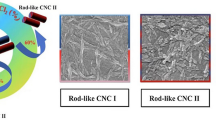
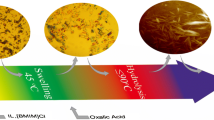
Abstract
To achieve large-scale production of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), it is crucial to investigate ecologically and environmentally acceptable solvent systems that can effectively hydrolyze cellulose. Lithium bromide molten salt hydrate (LiBr MSH), as a benign cellulose solvent, is thermally and chemically stable, and recyclable with minimal environmental hazard. In this study, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC, cellulose I) was treated with formic acid-acidified LiBr MSH to yield CNCs. Cellulose I and II nanocrystals with tunable morphologies (rod-like and sphere-like) and high yield (up to 71.5%) were isolated. The concentration of LiBr had the most significant influence on the structure of CNCs. With an increased LiBr concentration from 50 to 56%, the CNC allomorph transitioned from cellulose I to a mixture of cellulose I and II and finally to cellulose II. The rod-like CNCs exhibited decreasing lengths from 398.4 nm to 102.9 nm and ultimately transformed into sphere-like nanoparticles. The resulting CNCs showed an overall high crystallinity (up to 65.9%), high thermal stability (Tmax up to 334.6 °C), and good suspension stability (no significant settling within 30 days). Therefore, this work provides an environmentally friendly and effective approach to producing CNCs with adjustable size and allomorph.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors, Chuanshuang Hu and Jin Gu, upon reasonable request.
References
Amin KNM, Hosseinmardi A, Martin DJ, Annamalai PK (2022) A mixed acid methodology to produce thermally stable cellulose nanocrystal at high yield using phosphoric acid. J Bioresour Bioprod 7:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2021.12.002
Cao Y, Jiang Y, Song Y, Cao S, Miao M, Feng X, Fang J, Shi L (2015) Combined bleaching and hydrolysis for isolation of cellulose nanofibrils from waste sackcloth. Carbohydr Polym 131:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.05.063
Carvalho JPF, Silva ACQ, Silvestre AJD, Freire CSR, Vilela C (2021) Spherical cellulose micro and nanoparticles: a review of recent developments and applications. Nanomaterials 11:2744–2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102744
Chen L, Zhu JY, Baez C, Kitin P, Elder T (2016) Highly thermal-stable and functional cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils produced using fully recyclable organic acids. Green Chem 18:3835–3843. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6gc00687f
Chen R, Ma Z, Sun D, Wang X, Han Y (2022) Cellulose I nanocrystals (CNCs I) prepared in mildly acidic lithium bromide trihydrate (MALBTH) and their application for stabilizing pickering emulsions. Int J Biol Macromol 201:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.110
Cheng Z, Li J, Wang B, Zeng J, Xu J, Zhu S, Duan C, Chen K (2022) Comparative study on properties of nanocellulose derived from sustainable biomass resources. Cellulose 29:7083–7098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04717-0
De France K, Zeng Z, Wu T, Nystrom G (2021) Functional materials from nanocellulose: Utilizing structure-property relationships in bottom-up fabrication. Adv Mater 33:e2000657. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000657
de Oliveira TM, Ferrarezi MMF, Yoshida IVP, Gonçalves MdC (2013) Surface modification of cotton nanocrystals with a silane agent. Cellulose 20:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9820-3
Deng WH, Kennedy JR, Tsilomelekis G, Zheng WQ, Nikolakis V (2015) Cellulose hydrolysis in acidified LiBr molten salt hydrate media. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:5226–5236. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b00757
Dong SP, Roman M (2007) Fluorescently labeled cellulose nanocrystals for bioimaging applications. J Am Chem Soc 129:13810–13811. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja076196l
Du HS, Liu C, Mu XD, Gong WB, Lv D, Hong YM, Si CL, Li B (2016) Preparation and characterization of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals via a sustainable approach of FeCl3-catalyzed formic acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 23:2389–2407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0963-5
Fischer S, Leipner H, Thummler K, Brendler E, Peters J (2003) Inorganic molten salts as solvents for cellulose. Cellulose 10:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025128028462
Flauzino Neto WP, Putaux J-L, Mariano M, Ogawa Y, Otaguro H, Pasquini D, Dufresne A (2016) Comprehensive morphological and structural investigation of cellulose I and II nanocrystals prepared by sulphuric acid hydrolysis. RSC Adv 6:76017–76027. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra16295a
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Gomri C, Cretin M, Semsarilar M (2022) Recent progress on chemical modification of cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) and its application in nanocomposite films and membranes-a comprehensive review. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119790
Gu J, Hu C, Zhong R, Tu D, Yun H, Zhang W, Leu SY (2017) Isolation of cellulose nanocrystals from medium density fiberboards. Carbohydr Polym 167:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.110
Guo X, Liu L, Hu Y, Wu Y (2018) Water vapor sorption properties of tempo oxidized and sulfuric acid treated cellulose nanocrystal films. Carbohydr Polym 197:524–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.027
Han J, Zhou C, Wu Y, Liu F, Wu Q (2013) Self-assembling behavior of cellulose nanoparticles during freeze-drying: effect of suspension concentration, particle size, crystal structure, and surface charge. Biomacromol 14:1529–1540. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm4001734
Hao X, Shen W, Chen Z, Zhu J, Feng L, Wu Z, Wang P, Zeng X, Wu T (2015) Self-assembled nanostructured cellulose prepared by a dissolution and regeneration process using phosphoric acid as a solvent. Carbohydr Polym 123:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.01.055
Heise K, Kontturi E, Allahverdiyeva Y, Tammelin T, Linder MB, Nonappa and Ikkala O, (2021) Nanocellulose: Recent fundamental advances and emerging biological and biomimicking applications. Adv Mater 33:e2004349. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202004349
Holilah H, Bahruji H, Ediati R, Asranudin A, Jalil AA, Piluharto B, Nugraha RE, Prasetyoko D (2022) Uniform rod and spherical nanocrystalline celluloses from hydrolysis of industrial pepper waste (piper nigrum l.) using organic acid and inorganic acid. Int J Biol Macromol 204:593–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.045
Huang S, Liu X, Chang C, Wang Y (2020a) Recent developments and prospective food-related applications of cellulose nanocrystals: a review. Cellulose 27:2991–3011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-02984-3
Huang Z, Liu C, Feng X, Wu M, Tang Y, Li B (2020b) Effect of regeneration solvent on the characteristics of regenerated cellulose from lithium bromide trihydrate molten salt. Cellulose 27:9243–9256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03440-y
Jiang J, Zhu Y, Jiang F (2021) Sustainable isolation of nanocellulose from cellulose and lignocellulosic feedstocks: recent progress and perspectives. Carbohydr Polym 267:118188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118188
Jonoobi M, Oladi R, Davoudpour Y, Oksman K, Dufresne A, Hamzeh Y, Davoodi R (2015) Different preparation methods and properties of nanostructured cellulose from various natural resources and residues: a review. Cellulose 22:935–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0551-0
Jordan JH, Easson MW, Condon BD (2019) Alkali hydrolysis of sulfated cellulose nanocrystals: optimization of reaction conditions and tailored surface charge. Nanomater (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091232
Jordan JH, Easson MW, Condon BD (2020) Cellulose hydrolysis using ionic liquids and inorganic acids under dilute conditions: morphological comparison of nanocellulose. RSC Adv 10:39413–39424. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra05976e
Klemm D, Cranston ED, Fischer D, Gama M, Kedzior SA, Kralisch D, Kramer F, Kondo T, Lindström T, Nietzsche S, Petzold-Welcke K, Rauchfuß F (2018) Nanocellulose as a natural source for groundbreaking applications in materials science: today’s state. Mater Today 21:720–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2018.02.001
Kreze T, Malej S (2003) Structural characteristics of new and conventional regenerated cellulosic fibers. Text Res J 73:675–684. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051750307300804
Li B, Mou H, Li Y, Ni Y (2013) Synthesis and thermal decomposition behavior of zircoaluminate coupling agents. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:11980–11987. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie400888p
Li R, Wang S, Lu A, Zhang L (2015) Dissolution of cellulose from different sources in an naoh/urea aqueous system at low temperature. Cellulose 22:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0542-6
Li N, Bian HY, Zhu JY, Ciesielski PN, Pan XJ (2021) Tailorable cellulose ii nanocrystals (CNC II) prepared in mildly acidic lithium bromide trihydrate (MALBTH). Green Chem 23:2778–2791. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc00145k
Liu QY, Ma QZ, Sabnis SK, Zheng WQ, Vlachos DG, Fan W, Li WZ, Ma LL (2019) Production of high-yield short-chain oligomers from cellulose via selective hydrolysis in molten salt hydrates and separation. Green Chem 21:5030–5038. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9gc02297j
Liu Q, Chen N, Yin X, Long L, Hou X, Zhao J, Yuan X (2021) Preparation of cellulose nanospheres via combining ZnCl2·3H2O pretreatment and p-toluenesulfonic hydrolysis as a two-step method. Int J Biol Macromol 181:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.168
Lu P, Hsieh Y-L (2010) Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocrystals: rods, spheres, and network. Carbohydr Polym 82:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.04.073
Lu Q, Cai Z, Lin F, Tang L, Wang S, Huang B (2016) Extraction of cellulose nanocrystals with a high yield of 88% by simultaneous mechanochemical activation and phosphotungstic acid hydrolysis. ACS Sustaina Chem Eng 4:2165–2172. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01620
Lv D, Du H, Che X, Wu M, Zhang Y, Liu C, Nie S, Zhang X, Li B (2019) Tailored and integrated production of functional cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils via sustainable formic acid hydrolysis: kinetic study and characterization. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:9449–9463. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b00714
Mascheroni E, Rampazzo R, Ortenzi MA, Piva G, Bonetti S, Piergiovanni L (2016) Comparison of cellulose nanocrystals obtained by sulfuric acid hydrolysis and ammonium persulfate, to be used as coating on flexible food-packaging materials. Cellulose 23:779–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0853-2
Miao J, Yu Y, Jiang Z, Zhang L (2016) One-pot preparation of hydrophobic cellulose nanocrystals in an ionic liquid. Cellulose 23:1209–1219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0864-7
Mou H, Li B, Fardim P (2014) Pretreatment of corn stover with the modified hydrotropic method to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis. Energy Fuels 28:4288–4293. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef5001634
Nomura S, Kugo Y, Erata T (2020) 13C NMR and XRD studies on the enhancement of cellulose II crystallinity with low concentration naoh post-treatments. Cellulose 27:3553–3563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03036-6
Oudiani AE, Chaabouni Y, Msahli S, Sakli F (2011) Crystal transition from cellulose I to cellulose II in naoh treated agave americana l. Fibre Carbohydr Polym 86:1221–1229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.037
Pereira PHF, Ornaghi Júnior HL, Coutinho LV, Duchemin B, Cioffi MOH (2020) Obtaining cellulose nanocrystals from pineapple crown fibers by free-chlorite hydrolysis with sulfuric acid: physical, chemical and structural characterization. Cellulose 27:5745–5756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03179-6
Reddy KO, Maheswari CU, Dhlamini MS, Mothudi BM, Zhang J, Zhang J, Nagarajan R, Rajulu AV (2017) Preparation and characterization of regenerated cellulose films using borassus fruit fibers and an ionic liquid. Carbohydr Polym 160:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.051
Rodriguez Quiroz N, Padmanathan AMD, Mushrif SH, Vlachos DG (2019) Understanding acidity of molten salt hydrate media for cellulose hydrolysis by combining kinetic studies, electrolyte solution modeling, molecular dynamics simulations, and 13C NMR experiments. ACS Catal 9:10551–10561. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b03301
Saito T, Kimura S, Nishiyama Y, Isogai A (2007) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by tempo-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromol 8:2485–2491. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm0703970
Salminen R, Reza M, Pääkkönen T, Peyre J, Kontturi E (2017) Tempo-mediated oxidation of microcrystalline cellulose: limiting factors for cellulose nanocrystal yield. Cellulose 24:1657–1667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1228-7
Sebe G, Ham-Pichavant F, Ibarboure E, Koffi AL, Tingaut P (2012) Supramolecular structure characterization of cellulose II nanowhiskers produced by acid hydrolysis of cellulose I substrates. Biomacromol 13:570–578. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm201777j
Shang Z, An X, Seta FT, Ma M, Shen M, Dai L, Liu H, Ni Y (2019) Improving dispersion stability of hydrochloric acid hydrolyzed cellulose nano-crystals. Carbohydr Polym 222:115037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115037
Sharma PR, Varma AJ (2013) Functional nanoparticles obtained from cellulose: engineering the shape and size of 6-carboxycellulose. Chem Commun 49:8818–8820. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc44551h
Sharma PR, Varma AJ (2014) Functionalized celluloses and their nanoparticles: morphology, thermal properties, and solubility studies. Carbohydr Polym 104:135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.015
Shen C, Hu C, Zhang W, Lin X, Qi W, Zhang Z, Gu J (2022) Acidified ZnCl2 molten salt hydrate systems as hydrolytic media for cellulose I and II nanocrystal production: from rods to spheres. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04712-5
Smirnov MA, Sokolova MP, Tolmachev DA, Vorobiov VK, Kasatkin IA, Smirnov NN, Klaving AV, Bobrova NV, Lukasheva NV, Yakimansky AV (2020) Green method for preparation of cellulose nanocrystals using deep eutectic solvent. Cellulose 27:4305–4317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03100-1
Tan X, Chen L, Li X, Xie F (2019) Effect of anti-solvents on the characteristics of regenerated cellulose from 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ionic liquid. Int J Biol Macromol 124:314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.138
Tang Y, Yang S, Zhang N, Zhang J (2013) Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose via low-intensity ultrasonic-assisted sulfuric acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 21:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0158-2
Tian W, Gao X, Zhang J, Yu J, Zhang J (2022) Cellulose nanosphere: preparation and applications of the novel nanocellulose. Carbohydr Polym 277:118863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118863
Vanderfleet OM, Reid MS, Bras J, Heux L, Godoy-Vargas J, Panga MKR, Cranston ED (2018) Insight into thermal stability of cellulose nanocrystals from new hydrolysis methods with acid blends. Cellulose 26:507–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2175-7
Wada M, Ike M, Tokuyasu K (2010) Enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose I is greatly accelerated via its conversion to the cellulose II hydrate form. Polym Degrad and Stab 95:543–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2009.12.014
Wang N, Ding E, Cheng R (2007) Thermal degradation behaviors of spherical cellulose nanocrystals with sulfate groups. Polymer 48:3486–3493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2007.03.062
Wang S, Lu A, Zhang L (2016) Recent advances in regenerated cellulose materials. Prog Polym Sci 53:169–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2015.07.003
Xi Y, Zhang L, Tian Y, Song J, Ma J, Wang Z (2022) Rapid dissolution of cellulose in an AlCl3/ZnCl2 aqueous system at room temperature and its versatile adaptability in functional materials. Green Chem 24:885–897. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc03918k
Xing L, Gu J, Zhang W, Tu D, Hu C (2018) Cellulose I and II nanocrystals produced by sulfuric acid hydrolysis of tetra pak cellulose I. Carbohydr Polym 192:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.042
Xing L, Hu C, Zhang W, Guan L, Gu J (2020) Transition of cellulose supramolecular structure during concentrated acid treatment and its implication for cellulose nanocrystal yield. Carbohydr Polym 229:115539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115539
Yang YJ, Shin JM, Kang TH, Kimura S, Wada M, Kim UJ (2014) Cellulose dissolution in aqueous lithium bromide solutions. Cellulose 21:1175–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0183-9
Yudianti R, Syampurwadi A, Onggo H, Karina M, Uyama H, Azuma J (2016) Properties of bacterial cellulose transparent film regenerated from dimethylacetamide-LiCl solution. Polym Adv Technol 27:1102–1107. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.3782
Zhang J, Elder TJ, Pu Y, Ragauskas AJ (2007) Facile synthesis of spherical cellulose nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 69(3):607–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.01.019
Zhao J, Deng M, Li S, Guan Z, Xia Y, Yang J, Lin X (2022) Room temperature preparation of cellulose nanocrystals with high yield via a new ZnCl2 solvent system. Carbohydr Polym 278:118946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118946
Acknowledgements
This project is financially supported by Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Project# 2021A1515010863, 2020A1515111106, 2020B1515420005, and 2022A1515010502) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project# 22208116).
Funding
This project is financially supported by Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Project# 2021A1515010863, 2020A1515111106, 2020B1515420005, and 2022A1515010502) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project# 22208116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YW and HY. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YW. JG, LG, and WQ acquired funding. CH administrated the project. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This manuscript is our original work and has not been submitted to other journals. This paper presents research results clearly and honestly without fabrication, falsification or any inappropriate manipulation of data. All data were obtained, selected and processed in compliance with discipline-specific rules.
Consent for publication
All authors have seen and approved the submission of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Hu, C., Guan, L. et al. Rod-like and spherical cellulose I and II nanocrystals prepared through acidified lithium bromide molten salt hydrate treatment. Cellulose 30, 10935–10952 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05567-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05567-0