Abstract
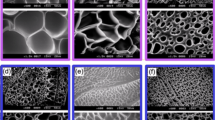
The work aims to research the effect of dibutyl succinate on the water-absorbing and water-holding properties of the composite superabsorbents enriched in the sodium salt of carboxymethyl cellulose. The synthesized composite superabsorbents with a different content of dibutyl succinate were analyzed by FTIR, SEM, XRD, DSC, and rheological measurements; equilibrium swelling ratio values, Qe, in distilled water and in a saline solution were determined; and swelling kinetics, water-holding properties, and regeneration ability were researched. It was found that adding 5% w of dibutyl succinate increases Qe values in distilled water up to 51% compared to blank superabsorbents. The effect of a plasticizer is due to its selective interaction with intramolecular H-bond-forming links, which increases the flexibility of the polymeric network and the availability of sorption sites for water molecules. The non-outwashing of a plasticizer in an aqueous medium was confirmed by HPLC–MS. The presence of dibutyl succinate does not change the water absorption mechanism controlled by chemisorption and pseudo-Fickian diffusion of water molecules but accelerates the equilibrium swelling ratio achievement. Also, there is no significant impact of a plasticizer on the water-holding properties of the synthesized superabsorbents at 80 °C, as well as on their reusability, which retains during several swelling-deswelling cycles. So, dibutyl succinate may be applied as an efficient plasticizer enhancing water sorption properties of the composite superabsorbents based on carboxymethyl cellulose sodium salt.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri M, Khazaeli P, Salehabadi A, Salavati-Niasari M (2021) Hydrogel beads-based nanocomposites in novel drug delivery platforms: recent trends and developments. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 288:102316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102316
Bao Y, Ma J, Li N (2011) Synthesis and swelling behaviors of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(AA-co-AM-co-AMPS)/MMT superabsorbent hydrogel. Carbohyd Polym 84:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.061
Behrouzi M, Moghadam PN (2018) Synthesis of a new superabsorbent copolymer based on acrylic acid grafted onto carboxymethyl tragacanth. Carbohyd Polym 202:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.094
Chavda HV, Patel CN (2011) Effect of crosslinker concentration on characteristics of superporous hydrogel. Int J Pharm Investig 1:17–21
Chen Y, Li W, Zhang S (2021) A multifunctional eco-friendly fertilizer used keratin-based superabsorbent as coatings for slow-release urea and remediation of contaminated soil. Prog Org Coat 154:106158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106158
Dai H, Zhang Y, Ma L, Zhang H, Huang H (2019) Synthesis and response of pineapple peel carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly (acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/graphene oxide hydrogels. Carbohyd Polym 215:366–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.03.090
Fang L, Catchmark JM (2014) Structure characterization of native cellulose during dehydration and rehydration. Cellulose 21:3951–3963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0435-8
Fang S, Wang G, Li P, Xing R, Liu S, Qin Y, Yu H, Chen X, Li K (2018) Synthesis of chitosan derivative graft acrylic acid superabsorbent polymers and its application as water retaining agent. Int J Biol Macromol 115:754–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.072
Fang S, Wang G, Xing R, Chen X, Liu S, Qin Y, Li K, Wang X, Li R, Li P (2019) Synthesis of superabsorbent polymers based on chitosan derivative graft acrylic acid-co-acrylamide and its property testing. Int J Biol Macromol 132:575–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.176
Ganji F, Vasheghani-Farahani S, Vasheghani-Farahani E (2010) Theoretical description of hydrogel swelling. a review. Iran Polym J 19:375–398
Haseeb MT, Hussain MA, Yuk SH, Bashir S, Nauman M (2016) Polysaccharides based superabsorbent hydrogel from Linseed: Dynamic swelling, stimuli responsive on–off switching and drug release. Carbohyd Polym 136:750–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.092
Hatakeyama T, Hatakeyama H (2004) Thermal properties of green polymers and biocomposites, vol 4. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordeht
Ho Y, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Hosseinzadeh H (2010) Controlled release of diclofenac sodium from pH-responsive carrageenan-g-poly(acrylic acid) superabsorbent hydrogel. J Chem Sci 122:651–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-010-0100-1
Jeong D, Joo S-W, Hu Y, Shinde VV, Cho E, Jung S (2018) Carboxymethyl cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels containing carboxymehtyl β-cyclodextrin for enhanced mechanical strength and effective drug delivery. Eur Polym J 105:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.05.023
Jeong D, Kim C, Kim Y, Jung S (2020) Dual crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylamide interpenetrating hydrogels with highly enhanced mechanical strength and superabsorbent properties. Eur Polym J 27:109586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109586
Khan S, Ranjha NM (2014) Effect of degree of cross-linking on swelling and on drug release of low viscous chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Polym Bull 7:2133–2158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1178-2
Khan H, Chaudhary JP, Meena R (2019) Anionic carboxymethylagarose-based pH-responsive smart superabsorbent hydrogels for controlled release of anticancer drug. Int J Biol Macromol 124:1220–1229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.045
Khushbu WSG, Kumar A (2019) Synthesis and assessment of carboxymethyl tamarind kernel gum based novel superabsorbent hydrogels for agricultural applications. Polymer 182:121823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121823
Kim B, Flamme KL, Peppas NA (2003) Dynamic swelling behaviour of pH-sensitive anionic hydrogels used for protein delivery. J Appl Polym Sci 89:1606–1613. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.12337
Lacoste C, Lopez-Cuesta J-M, Bergeret A (2019) Development of a biobased superabsorbant polymer from recycled cellulose for diapers applications. Eur Polym J 116:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.03.013
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens, Handlingar 24:1–39
Li S, Chen G (2019) Agricultural waste-derived superabsorbent hydrogels: preparation, performance, and socioeconomic impacts. J Clean Prod 251:119669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119669
Lin S-Y, Chen K-S, Run-Chu L (2000) Organic esters of plasticizers affecting the water absorption, adhesive property, glass transition temperature and plasticizer permanence of Eudragit acrylic films. J Control Release 68:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(00)00259-5
Liu X, Luan S, Li W (2019) Utilization of waste hemicelluloses lye for superabsorbent hydrogel synthesis. Int J Biol Macromol 132:954–962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.041
Lv X, Zhang W, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Hou M (2018) Hygroscopicity modulation of hydrogels based on carboxymethyl chitosan/Alginate polyelectrolyte complexes and its application as pH-sensitive delivery system. Carbohyd Polym 198:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.058
Mahon R, Balogun Y, Oluyemi G, Njuguna J (2020) Swelling performance of sodium polyacrylate and poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) potassium salt. SN Appl Sci 2:117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1874-5
Mehta P, Kaith BS (2021) Green synthesis of agar/gelatin based superabsorbent (BGCP) through gamma radiation cross-linking polymerization for castoff as sustained drug delivery device and in soil treatment for improved water retention. J Polym Environ 29:647–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01894-6
Mignon A, De Belie N, Dubruel P, Van Vlierberghe S (2019) Superabsorbent polymers: a review on the characteristics and applications of synthetic, polysaccharide-based, semi-synthetic and “smart” derivatives. Eur Polym J 117:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.04.054
Peppas NA, Brannon-Peppas L (1994) Water diffusion and sorption in amorphous macromolecular systems and foods. J Food Eng 22:189–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-85861-037-5.50015-1
Peppas NA, Khare AR (1993) Preparation, structure and diffusional behavior of hydrogels in controlled release. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 11:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-409X(93)90025-Y
Pourjavadi A, Ebrahimi AA, Barzegar S (2013) Preparation and evaluation of bioactive and compatible starch based superabsorbent for oral drug delivery systems. J Drug Del Sci Tech 23:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1773-2247(13)50074-8
Qureshi MA, Nishat N, Jadou S, Ansari MZ (2020) Polysaccharide based superabsorbent hydrogels and their methods of synthesis: a review. Carbohyd Polym Technol App 1:100014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2020.100014
Ravishankar K, Dhamodharan R (2020) Advances in chitosan-based hydrogels: evolution from covalently crosslinked systems to ionotropically crosslinked superabsorbents. React Funct Polym 149:104517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104517
Reshma G, Reshmi CR, Nair SV, Menon D (2020) Superabsorbent sodium carboxymethyl cellulose membranes based on a new cross-linker combination for female sanitary napkin applications. Carbohyd Polym 248:116763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116763
Saha A, Sekharan S, Manna U (2020) Superabsorbent hydrogel (SAH) as a soil amendment for drought management: A review. Soil till Res 204:104736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104736
Salleh KM, Zakaria S, Shaiful Sajab M, Gan S, Kaco H (2019) Superabsorbent hydrogel from oil palm empty fruit bunch cellulose and sodium carboxymethylcellulose. Int J Biol Macromol 131:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.028
Samadian H, Maleki H, Allahyari Z, Jaymand M (2020) Natural polymers-based light-induced hydrogels: promising biomaterials for biomedical applications. Coord Chem Rev 420:213432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213432
Seetapan N, Wongsawaeng J, Kiatkamjornwong S (2011) Gel strength and swelling of acrylamide-protic acid superabsorbent copolymers. Polym Adv Technol 22:1685–1695. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1658
Shatalov GV, Lavlinskaya MS, Pakhomova OA, Mokshina NY, Kuznetsov VA (2016) Copolymers of N-vinylcaprolactam with 1-vinyl- and 1-methacryloyl-3,5-dimethylpyrazole as sorbents of essential α-amino acids in liquid- and solid-phase extraction. Rus J Appl Chem 89:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1070427216010225
Singh J, Dhaliwal AS (2018) Synthesis, characterization and swelling behavior of silver nanoparticles containing superabsorbent based on grafted copolymer of polyacrylic acid/ Guar gum. Vacuum 157:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.08.017
Sorokin A, Lavlinskaya M (2021) Synthesis of the superabsorbents enriched in chitosan derivatives with excellent water absorption properties. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03521-9
Suo A, Qian J, Yao Y, Zhang W (2006) Synthesis and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose-graft-poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) as a novel cellulose-based superabsorbent. J App Polym Sci 103:1382–1388. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.23948
Vieira MGA, da Silva MA, dos Santos LO, Beppu MM (2011) Natural-based plasticizers and biopolymer films: a review. Eur Polym J 47:254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2010.12.011
Wang Z, Ning A, Xie P, Gao G, Xie L, Li X, Song A (2017) Synthesis and swelling behaviors of carboxymethyl cellulose-based superabsorbent resin hybridized with graphene oxide. Carbohyd Polym 157:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.09.070
Wei Q, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Chai W, Yang M, Zeng W, Wang M (2015) Study of the effects of water content and temperature on polyacrylamide/polyvinyl alcohol interpenetrating network hydrogel performance by a molecular dynamics method. E-Polymers 15(5):301–309. https://doi.org/10.1515/epoly-2015-0087
Wypych G (2017) Handbook of plasticizers, 3rd edn. ChemTec Publishing, Toronto
Acknowledgments
FTIR, SEM, HPLC-MS, and XRD data were obtained with the use of equipment of the Research Core Centre of Voronezh State University. DSC data were obtained with the use of equipment of the Research Core Centre of Voronezh State University of Engineering Technologies. Special thanks to Dr. Alexander Sinelnikov and Dr. Alexey Dontsov for their help with obtaining and interpretation of the XRD data.
Funding
The research was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project number 21–74-20053 (FTIR, SEM, HPLC–MS, and XRD research), and by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation in the framework of the national project “Science” (project FZGW-2020–0001, unique number of the register of State tasks 075001X39782002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorokin, A., Sukhanov, P., Popov, V. et al. A new approach to increasing the equilibrium swelling ratio of the composite superabsorbents based on carboxymethyl cellulose sodium salt. Cellulose 29, 159–173 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04326-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04326-3