subpopulations are essential for infarct repair with and without stem cell therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 62:1890–1901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.057
Berendes JN, Bredée JJ, Schipperheyn JJ, Mashhour YA (1982) Mechanisms of spinal cord injury after cross-clamping of the descending thoracic aorta. Circulation 66:I112-6
Bergeron EJ, Mosca MS, Aftab M, Justison G, Reece TB (2017) Neuroprotection strategies in aortic surgery. Cardiol Clin 35:453–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccl.2017.03.011
Boldrini M, Fulmore CA, Tartt AN, Simeon LR, Pavlova I, Poposka V et al (2018) Human hippocampal neurogenesis persists throughout aging. Cell Stem Cell 22:589-599.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2018.03.015
Brown C, McKee C, Bakshi S, Walker K, Hakman E, Halassy S et al (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells: cell therapy and regeneration potential. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 13:1738–1755. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2914
Calió ML, Marinho DS, Ko GM, Ribeiro RR, Carbonel AF, Oyama LM et al (2014) Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells decreases oxidative stress, apoptosis, and hippocampal damage in brain of a spontaneous stroke model. Free Radic Biol Med 70:141–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.01.024
Chen J, Yang Y, Shen L, Ding W, Chen X, Wu E et al (2017) Hypoxic preconditioning augments the therapeutic efficacy of bone marrow stromal cells in a rat ischemic stroke model. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:1115–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0445-1
Chen S, Yi M, Zhou G, Pu Y, Hu Y, Han M et al (2019) Abdominal aortic transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulates the expression of ciliary neurotrophic factor and inflammatory cytokines in a rat model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. Med Sci Monit 25:1960–1969. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.912697
Chiu IM, Chen A, Zheng Y, Kosaras B, Tsiftsoglou SA, Vartanian TK et al (2008) T lymphocytes potentiate endogenous neuroprotective inflammation in a mouse model of ALS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:17913–17918. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804610105
Cho DI, Kim MR, Jeong HY, Jeong HC, Jeong MH, Yoon SH et al (2014) Mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate the M1/M2 balance in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. Exp Mol Med 46:e70. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2013.135
Da Silva JS, Hare JM (2013) Cell-based therapies for myocardial repair: emerging role for bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the treatment of the chronically injured heart. Methods Mol Biol 1037:145–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-505-7_8
Davis S, Yancopoulos GD (1993) The molecular biology of the CNTF receptor. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 3:20–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-4388(93)90030-3
Davis S, Aldrich TH, Stahl N, Pan L, Taga T, Kishimoto T et al (1993) LIFR beta and gp130 as heterodimerizing signal transducers of the tripartite CNTF receptor. Science 260:1805–1808. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8390097
De Becker A, Riet IV (2016) Homing and migration of mesenchymal stromal cells: how to improve the efficacy of cell therapy? World J Stem Cells 8:73–87. https://doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v8.i3.73
Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, Milanesi M, Longoni PD, Matteucci P et al (2002) Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood 99:3838–3843. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v99.10.3838
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22:391–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01401-0
Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2004) The immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting. Immunity 21:137–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2004.07.017
El-Sherbiny IM, Yacoub MH (2013) Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: progress and challenges. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract 2013:316–42. https://doi.org/10.5339/gcsp.2013.38
Emanueli C, Schratzberger P, Kirchmair R, Madeddu P (2003) Paracrine control of vascularization and neurogenesis by neurotrophins. Br J Pharmacol 140:614–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0705458
Ernst A, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Perl S, Tisdale J et al (2014) Neurogenesis in the striatum of the adult human brain. Cell 156:1072–1083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.044
Fu Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Wang L, Wei X, Zhang B et al (2010) Regulation of NADPH oxidase activity is associated with miRNA-25-mediated NOX4 expression in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol 32:581–589. https://doi.org/10.1159/000322105
Gao X, Song L, Shen K, Wang H, Qian M, Niu W et al (2014) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote the repair of islets from diabetic mice through paracrine actions. Mol Cell Endocrinol 388:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2014.03.004
Garcia-Ovejero D, Arevalo-Martin A, Paniagua-Torija B, Florensa-Vila J, Ferrer I, Grassner L et al (2015) The ependymal region of the adult human spinal cord differs from other species and shows ependymoma-like features. Brain 138:1583–1597. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv089
Ghanem A, Müller A, Nähle CP, Kocurek J, Werner N, Hammerstingl C et al (2010) Risk and fate of cerebral embolism after transfemoral aortic valve implantation: a prospective pilot study with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:1427–1432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.12.026
Gopalakrishnan A, Shankarappa SA, Rajanikant GK (2019) Hydrogel Scaffolds: towards restitution of ischemic stroke-injured brain. Transl Stroke Res 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-018-0655-6
Granger DN, Kvietys PR (2015) Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: the evolution of a concept. Redox Biol 6:524–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.020
Grégoire CA, Goldenstein BL, Floriddia EM, Barnabé-Heider F, Fernandes KJ (2015) Endogenous neural stem cell responses to stroke and spinal cord injury. Glia 63:1469–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22851
Gu Z, Akiyama K, Ma X, Zhang H, Feng X, Yao G et al (2010) Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviates lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice. Lupus 19:1502–1514. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203310373782
Guo J, Yang J, Cao G, Fan H, Guo C, Ma YE et al (2011) Xenogeneic immunosuppression of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in a major histocompatibility complex-mismatched allogeneic acute graft-versus-host disease murine model. Eur J Haematol 87:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2011.01635.x
Hacke K, Falahati R, Flebbe-Rehwaldt L, Kasahara N, Gaensler KM (2009) Suppression of HLA expression by lentivirus-mediated gene transfer of siRNA cassettes and in vivo chemoselection to enhance hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Immunol Res 44:112–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-008-8088-z
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF (2001) Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:677–736. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.677
Hudetz JA, Iqbal Z, Gandhi SD, Patterson KM, Byrne AJ, Pagel PS (2011) Postoperative delirium and short-term cognitive dysfunction occur more frequently in patients undergoing valve surgery with or without coronary artery bypass graft surgery compared with coronary artery bypass graft surgery alone: results of a pilot study. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 25:811–816. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2010.05.003
Huynh TT, Miller CC 3rd, Estrera AL, Porat EE, Safi HJ (2002) Thoracoabdominal and descending thoracic aortic aneurysm surgery in patients aged 79 years or older. J Vasc Surg 36:469–75. https://doi.org/10.1067/mva.2002.127348
Hwang JY, Min SW, Jeon YT, Hwang JW, Park SH, Kim JH et al (2015) Effect of coenzyme Q10 on spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Neurosurg Spine 22:432–438. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.Spine14487
Ishibashi S, Sakaguchi M, Kuroiwa T, Yamasaki M, Kanemura Y, Shizuko I et al (2004) Human neural stem/progenitor cells, expanded in long-term neurosphere culture, promote functional recovery after focal ischemia in Mongolian gerbils. J Neurosci Res 78:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.20246
Jia Z, Jiao C, Zhao S, Li X, Ren X, Zhang L et al (2012) Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells in a rat corneal allograft rejection model. Exp Eye Res 102:44–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2012.06.008
Kahlert P, Knipp SC, Schlamann M, Thielmann M, Al-Rashid F, Weber M et al (2010) Silent and apparent cerebral ischemia after percutaneous transfemoral aortic valve implantation: a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. Circulation 121:870–878. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.109.855866
Kaji K, Norrby K, Paca A, Mileikovsky M, Mohseni P, Woltjen K (2009) Virus-free induction of pluripotency and subsequent excision of reprogramming factors. Nature 458:771–775. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07864
Kawai H, Yamashita T, Ohta Y, Deguchi K, Nagotani S, Zhang X et al (2010a) Tridermal tumorigenesis of induced pluripotent stem cells transplanted in ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1487–1493. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2010.32
Kernie SG, Parent JM (2010) Forebrain neurogenesis after focal Ischemic and traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis 37:267–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.11.002
Kim J, Hematti P (2009) Mesenchymal stem cell-educated macrophages: a novel type of alternatively activated macrophages. Exp Hematol 37:1445–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2009.09.004
Kim D, Kim CH, Moon JI, Chung YG, Chang MY, Han BS et al (2009) Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells by direct delivery of reprogramming proteins. Cell Stem Cell 4:472–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2009.05.005
Krampera M, Cosmi L, Angeli R, Pasini A, Liotta F, Andreini A et al (2006) Role for interferon-gamma in the immunomodulatory activity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 24:386–398. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2005-0008
Kurose T, Takahashi S, Otsuka T, Nakagawa K, Imura T, Sueda T et al (2019) Simulated microgravity-cultured mesenchymal stem cells improve recovery following spinal cord ischemia in rats. Stem Cell Res 41:101601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2019.101601
Law S, Chaudhuri S (2013) Mesenchymal stem cell and regenerative medicine: regeneration versus immunomodulatory challenges. Am J Stem Cells 2:22–38
Lee HJ, Lim IJ, Lee MC, Kim SU (2010) Human neural stem cells genetically modified to overexpress brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote functional recovery and neuroprotection in a mouse stroke model. J Neurosci Res 88:3282–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22474
Lee S, Yun S, Park KI, Jang JH (2016) Sliding fibers: slidable, injectable, and gel-like electrospun nanofibers as versatile cell carriers. ACS Nano 10:3282–94. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b06605
Lehnardt S, Schott E, Trimbuch T, Laubisch D, Krueger C, Wulczyn G et al (2008) A vicious cycle involving release of heat shock protein 60 from injured cells and activation of toll-like receptor 4 mediates neurodegeneration in the CNS. J Neurosci 28:2320–2331. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4760-07.2008
Leu S, Lin YC, Yuen CM, Yen CH, Kao YH, Sun CK et al (2010) Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells markedly attenuate brain infarct size and improve neurological function in rats. J Transl Med 8:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-8-63
Li J, Zhu H, Liu Y, Li Q, Lu S, Feng M et al (2010) Human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation protects against cerebral ischemic injury and upregulates interleukin-10 expression in Macacafascicularis. Brain Res 1334:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.080
Li G, Che MT, Zhang K, Qin LN, Zhang YT, Chen RQ et al (2016) Graft of the NT-3 persistent delivery gelatin sponge scaffold promotes axon regeneration, attenuates inflammation, and induces cell migration in rat and canine with spinal cord injury. Biomaterials 83:233–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.11.059
Li R, Zhao K, Ruan Q, Meng C, Yin F (2020) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-124-3p attenuates neurological damage in spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by downregulating Ern1 and promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Arthritis Res Ther 22:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-020-2146-x
Litchfield TM, Whiteley SJ, Yee KT, Tyers P, Usherwood EJ, Nash AA et al (1997) Characterisation of the immune response in a neural xenograft rejection paradigm. J Neuroimmunol 73:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5728(96)00192-0
Liu S, Chen Z (2019) Employing endogenous NSCs to promote recovery of spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Int 2019:1958631. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1958631
Liu N, Chen R, Du H, Wang J, Zhang Y, Wen J (2009a) Expression of IL-10 and TNF-alpha in rats with cerebral infarction after transplantation with mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Mol Immunol 6:207–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2009.28
Liu YP, Lang BT, Baskaya MK, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R (2009b) The potential of neural stem cells to repair stroke-induced brain damage. Acta Neuropathol 117:469–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0516-1
Liu Y, Mu R, Wang S, Long L, Liu X, Li R et al (2010) Therapeutic potential of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R210. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3187
Liu W, Xu B, Xue W, Yang B, Fan Y, Chen B et al (2020) A functional scaffold to promote the migration and neuronal differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells for spinal cord injury repair. Biomaterials 243:119941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119941
Lopez-Neblina F, Toledo AH, Toledo-Pereyra LH (2005) Molecular biology of apoptosis in ischemia and reperfusion. J Invest Surg 18:335–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941930500328862
Lü C, Liu Q, Zeng X (2017) Effects of interleukin 10 gene modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on expression of inflammatory cytokines and neuronal apoptosis in rats after cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 31:240–245. https://doi.org/10.7507/1002-1892.201605095
Maggini J, Mirkin G, Bognanni I, Holmberg J, Piazzón IM, Nepomnaschy I et al (2010) Mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells turn activated macrophages into a regulatory-like profile. PLoS ONE 5:e9252. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009252
Maron DJ, Hochman JS, Reynolds HR, Bangalore S, O’Brien SM, Boden WE et al (2020) Initial invasive or conservative strategy for stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med 382:1395–1407. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1915922
Martí-Fàbregas J, Romaguera-Ros M, Gómez-Pinedo U, Martínez-Ramírez S, Jiménez-Xarrié E, Marín R et al (2010) Proliferation in the human ipsilateral subventricular zone after ischemic stroke. Neurology 74:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181cbccec
Mohamad O, Drury-Stewart D, Song M, Faulkner B, Chen D, Yu SP et al (2013) Vector-free and transgene-free human iPS cells differentiate into functional neurons and enhance functional recovery after ischemic stroke in mice. PLoS ONE 8:e64160. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064160
Moon SM, Kim W, Chung JY, Im W, Yoo DY, Jung HY et al (2014) Neuroprotective effects of adipose-derived stem cells are maintained for 3 weeks against ischemic damage in the rabbit spinal cord. Biomed Res Int 2014:539051. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/539051
Nakajima H, Uchida K, Guerrero AR, Watanabe S, Sugita D, Takeura N et al (2012) Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells promotes an alternative pathway of macrophage activation and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 29:1614–1625. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2011.2109
Nakamura M, Okano H (2013) Cell transplantation therapies for spinal cord injury focusing on induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res 23:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.171
Nakata T, Kawachi K, Nagashima M, Yasugi T, Izutani H, Ryugo M et al (2011) Transient ischemia-induced paresis and complete paraplegia displayed distinct reactions of microglia and macrophages. Brain Res 1420:114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.08.074
Newman MF, Kirchner JL, Phillips-Bute B, Gaver V, Grocott H, Jones RH et al (2001) Longitudinal assessment of neurocognitive function after coronary-artery bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 344:395–402. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200102083440601
Nguyen H, Zarriello S, Coats A, Nelson C, Kingsbury C, Gorsky A et al (2019) Stem cell therapy for neurological disorders: a focus on aging. Neurobiol Dis 126:85–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.09.011
Okano H, Nakamura M, Yoshida K, Okada Y, Tsuji O, Nori S et al (2013) Steps toward safe cell therapy using induced pluripotent stem cells. Circ Res 112:523–533. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.111.256149
Oki K, Tatarishvili J, Wood J, Koch P, Wattananit S, Mine Y et al (2012) Human-induced pluripotent stem cells form functional neurons and improve recovery after grafting in stroke-damaged brain. Stem Cells 30:1120–1133. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1104
Okubo T, Iwanami A, Kohyama J, Itakura G, Kawabata S, Nishiyama Y et al (2016) Pretreatment with a γ-secretase inhibitor prevents tumor-like overgrowth in human iPSC-derived transplants for spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Rep 7:649–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.08.015
Okubo T, Nagoshi N, Kohyama J, Tsuji O, Shinozaki M, Shibata S et al (2018) Treatment with a gamma-secretase inhibitor promotes functional recovery in human iPSC-derived transplants for chronic spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Rep 11:1416–1432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.10.022
Otero L, Zurita M, Bonilla C, Aguayo C, Rico MA, Rodríguez A et al (2012) Allogeneic bone marrow stromal cell transplantation after cerebral hemorrhage achieves cell transdifferentiation and modulates endogenous neurogenesis. Cytotherapy 14:34–44. https://doi.org/10.3109/14653249.2011.608349
Palencia G, Medrano JÁN, Ortiz-Plata A, Farfán DJ, Sotelo J, Sánchez A et al (2015) Anti-apoptotic, anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects of thalidomide on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Neurol Sci 351:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2015.02.043
Palma-Tortosa S, Tornero D, Grønning HM, Monni E, Hajy M, Kartsivadze S et al (2020) Activity in grafted human iPS cell-derived cortical neurons integrated in stroke-injured rat brain regulates motor behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:9094–9100. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2000690117
Palma-Tortosa S, Coll-San Martin B, Kokaia Z, Tornero D (2021) Neuronal replacement in stem cell therapy for stroke: filling the gap. Front Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.662636
Paniagua-Torija B, Norenberg M, Arevalo-Martin A, Carballosa-Gautam MM, Campos-Martin Y, Molina-Holgado E et al (2018) Cells in the adult human spinal cord ependymal region do not proliferate after injury. J Pathol 246:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5151
Redondo-Castro E, Cunningham CJ, Miller J, Brown H, Allan SM, Pinteaux E (2018) Changes in the secretome of tri-dimensional spheroid-cultured human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro by interleukin-1 priming. Stem Cell Res Ther 9:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-017-0753-5
Rhee YH, Ko JY, Chang MY, Yi SH, Kim D, Kim CH et al (2011) Protein-based human iPS cells efficiently generate functional dopamine neurons and can treat a rat model of Parkinson disease. J Clin Invest 121:2326–2335. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci45794
Rodríguez-Jimnez FJ, Alastrue-Agudo A, Erceg S, Stojkovic M, Moreno-Manzano V (2012) FM19G11 favors spinal cord injury regeneration and stem cell self-renewal by mitochondrial uncoupling and glucose metabolism induction. Stem Cells 30:2221–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1189
Ruzicka J, Romanyuk N, Jirakova K, Hejcl A, Janouskova O, Machova LU et al (2019) The effect of iPS-derived neural progenitors seeded on laminin-coated pHEMA-MOETACl hydrogel with dual porosity in a rat model of chronic spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant 28:400–412. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689718823705
Sabelström H, Stenudd M, Réu P, Dias DO, Elfineh M, Zdunek S et al (2013) Resident neural stem cells restrict tissue damage and neuronal loss after spinal cord injury in mice. Science 342:637–640. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1242576
Sakai D, Mochida J, Iwashina T, Watanabe T, Nakai T, Ando K et al (2005) Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells transplanted to a rabbit degenerative disc model: potential and limitations for stem cell therapy in disc regeneration. Spine 30:2379–87. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000184365.28481.e3
Salameh A, Dhein S, Dähnert I, Klein N (2016) Neuroprotective strategies during cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111945
Salewski RP, Buttigieg J, Mitchell RA, van der Kooy D, Nagy A, Fehlings MG (2013) The generation of definitive neural stem cells from PiggyBac transposon-induced pluripotent stem cells can be enhanced by induction of the NOTCH signaling pathway. Stem Cells Dev 22:383–96. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2012.0218
Salewski RP, Mitchell RA, Li L, Shen C, Milekovskaia M, Nagy A et al (2015) Transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem cells mediate functional recovery following thoracic spinal cord injury through remyelination of axons. Stem Cells Transl Med 4:743–754. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2014-0236
Seki T, Yuasa S, Oda M, Egashira T, Yae K, Kusumoto D et al (2010) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human terminally differentiated circulating T cells. Cell Stem Cell 7:11–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2010.06.003
Shalaby SM, Sabbah NA, Saber T, Abdel Hamid RA (2016) Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate the immune response in chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model. IUBMB Life 68:106–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1469
Shi E, Kazui T, Jiang X, Washiyama N, Yamashita K, Terada H et al (2007) Therapeutic benefit of intrathecal injection of marrow stromal cells on ischemia-injured spinal cord. Ann Thorac Surg 83:1484–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2006.11.048
Smith PD, Puskas F, Meng X, Lee JH, Cleveland JC Jr, Weyant MJ et al (2012) The evolution of chemokine release supports a bimodal mechanism of spinal cord ischemia and reperfusion injury. Circulation 126:S110–S117. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.111.080275
Sondell M, Sundler F, Kanje M (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a neurotrophic factor which stimulates axonal outgrowth through the flk-1 receptor. Eur J Neurosci 12:4243–54. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0953-816x.2000.01326.x
Spalding KL, Bergmann O, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Huttner HB et al (2013) Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell 153:1219–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.002
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126:663–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K et al (2007) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131:861–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019
Takahashi S, Nakagawa K, Tomiyasu M, Nakashima A, Katayama K, Imura T et al (2018) Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy improves lower limb movement after spinal cord ischemia in rats. Ann Thorac Surg 105:1523–1530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2017.12.014
Tang JD, Lampe KJ (2018) From de novo peptides to native proteins: advancements in biomaterial scaffolds for acute ischemic stroke repair. Biomed Mater 13:034103. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-605X/aaa4c3
Tang Y, Wang J, Lin X, Wang L, Shao B, Jin K et al (2014) Neural stem cell protects aged rat brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury through neurogenesis and angiogenesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:1138–1147. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2014.61
Tang YH, Ma YY, Zhang ZJ, Wang YT, Yang GY (2015) Opportunities and challenges: stem cell-based therapy for the treatment of ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther 21:337–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12386
Tashiro S, Nishimura S, Iwai H, Sugai K, Zhang L, Shinozaki M et al (2016) Functional recovery from neural stem/progenitor cell transplantation combined with treadmill training in mice with chronic spinal cord injury. Sci Rep 6:30898. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30898
Theus MH, Wei L, Cui L, Francis K, Hu X, Keogh C et al (2008) In vitro hypoxic preconditioning of embryonic stem cells as a strategy of promoting cell survival and functional benefits after transplantation into the ischemic rat brain. Exp Neurol 210:656–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.12.020
Trakhtenberg EF, Goldberg JL (2011) Immunology. Neuroimmune Commun Sci 334:47–48. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1213099
Tronci G, Ajiro H, Russell SJ, Wood DJ, Akashi M (2014) Tunable drug-loading capability of chitosan hydrogels with varied network architectures. Acta Biomater 10:821–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2013.10.014
Tsai HL, Chiu WT, Fang CL, Hwang SM, Renshaw PF, Lai WF (2014) Different forms of tenascin-C with tenascin-R regulate neural differentiation in bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A 20:1908–21. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEA.2013.0188
Varga ZV, Kupai K, Szűcs G, Gáspár R, Pálóczi J, Faragó N et al (2013) MicroRNA-25-dependent up-regulation of NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) mediates hypercholesterolemia-induced oxidative/nitrative stress and subsequent dysfunction in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 62:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.05.009
Vrselja Z, Daniele SG, Silbereis J, Talpo F, Morozov YM, Sousa AMM et al (2019) Restoration of brain circulation and cellular functions hours post-mortem. Nature 568:336–343. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1099-1
Wang J, Yang W, Xie H, Song Y, Li Y, Wang L (2014) Ischemic stroke and repair: current trends in research and tissue engineering treatments. Regen Med Res 2:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/2050-490x-2-3
Wang Y, Zhao Z, Rege SV, Wang M, Si G, Zhou Y et al (2016a) 3K3A-activated protein C stimulates postischemic neuronal repair by human neural stem cells in mice. Nat Med 22:1050–1055. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4154
Wang Z, Fang B, Tan Z, Zhang D, Ma H (2016b) Hypoxic preconditioning increases the protective effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep 13:1953–60. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.4753
Wang J, Sun R, Li Z, Pan Y (2019a) Combined bone marrow stromal cells and oxiracetam treatments ameliorates acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through TRPC6. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 51:767–777. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmz059
Wang Y, Smith W, Hao D, He B, Kong L (2019b) M1 and M2 macrophage polarization and potentially therapeutic naturally occurring compounds. Int Immunopharmacol 70:459–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.02.050
Wei L, Wei ZZ, Jiang MQ, Mohamad O, Yu SP (2017) Stem cell transplantation therapy for multifaceted therapeutic benefits after stroke. Prog Neurobiol 157:49–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.03.003
Xiao J, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Zhao J, Liang J et al (2012) Transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into a murine model of passive chronic immune thrombocytopenia. Transfusion 52:2551–2558. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1537-2995.2012.03642.x
Yin F, Guo L, Meng CY, Liu YJ, Lu RF, Li P et al (2014a) Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells exerts anti-apoptotic effects in adult rats after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Res 1561:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.02.047
Yin F, Meng C, Lu R, Li L, Zhang Y, Chen H et al (2014b) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells repair spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury by promoting axonal growth and anti-autophagy. Neural Regen Res 9:1665–1671. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.141801
Yoo SH, Lee SH, Lee S, Park JH, Lee S, Jin H et al (2020) The effect of human mesenchymal stem cell injection on pain behavior in chronic post-ischemia pain mice. Korean J Pain 33:23–29. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2020.33.1.23
Yu H, Cao B, Feng M, Zhou Q, Sun X, Wu S et al (2010) Combinated transplantation of neural stem cells and collagen type I promote functional recovery after cerebral ischemia in rats. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 293:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.20941
Zamproni LN, Mundim M, Porcionatto MA (2021) Neurorepair and regeneration of the brain: a decade of bioscaffolds and engineered microtissue. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:649891. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.649891
Zhao L, Jiang X, Shi J, Gao S, Zhu Y, Gu T et al (2019) Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing microRNA-25 protect spinal cords against transient ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 157:508–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.07.095
Zhou B, Yuan J, Zhou Y, Ghawji M Jr, Deng YP, Lee AJ et al (2011a) Administering human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to prevent and treat experimental arthritis. Clin Immunol 141:328–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2011.08.014
Zhou Y, Yuan J, Zhou B, Lee AJ, Lee AJ, Ghawji M Jr et al (2011b) The therapeutic efficacy of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells on experimental autoimmune hearing loss in mice. Immunology 133:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03421.x
Zhou G, Wang Y, Gao S, Fu X, Cao Y, Peng Y et al (2021) Potential mechanisms and perspectives in ischemic stroke treatment using stem cell therapies. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:646927. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.646927
Zhu P, Li JX, Fujino M, Zhuang J, Li XK (2013) Development and treatments of inflammatory cells and cytokines in spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mediators Inflamm 2013:701970. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/701970
Zhu Y, Uezono N, Yasui T, Nakashima K (2018) Neural stem cell therapy aiming at better functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Dev Dyn 247:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.24558
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 82001301, 81974019) to GL and PZ; the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Nos. 2018YFA0108700, 2017YFA0105602) and NSFC Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges (Grant No. 81720108004) to PZ; the key program of Guangzhou science research plan (Grant No. 201904020047) to PZ; and the Special Project of Dengfeng Program of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Grant Nos. DFJHBF202111, KJ012020630, DFJH201812, KJ012019119, KJ012019423) to GL and PZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors analyzed and discussed the literature, commenting on and approving the manuscript. QS-S, MN, XS, GD, and GL performed the bibliographic research, drafted the manuscript, and created the table. DL-Z prepared the figures. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Qs., Zhuang, DL., Nasser, M.I. et al. Stem Cell Therapies for Restorative Treatments of Central Nervous System Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 491–510 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01204-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01204-9