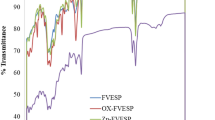
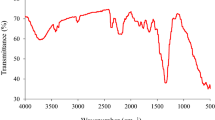
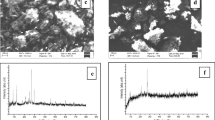
Abstract
Water pollution caused by dyes continues to be the most current and vital problem of today. In this study, which aims to contribute to solving the aforementioned problem, hemp fiber (HF) which are eco-friendly, biodegradable, economical and easily available, was used as an adsorbent raw material to remove dyes from aqueous solution. Hemp fibers were modified with H2SO4 to improve its adsorptive properties and sulphated bio-adsorbent (SHF) was prepared. The prepared adsorbent was thoroughly characterized by using FTIR, SEM, EDX, BET, XRD, Boehm Titration techniques and calculating pHpzc. It is aimed to remove Malachite Green Oxalate (MGO) from wastewater. The effects of adsorbent amount, pH, initial dye concentration, contact time, temperature and ionic strength on adsorption were investigated in adsorption studies performed by batch method. Reusability study was carried out by performing desorption and adsorption processes with ten repetitions. It was observed that MGO adsorption onto SHF was fitted to the pseudo-second order kinetic and the Langmuir isotherm models. According to the Langmuir model, the adsorption capacity of MGO onto SHF is 1250.2, 1538.5, 1666.7 and 2000.8 mg/g at 298 K, 308 K, 318 K and 333 K, respectively. Thermodynamic parameters revealed that the adsorption process was endothermic and spontaneous. It was observed that it was almost unaffected by the ionic strength. It is seen that the decrease in percent dye removal efficiency after ten reuses is not significant. It was concluded that MGO from aqueous solution could be removed by the SHF with a very fast, high efficiency and capacity.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Abuzerr S, Darwish M, Mahvi AH (2017) Simultaneous removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic reactive red 198 dyes using magnetic activated carbon nanoparticles: equilibrium, and kinetics analysis. Water Sci Technol 2:534–545
Adebayo MA, Adebomi JI, Abe TO, Areo FI (2020) Removal of aqueous Congo red and malachite green using ackee apple seed–bentonite composite. Colloids Interface Sci Commun 38:100311
Ahmad MA, Ahmad N, Bello OS (2014) Adsorptive removal of malachite green dye using durian seed-based activated carbon. Wat Air and Soil Poll 225(8):2057
Akar E, Altinişik A, Seki Y (2013) Using of activated carbon produced from spent tea leaves for the removal of malachite green from aqueous solution. Ecol Eng 52:19–27
Akköz Y, Coşkun R, Delibaş A (2019) Preparation and characterization of sulphonated bio-adsorbent from waste hawthorn kernel for dye (MB) removal. J Mol Liq 287:110988
Banerjee S, Sharma GC, Gautam RK, Chattopadhyaya MC, Upadhyay SN, Sharma YC (2016) Removal of Malachite Green, a hazardous dye from aqueous solutions using Avena sativa (oat) hull as a potential adsorbent. J Mol Liq 213:162–172
Bayramoglu G, Altintas B, Arica MY (2009) Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamic parameters of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by using a new strong cation-exchange resin. Chem Eng J 152(2):339–346
Bhatti HN, Jabeen A, Iqbal M, Noreen S, Naseem Z (2017) Adsorptive behavior of rice bran-based composites for malachite green dye: isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 237:322–333
Bouaziz F, Koubaa M, Kallel F, Ghorbel RE, Chaabouni SE (2017) Adsorptive removal of malachite green from aqueous solutions by almond gum: kinetic study and equilibrium isotherms. Int J Biol Macromol 105:56–65
Bushra R, Mohamad S, Alias Y, Jin Y, Ahmad M (2021) Current approaches and methodologies to explore the perceptive adsorption mechanism of dyes on low-cost agricultural waste: a review. Micropor Mesopor Mat 319:111040
Büyükbektaş A, Delibaş A, Benk A, Coşkun R (2021) Laponite-AMPS/AA composite hydrogels for efficient removal of methylene blue (MB). J Polym Res 28(8):307
Chieng HI, Lim LBL, Priyantha N (2015) Enhancing adsorption capacity of toxic malachite green dye through chemically modified breadnut peel: equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics and regeneration studies. Environ Technol 36(1):86–97
Coşkun R, Er E, Delibaş A (2018) Synthesis of novel resin containing carbamothiolylimidamide group and application for Cr(VI) removal. Polym Bull 75(3):963–983
El-Nemr MA, Yılmaz M, Ragab S, El Nemr A (2022) Biochar-SO prepared from pea peels by dehydration with sulfuric acid improves the adsorption of Cr6+ from water. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02378-4
Elwakeel KZ, El-Bindary AA, Ismail A, Morshidy AM (2016) Sorptive removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R from aqueous solution by diethylenetriamine functionalized magnetic macro-reticular hybrid material. RSC Adv 6(27):22395–22410
Ferreira AM, Coutinho JAP, Fernandes AM, Freire MG (2014) Complete removal of textile dyes from aqueous media using ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep Purif Technol 128:58–66
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2012) Preparation, characterization and evaluation of adsorptive properties of orange peel based activated carbon via microwave induced K2CO3 activation. Bioresour Technol 104:679–686
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609
Ghaedi M, Shojaeipour E, Ghaedi AM, Sahraei R (2015) Isotherm and kinetics study of malachite green adsorption onto copper nanowires loaded on activated carbon: artificial neural network modeling and genetic algorithm optimization. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 142:135–149
Ghosh K, Bar N, Roymahapatra G, Biswas AB, Das SK (2022) Adsorptive removal of toxic malachite green from its aqueous solution by Bambusa vulgaris leaves and its acid-treated form: DFT, MPR and GA modeling. J Mol Liq 363:119841
Goodman BA (2020) Utilization of waste straw and husks from rice production: a review. J Bioresour Bioprod 5(3):143–162
Gupta K, Khatri OP (2019) Fast and efficient adsorptive removal of organic dyes and active pharmaceutical ingredient by microporous carbon: effect of molecular size and charge. Chem Eng J 378:122218
Gümüşkaya E, Usta M, Balaban M (2007) Carbohydrate components and crystalline structure of organosolv hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) bast fibers pulp. Bioresour Technol 98(3):491–497
Hajialigol S, Masoum S (2019) Optimization of biosorption potential of nano biomass derived from walnut shell for the removal of Malachite Green from liquids solution: experimental design approaches. J Mol Liq 286:110904
Hemmati F, Norouzbeigi R, Sarbisheh F, Shayesteh H (2016) Malachite green removal using modified sphagnum peat moss as a low-cost biosorbent: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 58:482–489
Ismail M, Akhtar K, Khan MI, Kamal T, Khan AM, Asiri MA, Seo J, Khan BS (2019) Pollution, toxicity and carcinogenicity of organic dyes and their catalytic bio-remediation. Curr Pharm Des 25(34):3645–3663
Jain SN, Gogate PR (2018) Efficient removal of Acid Green 25 dye from wastewater using activated Prunus Dulcis as biosorbent: batch and column studies. J Environ Manage 210:226–238
Jawad AH, Kadhum AM, Ngoh YS (2018) Applicability of dragon fruit (Hylocereus polyrhizus) peels as low-cost biosorbent for adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies. Desalin Water Treat 109:231–240
Kataoka Y, Kondo T (1998) FT-IR microscopic analysis of changing cellulose crystalline structure during wood cell wall formation. Macromolecules 31(3):760–764
Khamis MI, Ibrahim TH, Jumean FH, Sara ZA, Atallah BA (2020) Cyclic sequential removal of alizarin red S dye and Cr(VI) ions using wool as a low-cost adsorbent. Processes 8(5):556
Krishna Murthy TP, Gowrishankar BS, Chandra Prabha MN, Kruthi M, Hari Krishna R (2019) Studies on batch adsorptive removal of malachite green from synthetic wastewater using acid treated coffee husk: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Microchem J 146:192–201
Krishnamoorthi R, Anbazhagan R, Tsai HC, Wang CF, Lai JY (2022) Biodegradable, superwettable caffeic acid/chitosan polymer coated cotton fibers for the simultaneous removal of oils, dyes, and metal ions from water. Chem Eng J 427:131920
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24:1–39
Leng L, Yuan X, Zeng G, Shao J, Chen X, Wu Z, Wang H, Peng X (2015) Surface characterization of rice husk bio-char produced by liquefaction and application for cationic dye (Malachite green) adsorption. Fuel 155:77–85
Maleš L, Fakin D, Bračič M, Gorgieva S (2020) Efficiency of differently processed membranes based on cellulose as cationic dye adsorbents. Nanomater 10(4):642
Mashkoor F, Nasar A, Inamuddin (2020) Carbon nanotube-based adsorbents for the removal of dyes from waters: a review. Environ Chem Lett 18(3):605–629
Moussavi G, Alahabadi A, Yaghmaeian K, Eskandari M (2013) Preparation, characterization and adsorption potential of the NH4Cl-induced activated carbon for the removal of amoxicillin antibiotic from water. Chem Eng J 217:119–128
Njoku VO, Hameed BH (2011) Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from corncob by chemical activation with H3PO4 for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid adsorption. Chem Eng J 173(2):391–399
Nordin AH, Wong S, Ngadi N, Mohammad ZM, Abd Latif NAF, Nabgan W (2021) Surface functionalization of cellulose with polyethyleneimine and magnetic nanoparticles for efficient removal of anionic dye in wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104639
Quesada HB, Cusioli LF, de Bezerra C, Baptista AT, Nishi L, Gomes RG, Bergamasco R (2019) Acetaminophen adsorption using a low-cost adsorbent prepared from modified residues of Moringa oleifera Lam. seed husks. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94(10):3147–3157
Rashid RA, Jawad AH, Ishak MAM, Kasim NN (2016) KOH-activated carbon developed from biomass waste: adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for Methylene blue uptake. Desalin Water Treat 57(56):27226–27236
Ratan JK, Kau M, Adiraju B (2018) Synthesis of activated carbon from agricultural waste using a simple method: characterization, parametric and isotherms study. Mater Today Proc 5(2part1):3334–3345
Sangon S, Hunt AJ, Attard TM, Mengchang P, Ngernyen Y, Supanchaiyamat N (2018) Valorisation of waste rice straw for the production of highly effective carbon based adsorbents for dyes removal. J Clean Prod 172:1128–1139
Sartape AS, Mandhare AM, Jadhav VV, Raut PD, Anuse MA, Kolekar SS (2017) Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution with adsorption technique using Limonia acidissima (wood apple) shell as low cost adsorbent. Arab J Chem 10:S3229–S3238
Sathishkumar P, Arulkumar M, Palvannan T (2012) Utilization of agro-industrial waste Jatropha curcas pods as an activated carbon for the adsorption of reactive dye Remazol Brilliant Blue R (RBBR). J Clean Prod 22(1):67–75
Singh NB, Nagpal G, Agrawal S, Rachna (2018) Water purification by using adsorbents: a review. Environ Technol Innov 11:187–240
Sonawane GH, Shrivastava VS (2009) Kinetics of decolourization of malachite green from aqueous medium by maize cob (Zea maize): an agricultural solid waste. Desalination 247(1):430–441
Uma BS, Sharma YC (2013) Equilibrium and kinetic studies for removal of malachite green from aqueous solution by a low cost activated carbon. J Ind Eng Chem 19(4):1099–1105
Wen X, Liu H, Zhang L, Zhang J, Fu C, Shi X, Chen X, Mijowska E, Chen MJ, Wang DY (2019) Large-scale converting waste coffee grounds into functional carbon materials as high-efficient adsorbent for organic dyes. Bioresour Technol 272:92–98
You X, Zhou R, Zhu Y, Bu D, Cheng D (2022) Adsorption of dyes methyl violet and malachite green from aqueous solution on multi-step modified rice husk powder in single and binary systems: Characterization, adsorption behavior and physical interpretations. J Hazard Mater 430:128445
Zhu Y, Wu J, Wang H, Wang J, Shen H, Ying Z (2021) Interference effect of experimental parameters on the mercury removal mechanism of biomass char under an oxy-fuel atmosphere. ACS Omega 6(50):35124–35133
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the financial support provided by the Scientific Research Projects Unit of Yozgat Bozok University (Grant No. 6602c-FEF/21-460)
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I declare that all the authors had a significant participation in the development of this work. Yasin AKKÖZ: Methodology, investigation, data curation, conceptualization, writing. Ramazan Coşkun: Validation, supervision, resources, review, writing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rights holder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akköz, Y., Coşkun, R. Preparation of highly effective bio-adsorbent from hemp fiber for removal of malachite green oxalate (MGO). Cellulose 30, 4511–4525 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05167-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05167-y