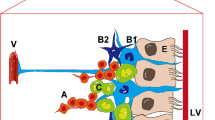
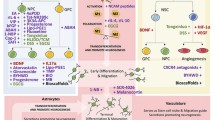
Abstract
Acute injuries to CNS such as stroke induce neural progenitor proliferation in adult brain which might be an endogenous attempt to self-repair. This process is known to be altered by several exogenous and endogenous modulators including growth factors that could help to reinforce the post-stroke neurogenesis. Increasing the neurogenesis may be a future therapeutic option to decrease the cognitive and behavioral deficits following stroke. In addition, transplantation of various types of stem cells into the injured brain is currently thought to be an exciting option to replace the neurons lost in the post-ischemic brain. These include immortalized stem cell lines, neural progenitors prepared from embryonic and adult animals and mesenchymal stem cells. Using exogenous stem cells in addition to modulating endogenous neurogenesis, we may be able to repair the injured brain after a devastating stroke. This article reviewed the current literature of these two issues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J (1962) Are new neurons formed in the brains of adult mammals? Science 135:1127–1128. doi:10.1126/science.135.3509.1127
Altman J (1969) Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis. IV. Cell proliferation and migration in the anterior forebrain, with special reference to persisting neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 137:433–457. doi:10.1002/cne.901370404
Andrews EM, Tsai SY, Johnson SC, Farrer JR, Wagner JP, Kopen GC, Kartje GL (2008) Human adult bone marrow-derived somatic cell therapy results in functional recovery and axonal plasticity following stroke in the rat. Exp Neurol 211:588–592. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.02.027
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2002) Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med 8:963–970. doi:10.1038/nm747
Baldauf K, Reymann KG (2005) Influence of EGF/bFGF treatment on proliferation, early neurogenesis and infarct volume after transient focal ischemia. Brain Res 1056:158–167. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.07.035
Borlongan CV, Tajima Y, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Sanberg PR (1998) Transplantation of cryopreserved human embryonal carcinoma-derived neurons (NT2N cells) promotes functional recovery in ischemic rats. Exp Neurol 149:310–321. doi:10.1006/exnr.1997.6730
Briones TL, Suh E, Hattar H, Wadowska M (2005) Dentate gyrus neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia and behavioral training. Biol Res Nurs 6:167–179. doi:10.1177/1099800404271328
Brown J, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Kempermann G, Van Praag H, Winkler J, Gage FH, Kuhn HG (2003) Enriched environment and physical activity stimulate hippocampal but not olfactory bulb neurogenesis. Eur J NeuroSci 17:2042–2046. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02647.x
Buhnemann C, Scholz A, Bernreuther C, Malik CY, Braun H, Schachner M, Reymann KG, Dihne M (2006) Neuronal differentiation of transplanted embryonic stem cell-derived precursors in stroke lesions of adult rats. Brain 129:3238–3248. doi:10.1093/brain/awl261
Cairns K, Finklestein SP (2003) Growth factors and stem cells as treatments for stroke recovery. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14:S135–S142. doi:10.1016/S1047-9651(02)00059-1
Caplan AI, Dennis JE (2006) Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J Cell Biochem 98:1076–1084. doi:10.1002/jcb.20886
Chang CF, Lin SZ, Chiang YH, Morales M, Chou J, Lein P, Chen HL, Hoffer BJ, Wang Y (2003) Intravenous administration of bone morphogenetic protein-7 after ischemia improves motor function in stroke rats. Stroke 34:558–564. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000051507.64423.00
Charytoniuk DA, Traiffort E, Pinard E, Issertial O, Seylaz J, Ruat M (2000) Distribution of bone morphogenetic protein and bone morphogenetic protein receptor transcripts in the rodent nervous system and up-regulation of bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II in hippocampal dentate gyrus in a rat model of global cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 100:33–43. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(00)00246-3
Chen CP, Lee YJ, Chiu ST, Shyu WC, Lee MY, Huang SP, Li H (2006) The application of stem cells in the treatment of ischemic diseases. Histol Histopathol 21:1209–1216
Choi YS, Lee MY, Sung KW, Jeong SW, Choi JS, Park HJ, Kim ON, Lee SB, Kim SY (2003) Regional differences in enhanced neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult rats after transient forebrain ischemia. Mol Cell 16:232–238
Chou J, Harvey BK, Chang CF, Shen H, Morales M, Wang Y (2006) Neuroregenerative effects of BMP7 after stroke in rats. J Neurol Sci 240:21–29. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2005.08.015
Curtis MA, Penney EB, Pearson J, Dragunow M, Connor B, Faull RL (2005) The distribution of progenitor cells in the subependymal layer of the lateral ventricle in the normal and Huntington’s disease human brain. Neuroscience 132:777–788. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.12.051
Darsalia V, Kallur T, Kokaia Z (2007) Survival, migration and neuronal differentiation of human fetal striatal and cortical neural stem cells grafted in stroke-damaged rat striatum. Eur J NeuroSci 26:605–614. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05702.x
Dempsey RJ, Sailor KA, Bowen KK, Türeyen K, Vemuganti R (2003) Stroke-induced progenitor cell proliferation in the adult spontaneously hypertensive rat brain: effect of exogenous IGF-1 and GDNF. J Neurochem 87:586–597
Dempsey RJ, Kalluri HS (2007) Ischemia-induced neurogenesis: role of growth factors. Neurosurg Clin N Am 18:183–190. doi:10.1016/j.nec.2006.10.011
Dickinson ME, McMahon AP (1992) The role of Wnt genes in vertebrate development. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2:562–566. doi:10.1016/S0959-437X(05)80172-8
Doetsch F, Caille I, Lim DA, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (1999) Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 97:703–716. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80783-7
Ekdahl CT, Claasen JH, Bonde S, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2003) Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13632–13637. doi:10.1073/pnas.2234031100
Ekdahl CT, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2008) Brain inflammation and adult neurogenesis: the dual role of microglia. Neuroscience 158:1021–1029. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.052
Emanuelia C, Madeddu P (2003) Human tissue kallikrein: a new bullet for the treatment of ischemia. Curr Pharm Des 9:589–597. doi:10.2174/1381612033391315
Esneault E, Pacary E, Eddi D, Freret T, Tixier E, Toutain J, Touzani O, Schumann-Bard P, Petit E, Roussel S, Bernaudin M (2008) Combined therapeutic strategy using erythropoietin and mesenchymal stem cells potentiates neurogenesis after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1552–1563. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2008.40
Evans MJ, Kaufman MH (1981) Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292:154–156. doi:10.1038/292154a0
Gao X, Arlotta P, Macklis JD, Chen J (2007) Conditional knock-out of beta-catenin in postnatal-born dentate gyrus granule neurons results in dendritic malformation. J Neurosci 27:14317–14325. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3206-07.2007
Gluckman P, Klempt N, Guan J, Mallard C, Sirimanne E, Dragunow M, Klempt M, Singh K, Williams C, Nikolics K (1992) A role for IGF-1 in the rescue of CNS neurons following hypoxic–ischemic injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 182:593–599. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)91774-K
Greenberg DA, Jin K (2006) Growth factors and stroke. NeuroRx 3:458–465. doi:10.1016/j.nurx.2006.08.003
Han Y, Chen X, Shi F, Li S, Huang J, Xie M, Hu L, Hoidal JR, Xu P (2007) CPG15, a new factor upregulated after ischemic brain injury, contributes to neuronal network re-establishment after glutamate-induced injury. J Neurotrauma 24:722–731. doi:10.1089/neu.2006.0174
Hara K, Yasuhara T, Maki M, Matsukawa N, Masuda T, Yu SJ, Ali M, Yu G, Xu L, Kim SU, Hess DC, Borlongan CV (2008) Neural progenitor NT2N cell lines from teratocarcinoma for transplantation therapy in stroke. Prog Neurobiol 85:318–334. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.04.005
Hayashi J, Takagi Y, Fukuda H, Imazato T, Nishimura M, Fujimoto M, Takahashi J, Hashimoto N, Nozaki K (2006) Primate embryonic stem cell-derived neuronal progenitors transplanted into ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:906–914. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600247
Hoehn BD, Palmer TD, Steinberg GK (2005) Neurogenesis in rats after focal cerebral ischemia is enhanced by indomethacin. Stroke 36:2718–2724. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000190020.30282.cc
Horita Y, Honmou O, Harada K, Houkin K, Hamada H, Kocsis JD (2006) Intravenous administration of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells protects against injury in a cerebral ischemia model in the adult rat. J Neurosci Res 84:1495–1504. doi:10.1002/jnr.21056
Ishibashi S, Kuroiwa T, Sakaguchi M, Sun L, Kadoya T, Okano H, Mizusawa H (2007) Galectin-1 regulates neurogenesis in the subventricular zone and promotes functional recovery after stroke. Exp Neurol 207:302–313. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.06.024
Ishibashi S, Sakaguchi M, Kuroiwa T, Yamasaki M, Kanemura Y, Shizuko I, Shimazaki T, Onodera M, Okano H, Mizusawa H (2004) Human neural stem/progenitor cells, expanded in long-term neurosphere culture, promote functional recovery after focal ischemia in Mongolian gerbils. J Neurosci Res 78:215–223. doi:10.1002/jnr.20246
Jiang W, Gu W, Brannstrom T, Rosqvist R, Wester P (2001) Cortical neurogenesis in adult rats after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 32:1201–1207
Jin K, Minami M, Lan JQ, Mao XO, Batteur S, Simon RP, Greenberg DA (2001) Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4710–4715. doi:10.1073/pnas.081011098
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Greenberg DA (2004) Post-ischemic administration of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) reduces infarct size and modifies neurogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:399–408. doi:10.1097/00004647-200404000-00005
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Mao XO, Childs J, Peel A, Logvinova A, Banwait S, Greenberg DA (2005) Comparison of ischemia-directed migration of neural precursor cells after intrastriatal, intraventricular, or intravenous transplantation in the rat. Neurobiol Dis 18:366–374. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2004.10.010
Kalluri HS, Dempsey RJ (2008) Growth factors, stem cells, and stroke. Neurosurg Focus 24:E14. doi:10.3171/FOC/2008/24/3-4/E13
Kaufmann WE, Worley PF, Pegg J, Bremer M, Isakson P (1996) COX-2, a synaptically induced enzyme, is expressed by excitatory neurons at postsynaptic sites in rat cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2317–2321. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.6.2317
Kawai T, Takagi N, Miyake-Takagi K, Okuyama N, Mochizuki N, Takeo S (2004) Characterization of BrdU-positive neurons induced by transient global ischemia in adult hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:548–555. doi:10.1097/00004647-200405000-00009
Kee NJ, Preston E, Wojtowicz JM (2001) Enhanced neurogenesis after transient global ischemia in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Exp Brain Res 136:313–320. doi:10.1007/s002210000591
Kelly S, Bliss TM, Shah AK, Sun GH, Ma M, Foo WC, Masel J, Yenari MA, Weissman IL, Uchida N, Palmer T, Steinberg GK (2004) Transplanted human fetal neural stem cells survive, migrate, and differentiate in ischemic rat cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11839–11844. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404474101
Kelsen J, Kjaer K, Chen G, Pedersen M, Rohl L, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S, Nyengaard JR, Ronn LC (2006) Parecoxib is neuroprotective in spontaneously hypertensive rats after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion: a divided treatment response? J Neuroinflammation 3:31. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-3-31
Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH (1997) More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature 386:493–495. doi:10.1038/386493a0
Kim SS, Yoo SW, Park TS, Ahn SC, Jeong HS, Kim JW, Chang DY, Cho KG, Kim SU, Huh Y, Lee JE, Lee SY, Lee YD, Suh-Kim H (2008) Neural induction with neurogenin1 increases the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in the ischemic brain. Stem Cells 26:2217–2228. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2008-0108
Kluska MM, Witte OW, Bolz J, Redecker C (2005) Neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus after cortical infarcts: effects of infarct location, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor blockade and anti-inflammatory treatment. Neuroscience 135:723–735. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.06.082
Koh SH, Kim KS, Choi MR, Jung KH, Park KS, Chai YG, Roh W, Hwang SJ, Ko HJ, Huh YM, Kim HT, Kim SH (2008) Implantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a neuroprotective therapy for ischemic stroke in rats. Brain Res 229:233–248. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.087
Koketsu D, Furuichi Y, Maeda M, Matsuoka N, Miyamoto Y, Hisatsune T (2006) Increased number of new neurons in the olfactory bulb and hippocampus of adult non-human primates after focal ischemia. Exp Neurol 199:92–102. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.03.012
Kokovay E, Li L, Cunningham LA (2006) Angiogenic recruitment of pericytes from bone marrow after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:545–555. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600214
Komitova M, Mattsson B, Johansson BB, Eriksson PS (2005) Enriched environment increases neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of stroke-lesioned adult rats. Stroke 36:1278–1282. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000166197.94147.59
Komitova M, Zhao LR, Gido G, Johansson BB, Eriksson P (2005) Postischemic exercise attenuates whereas enriched environment has certain enhancing effects on lesion-induced subventricular zone activation in the adult rat. Eur J NeuroSci 21:2397–2405. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04072.x
Krampera M, Marconi S, Pasini A, Galie M, Rigotti G, Mosna F, Tinelli M, Lovato L, Anghileri E, Andreini A, Pizzolo G, Sbarbati A, Bonetti B (2007) Induction of neural-like differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, fat, spleen and thymus. Bone 40:382–390. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2006.09.006
Kuhn HG, Winkler J, Kempermann G, Thal LJ, Gage FH (1997) Epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 have different effects on neural progenitors in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci 17:5820–5829
Kumihashi K, Uchida K, Miyazaki H, Kobayashi J, Tsushima T, Machida T (2001) Acetylsalicylic acid reduces ischemia-induced proliferation of dentate cells in gerbils. NeuroReport 12:915–917. doi:10.1097/00001756-200104170-00010
Lee J, Kuroda S, Shichinohe H, Ikeda J, Seki T, Hida K, Tada M, Sawada K, Iwasaki Y (2003) Migration and differentiation of nuclear fluorescence-labeled bone marrow stromal cells after transplantation into cerebral infarct and spinal cord injury in mice. Neuropathology 23:169–180. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1789.2003.00496.x
Lee SH, Kim YH, Kim YJ, Yoon BW (2008) Enforced physical training promotes neurogenesis in the subgranular zone after focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurol Sci 269:54–61. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2007.12.028
Lee SH, Kim YJ, Lee KM, Ryu S, Yoon BW (2007) Ischemic preconditioning enhances neurogenesis in the subventricular zone. Neuroscience 146:1020–1031. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.02.058
Lee TH, Yoon JG (2008) Intracerebral transplantation of human adipose tissue stromal cells after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Clin Neurosci 15:907–912. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2007.03.016
Lei ZN, Zhang LM, Sun FY (2008) Beta-catenin siRNA inhibits ischemia-induced striatal neurogenesis in adult rat brain following a transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurosci Lett 435:108–112. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.02.031
Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, Desire L, Mira H, Consiglio A, Lein ES, Jessberger S, Lansford H, Dearie AR, Gage FH (2005) Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature 437:1370–1375. doi:10.1038/nature04108
Lin S, Fan LW, Pang Y, Rhodes PG, Mitchell HJ, Cai Z (2005) IGF-1 protects oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and improves neurological functions following cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in the neonatal rat. Brain Res 1063:15–26. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.09.042
Lin TN, Wong YP, Chen JJ, Cheng JT, Yu SF, Sun SH, Chi SI, Chai CY (1997) Elevated basic fibroblast growth factor levels in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuroscience 76:557–570. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(96)00391-0
Ling L, Hou Q, Xing S, Yu J, Pei Z, Zeng J (2008) Exogenous kallikrein enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis in the subventricular zone and the peri-infarction region and improves neurological function after focal cortical infarction in hypertensive rats. Brain Res 1206:89–97. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.099
Liu J, Solway K, Messing RO, Sharp FR (1998) Increased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia in gerbils. J Neurosci 18:7768–7778
Liu Z, Fan Y, Won SJ, Neumann M, Hu D, Zhou L, Weinstein PR, Liu J (2007) Chronic treatment with minocycline preserves adult new neurons and reduces functional impairment after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 38:146–152. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000251791.64910.cd
Lledo PM, Alonso M, Grubb MS (2006) Adult neurogenesis and functional plasticity in neuronal circuits. Natl Rev 7:179–193. doi:10.1038/nrn1867
Lois C, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (1996) Chain migration of neuronal precursors. Science 271:978–981. doi:10.1126/science.271.5251.978
Lowry WE, Richter L, Yachechko R, Pyle AD, Tchieu J, Sridharan R, Clark AT, Plath K (2008) Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells from dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2883–2888. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711983105
Madden K (2002) Optimal timing of thrombolytic therapy in acute ischaemic stroke. CNS Drugs 16:213–218. doi:10.2165/00023210-200216040-00001
Martin GR (1981) Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:7634–7638. doi:10.1073/pnas.78.12.7634
Matsumori Y, Hong SM, Fan Y, Kayama T, Hsu CY, Weinstein PR, Liu J (2006) Enriched environment and spatial learning enhance hippocampal neurogenesis and salvages ischemic penumbra after focal cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 22:187–198. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2005.10.015
Meschia JF, Brott TG (2001) New insights on thrombolytic treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 1:19–25
Ming GL, Song H (2005) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:223–250. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.28.051804.101459
Monje ML, Toda H, Palmer TD (2003) Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science 302:1760–1765. doi:10.1126/science.1088417
Nakagawa M, Koyanagi M, Tanabe K, Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, Aoi T, Okita K, Mochiduki Y, Takizawa N, Yamanaka S (2008) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotechnol 26:101–106. doi:10.1038/nbt1374
Nakatomi H, Kuriu T, Okabe S, Yamamoto S, Hatano O, Kawahara N, Tamura A, Kirino T, Nakafuku M (2002) Regeneration of hippocampal pyramidal neurons after ischemic brain injury by recruitment of endogenous neural progenitors. Cell 110:429–441. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00862-0
Naylor M, Bowen KK, Sailor KA, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R (2005) Preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance stimulates growth factor expression and neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. Neurochem Int 47:565–572. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2005.07.003
Nedivi E, Hevroni D, Naot D, Israeli D, Citri Y (1993) Numerous candidate plasticity-related genes revealed by differential cDNA cloning. Nature 363:718–722. doi:10.1038/363718a0
Nedivi E, Wu GY, Cline HT (1998) Promotion of dendritic growth by CPG15, an activity-induced signaling molecule. Science 281:1863–1866. doi:10.1126/science.281.5384.1863
Ninomiya M, Yamashita T, Araki N, Okano H, Sawamoto K (2006) Enhanced neurogenesis in the ischemic striatum following EGF-induced expansion of transit-amplifying cells in the subventricular zone. Neurosci Lett 403:63–67. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2006.04.039
Nygren J, Wieloch T, Pesic J, Brundin P, Deierborg T (2006) Enriched environment attenuates cell genesis in subventricular zone after focal ischemia in mice and decreases migration of newborn cells to the striatum. Stroke 37:2824–2829. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000244769.39952.90
Okazaki T, Magaki T, Takeda M, Kajiwara Y, Hanaya R, Sugiyama K, Arita K, Nishimura M, Kato Y, Kurisu K (2008) Intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells increases survivin and Bcl-2 protein expression and improves sensorimotor function following ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 430:109–114. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.10.046
Overstreet-Wadiche LS, Westbrook GL (2006) Functional maturation of adult-generated granule cells. Hippocampus 16:208–215. doi:10.1002/hipo.20152
Parent JM, Vexler ZS, Gong C, Derugin N, Ferriero DM (2002) Rat forebrain neurogenesis and striatal neuron replacement after focal stroke. Ann Neurol 52:802–813. doi:10.1002/ana.10393
Park IH, Zhao R, West JA, Yabuuchi A, Huo H, Ince TA, Lerou PH, Lensch MW, Daley GQ (2008) Reprogramming of human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature 451:141–146. doi:10.1038/nature06534
Park SW, Yan YP, Satriotomo I, Vemuganti R, Dempsey RJ (2007) Substance P is a promoter of adult neural progenitor cell proliferation under normal and ischemic conditions. J Neurosurg 107:593–599. doi:10.3171/JNS-07/09/0593
Pavlichenko N, Sokolova I, Vijde S, Shvedova E, Alexandrov G, Krouglyakov P, Fedotova O, Gilerovich EG, Polyntsev DG, Otellin VA (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells transplantation could be beneficial for treatment of experimental ischemic stroke in rats. Brain Res 1233:203–213. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.123
Pluchino S, Muzio L, Imitola J, Deleidi M, Alfaro-Cervello C, Salani G, Porcheri C, Brambilla E, Cavasinni F, Bergamaschi A, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Comi G, Khoury SJ, Martino G (2008) Persistent inflammation alters the function of the endogenous brain stem cell compartment. Brain 131:2564–2578. doi:10.1093/brain/awn198
Pollock K, Stroemer P, Patel S, Stevanato L, Hope A, Miljan E, Dong Z, Hodges H, Price J, Sinden JD (2006) A conditionally immortal clonal stem cell line from human cortical neuroepithelium for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol 199:143–155. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.12.011
Quinones-Hinojosa A, Sanai N, Soriano-Navarro M, Gonzalez-Perez O, Mirzadeh Z, Gil-Perotin S, Romero-Rodriguez R, Berger MS, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (2006) Cellular composition and cytoarchitecture of the adult human subventricular zone: a niche of neural stem cells. J Comp Neurol 494:415–434. doi:10.1002/cne.20798
Rameshwar P (1997) Substance P: a regulatory neuropeptide for hematopoiesis and immune functions. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 85:129–133. doi:10.1006/clin.1997.4446
Sakaguchi M, Shingo T, Shimazaki T, Okano HJ, Shiwa M, Ishibashi S, Oguro H, Ninomiya M, Kadoya T, Horie H, Shibuya A, Mizusawa H, Poirier F, Nakauchi H, Sawamoto K, Okano H (2006) A carbohydrate-binding protein, Galectin-1, promotes proliferation of adult neural stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:7112–7117. doi:10.1073/pnas.0508793103
Salazar-Colocho P, Lanciego JL, Del Rio J, Frechilla D (2008) Ischemia induces cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the gerbil hippocampus in response to neuronal death. Neurosci Res 61:27–37. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2008.01.008
Saporta S, Borlongan CV, Sanberg PR (1999) Neural transplantation of human neuroteratocarcinoma (hNT) neurons into ischemic rats. A quantitative dose-response analysis of cell survival and behavioral recovery. Neuroscience 91:519–525. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(98)00610-1
Sasaki T, Kitagawa K, Sugiura S, Omura-Matsuoka E, Tanaka S, Yagita Y, Okano H, Matsumoto M, Hori M (2003) Implication of cyclooxygenase-2 on enhanced proliferation of neural progenitor cells in the adult mouse hippocampus after ischemia. J Neurosci Res 72:461–471. doi:10.1002/jnr.10595
Sasaki T, Kitagawa K, Yagita Y, Sugiura S, Omura-Matsuoka E, Tanaka S, Matsushita K, Okano H, Tsujimoto Y, Hori M (2006) Bcl2 enhances survival of newborn neurons in the normal and ischemic hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 84:1187–1196. doi:10.1002/jnr.21036
Schabitz WR, Steigleder T, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Schwab S, Sommer C, Schneider A, Kuhn HG (2007) Intravenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances poststroke sensorimotor recovery and stimulates neurogenesis. Stroke 38:2165–2172. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.106.477331
Schneider A, Wysocki R, Pitzer C, Kruger C, Laage R, Schwab S, Bach A, Schabitz WR (2006) An extended window of opportunity for G-CSF treatment in cerebral ischemia. BMC Biol 4:36. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-4-36
Schwarting S, Litwak S, Hao W, Bahr M, Weise J, Neumann H (2008) Hematopoietic stem cells reduce postischemic inflammation and ameliorate ischemic brain injury. Stroke 39:2867–2875. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.513978
Sehara Y, Hayashi T, Deguchi K, Zhang H, Tsuchiya A, Yamashita T, Lukic V, Nagai M, Kamiya T, Abe K (2007) Potentiation of neurogenesis and angiogenesis by G-CSF after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1151:142–149. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.149
Shen LH, Li Y, Chen J, Cui Y, Zhang C, Kapke A, Lu M, Savant-Bhonsale S, Chopp M (2007) One-year follow-up after bone marrow stromal cell treatment in middle-aged female rats with stroke. Stroke 38:2150–2156. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.106.481218
Shen LH, Li Y, Chen J, Zacharek A, Gao Q, Kapke A, Lu M, Raginski K, Vanguri P, Smith A, Chopp M (2007) Therapeutic benefit of bone marrow stromal cells administered 1 month after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:6–13. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600311
Shin HY, Kim JH, Phi JH, Park CK, Kim JE, Kim JH, Paek SH, Wang KC, Kim DG (2008) Endogenous neurogenesis and neovascularization in the neocortex of the rat after focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res 86:356–367. doi:10.1002/jnr.21494
Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Chiang MF, Su CY, Li H (2006) Intracerebral peripheral blood stem cell (CD34+) implantation induces neuroplasticity by enhancing beta1 integrin-mediated angiogenesis in chronic stroke rats. J Neurosci 26:3444–3453. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5165-05.2006
Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Yang HI, Tzeng YS, Pang CY, Yen PS, Li H (2004) Functional recovery of stroke rats induced by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-stimulated stem cells. Circulation 110:1847–1854. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000142616.07367.66
Sokolova IB, Fedotova OR, Zin’kova NN, Kruglyakov PV, Polyntsev DG (2006) Effect of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on cognitive functions in rats with ischemic stroke. Bull Exp Biol Med 142:511–514. doi:10.1007/s10517-006-0405-8
Sun Y, Jin K, Childs JT, Xie L, Mao XO, Greenberg DA (2005) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and ischemia-induced neurogenesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:485–492. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600049
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest 111:1843–1851
Suzuki S, Gerhold LM, Bottner M, Rau SW, Dela Cruz C, Yang E, Zhu H, Yu J, Cashion AB, Kindy MS, Merchenthaler I, Gage FH, Wise PM (2007) Estradiol enhances neurogenesis following ischemic stroke through estrogen receptors alpha and beta. J Comp Neurol 500:1064–1075. doi:10.1002/cne.21240
Takagi Y, Nishimura M, Morizane A, Takahashi J, Nozaki K, Hayashi J, Hashimoto N (2005) Survival and differentiation of neural progenitor cells derived from embryonic stem cells and transplanted into ischemic brain. J Neurosurg 103:304–310
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S (2007) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131:861–872. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019
Takahashi K, Yasuhara T, Shingo T, Muraoka K, Kameda M, Takeuchi A, Yano A, Kurozumi K, Agari T, Miyoshi Y, Kinugasa K, Date I (2008) Embryonic neural stem cells transplanted in middle cerebral artery occlusion model of rats demonstrated potent therapeutic effects, compared to adult neural stem cells. Brain Res 234:172–182. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.07.086
Takami K, Iwane M, Kiyota Y, Miyamoto M, Tsukuda R, Shiosaka S (1992) Increase of basic fibroblast growth factor immunoreactivity and its mRNA level in rat brain following transient forebrain ischemia. Exp Brain Res 90:1–10. doi:10.1007/BF00229250
Takasawa K, Kitagawa K, Yagita Y, Sasaki T, Tanaka S, Matsushita K, Ohstuki T, Miyata T, Okano H, Hori M, Matsumoto M (2002) Increased proliferation of neural progenitor cells but reduced survival of newborn cells in the contralateral hippocampus after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:299–307. doi:10.1097/00004647-200203000-00007
Taupin P (2006) Stroke-induced neurogenesis: physiopathology and mechanisms. Curr Neurovasc Res 3:67–72. doi:10.2174/156720206775541769
Theus MH, Wei L, Cui L, Francis K, Hu X, Keogh C, Yu SP (2008) In vitro hypoxic preconditioning of embryonic stem cells as a strategy of promoting cell survival and functional benefits after transplantation into the ischemic rat brain. Exp Neurol 210:656–670. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.12.020
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282:1145–1147. doi:10.1126/science.282.5391.1145
Thomson JA, Odorico JS (2000) Human embryonic stem cell and embryonic germ cell lines. Trends Biotechnol 18:53–57. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(99)01410-9
Thored P, Arvidsson A, Cacci E, Ahlenius H, Kallur T, Darsalia V, Ekdahl CT, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2006) Persistent production of neurons from adult brain stem cells during recovery after stroke. Stem Cells 24:739–747. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2005-0281
Tonchev AB, Yamashima T, Sawamoto K, Okano H (2005) Enhanced proliferation of progenitor cells in the subventricular zone and limited neuronal production in the striatum and neocortex of adult macaque monkeys after global cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res 81:776–788. doi:10.1002/jnr.20604
Tonchev AB, Yamashima T, Zhao L, Okano HJ, Okano H (2003) Proliferation of neural and neuronal progenitors after global brain ischemia in young adult macaque monkeys. Mol Cell Neurosci 23:292–301. doi:10.1016/S1044-7431(03)00058-7
Tureyen K, Vemuganti R, Bowen KK, Sailor KA, Dempsey RJ (2005) EGF and FGF-2 infusion increases post-ischemic neural progenitor cell proliferation in the adult rat brain. Neurosurgery 57:1254–1263. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000186040.96929.8A
van Gijn J, Dennis MS (1998) Issues and answers in stroke care. Lancet 352(Suppl 3):SIII23–SIII27
Vaught JL (1998) Substance P antagonists and analgesia: a review of the hypothesis. Life Sci 43:1419–1431. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(88)90253-6
Wang SH, Zhang ZJ, Guo YJ, Teng GJ, Chen BA (2008) Hippocampal neurogenesis and behavioural studies on adult ischemic rat response to chronic mild stress. Behav Brain Res 189:9–16. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2007.11.028
Wang Y, Jin K, Mao XO, Xie L, Banwait S, Marti HH, Greenberg DA (2007) VEGF-overexpressing transgenic mice show enhanced post-ischemic neurogenesis and neuromigration. J Neurosci Res 85:740–747. doi:10.1002/jnr.21169
Watanabe T, Okuda Y, Nonoguchi N, Zhao MZ, Kajimoto Y, Furutama D, Yukawa H, Shibata MA, Otsuki Y, Kuroiwa T, Miyatake S (2004) Postischemic intraventricular administration of FGF-2 expressing adenoviral vectors improves neurologic outcome and reduces infarct volume after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:1205–1213. doi:10.1097/01.WCB.0000136525.75839.41
Wei L, Cui L, Snider BJ, Rivkin M, Yu SS, Lee CS, Adams LD, Gottlieb DI, Johnson EM Jr, Yu SP, Choi DW (2005) Transplantation of embryonic stem cells overexpressing Bcl-2 promotes functional recovery after transient cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 19:183–193. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2004.12.016
Widestrand A, Faijerson J, Wilhelmsson U, Smith PL, Li L, Sihlbom C, Eriksson PS, Pekny M (2007) Increased neurogenesis and astrogenesis from neural progenitor cells grafted in the hippocampus of GFAP−/− Vim−/− mice. Stem Cells 25:2619–2627. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0122
Wiltrout C, Lang B, Yan Y, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R (2007) Repairing brain after stroke: a review on post-ischemic neurogenesis. Neurochem Int 50:1028–1041. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2007.04.011
Winkelheide U, Engelhard K, Kaeppel B, Winkler J, Hutzler P, Werner C, Kochs E (2008) Cerebral ischemia and neurogenesis: a two-time comparison. Neurocrit Care 9:387–393. doi:10.1007/s12028-008-9121-8
Wu J, Sun Z, Sun HS, Wu J, Weisel RD, Keating A, Li ZH, Feng ZP, Li RK (2008) Intravenously administered bone marrow cells migrate to damaged brain tissue and improve neural function in ischemic rats. Cell Transplant 16:993–1005. doi:10.3727/000000007783472435
Wu M, Yang L, Liu S, Li H, Hui N, Wang F, Liu H (2006) Differentiation potential of human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells for skin-related tissue. Br J Dermatol 155:282–291. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07357.x
Xia CF, Yin H, Yao YY, Borlongan CV, Chao L, Chao J (2006) Kallikrein protects against ischemic stroke by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation and promoting angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Hum Gene Ther 17:206–219. doi:10.1089/hum.2006.17.206
Yagita Y, Kitagawa K, Ohtsuki T, Takasawa K, Miyata T, Okano H, Hori M, Matsumoto M (2001) Neurogenesis by progenitor cells in the ischemic adult rat hippocampus. Stroke 32:1890–1896
Yamashima T, Tonchev AB, Vachkov IH, Popivanova BK, Seki T, Sawamoto K, Okano H (2004) Vascular adventitia generates neuronal progenitors in the monkey hippocampus after ischemia. Hippocampus 14:861–875. doi:10.1002/hipo.20001
Yamashita T, Ninomiya M, Hernandez Acosta P, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Sunabori T, Sakaguchi M, Adachi K, Kojima T, Hirota Y, Kawase T, Araki N, Abe K, Okano H, Sawamoto K (2006) Subventricular zone-derived neuroblasts migrate and differentiate into mature neurons in the post-stroke adult striatum. J Neurosci 26:6627–6636. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0149-06.2006
Yan YP, Sailor KA, Vemuganti R, Dempsey RJ (2006) Insulin-like growth factor-1 is an endogenous mediator of focal ischemia-induced neural progenitor proliferation. Eur J NeuroSci 24:45–54. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04872.x
Yan YP, Sailor KA, Lang BT, Park SW, Vemuganti R, Dempsey RJ (2007) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 plays a critical role in neuroblast migration after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1213–1224. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600432
Yao DL, Masonic K, Petullo D, Li LY, Lincoln C, Wibberley L, Alderson RF, Antonaccio M (1999) Pretreatment with intravenous FGF-13 reduces infarct volume and ameliorates neurological deficits following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 818:140–146. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(98)01118-4
Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA, Ruotti V, Stewart R, Slukvin II, Thomson JA (2007) Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 318:1917–1920. doi:10.1126/science.1151526
Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Chopp M (2001) Proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells in the cortex and the subventricular zone in the adult rat after focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 105:33–41. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(01)00117-8
Zhu DY, Liu SH, Sun HS, Lu YM (2003) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase after focal cerebral ischemia stimulates neurogenesis in the adult rodent dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 23:223–229
Zhu W, Fan Y, Frenzel T, Gasmi M, Bartus RT, Young WL, Yang GY, Chen Y (2008) Insulin growth factor-1 gene transfer enhances neurovascular remodeling and improves long-term stroke outcome in mice. Stroke 39:1254–1261. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.500801
Zhu W, Mao Y, Zhao Y, Zhou LF, Wang Y, Zhu JH, Zhu Y, Yang GY (2005) Transplantation of vascular endothelial growth factor-transfected neural stem cells into the rat brain provides neuroprotection after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosurgery 57:325–333. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000166682.50272.BC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y.P., Lang, B.T., Baskaya, M.K. et al. The potential of neural stem cells to repair stroke-induced brain damage. Acta Neuropathol 117, 469–480 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0516-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0516-1