Abstract
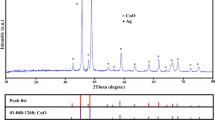
Herein we present facile and green two-steps method for the fabrication of silver-carboxylated nanocellulose (Ag-ONCs) nanocomposite. Respecting the Circular Economy principle, the ONCs are prepared starting from the treatment of agriculture bagasse waste with ammonium persulfate—APS. This method permits to obtain ONCs fibers with rod or whisker shapes, with size and length in the range 6–10 nm and 90–150 nm, respectively. Ag-ONCs are then fabricated using a green photochemical approach. The UV irradiation works as radical initiator for the silver reduction, in water solution and at room temperature. The ONCs act as a template and reducing agent for silver nanoparticles formation, due to the specific hydroxyl and carboxyl groups on the cellulose surface. The structural and morphological properties of ONCs and Ag-ONCs nanocomposite are well evaluated by FT-IR, XRD, UV–Vis, AFM, SEM and TEM characterizations. The results showed that well crystalline, quasi-spherical silver nanoparticles of about 4–10 nm dispersed in the ONCs matrix are fabricated. Qualitative antibacterial tests towards gram negative (Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and gram positive (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis) bacteria are carried out and the results demonstrated that the Ag-ONCs inhibit the bacteria growth, with 12–14 mm of inhibition zone for both the bacteria groups. Also, quantitative antibacterial tests for E. coli, chosen as representative for its diffusion, are carried out and the bacteria growth rate and the inhibition rate for Ag-ONCs at different concentrations are evaluated. The analysis showed that the MIC (minimum inhibition concentration) for Ag is about 110 µg/mL for E. coli. These results demonstrated that the Ag-ONCs possess suitable and promising antibacterial behavior and could be used for industrial and technological application.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu AS, Oliveira M, Sá A, Rodrigues RM, Cerqueira MA, Vicente AA, Machado AV (2015) Antimicrobial nanostructured starch based films for packaging. Carbohydr Polym 129(20):127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.04.021
Adel AM, El-Wahab ZHA, Ibrahim AA, Al-Shemy MT (2010) Characterization of microcrystalline cellulose prepared from lignocellulosic materials. Part I: Acid catalyzed hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 101:124446–124455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.047
Adel AM, Ahmed EO, Ibrahim MM, El-Zawawy WK, Dufresne A (2016a) Microfibrillated cellulose from agricultural residues. Part II: Strategic evaluation and market analysis for MFCE30. Ind Crops Prod 93:175–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.042
Adel MA, El-Gendy AA, Mohamed DA, Abou-Zeid RE, El-Zawawy WK, Dufresne A (2016b) Microfibrillated cellulose from agricultural residues. Part I: Papermaking application. Ind Crops Prod 93:161–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.043
Adel AM, El-Shafei A, Al-Shemy MT, Ibrahim A, Rabia A (2017) Influence of cellulose polymorphism on tunable mechanical and barrier properties of chitosan/oxidized nanocellulose bio-composites. Egypt J Chem 60(4):639–652. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2017.1194.1062
Adel AM, El-Shafei A, Ibrahim A, Al-Shemy MT (2018) Extraction of oxidized nanocellulose from date palm (Phoenix Dactylifera L.) sheath fibers: influence of CI and CII polymorphs on the properties of chitosan/bionanocomposite films. Ind Crops Prod 124:155–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.07.073
Atef AI, Adel AM, Abd El-Wahab ZH, Al-Shemy MT (2011) Utilization of carboxymethyl cellulose based on bean hulls as chelating agent. Synthesis, characterization and biological activity. Carbohydr Polym 83(1):94–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.07.026
Bejoy T, Midhun CR, Athira KB, Rubiyah MH, Jithin J, Moores A, Drisko GL, Sanchez C (2018) Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: from biosources to materials and their applications. Chem Rev 118(24):11575–11625. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00627
Berndt S, Wesarg F, Wiegand C, Kralisch D, Müller FA (2013) Antimicrobial porous hybrids consisting of bacterial nanocellulose and silver nanoparticles. Cellulose 20:771–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9870-1
Bondeson D, Mathew A, Oksman K (2006) Optimization of the isolation of nanocrystals from microcrystalline cellulose by acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 13(2):171–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-006-9061-4
Caschera D, Federici F, Focanti F, Curulli A, Zane D, Padeletti G (2009) Gold nanoparticles-modified GC electrodes: electrochemical behaviour dependence of different neurotransmitters and molecules of biological interest on the size and the shape of the particles. J Nanopart Res 11:1925–1936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9547-0
Cheng M, Qin Z, Liu Y, Qin Y, Li T, Chen L, Zhua M (2014) Efficient extraction of carboxylated spherical cellulose nanocrystals with narrow distribution through hydrolysis of lyocell fibers by using ammonium persulfate as an oxidant. J Mater Chem A 2(1):251–258. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA13653A
Coronato CL, de Oliveira R, Silva F, Gomes L (2007) A simple method to synthesize silver nanoparticles by photo-reduction. Colloid Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 305:54–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.04.052
Di Carlo G, Curulli A, Toro RG, Bianchini C, de Caro T, Padeletti G, Zane D, Ingo GM (2012) Green synthesis of gold-chitosan nanocomposites for caffeic acid sensing. Langmuir 28:5471–5479. https://doi.org/10.1021/la204924d
Drogat N, Granet R, Sol V, Memmi A, Saad N, Klein KC, Bressollier P, Krausz P (2011) Antimicrobial silver nanoparticles generated on cellulose nanocrystals. J Nanopart Res 13:1557–1562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9995-1
Dufresne A (2017) Nanocellulose: from nature to high performance tailored materials. Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co, Berlin
El-Wakil NA, Hassan EA, Abou-Zeid RE, Dufresne A (2015) Development of wheat gluten/nanocellulose/titanium dioxide nanocomposites for active food packaging. Carbohydr Polym 124:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.01.076
Emam H, Ahmed H (2016) Polysaccharides templates for assembly of nanosilver. Carbohydr Polym 135:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.08.095
Errokh A, Magnin A, Putaux J-L, Boufi S (2019) Hybrid nanocellulose decorated with silver nanoparticles as reinforcing filler with antibacterial properties. Mater Sci Eng C 105:110044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110044
Esmat M, Farghali AA, Khedr MH, El-Sherbiny IM (2017) Alginate-based nanocomposites for efficient removal of heavy metal ions. Int J Biol Macromol 102:272–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.021
Feng J, Shi Q, Li W, Shu X, Chen A, Xie X, Huang X (2014) Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles in situ growth on TEMPO-mediated oxidized bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 21:4557–4567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0449-2
Fortunati E, Rinaldi S, Peltzer M, Bloise N, Visai L, Armentano I, Jiménez A, Latterini L, Kenny JM (2014) Nano-biocomposite films with modified cellulose nanocrystals and synthesized silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 101(1):1122–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.055
García A, Labidi J, Belgacem MN, Bras J (2017) The nanocellulose biorefinery: woody versus herbaceous agricultural wastes for NCC production. Cellulose 24:693–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1144-2
Habibi Y (2014) Key advances in the chemical modification of nanocelluloses. Chem Soc Rev 43(5):1519–1542. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60204D
Habibi Y, Chanzy H, Vignon MR (2006) TEMPO-mediated surface oxidation of cellulose whiskers. Cellulose 13(6):679–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1319-5
Harada M, Katagiri E (2010) Mechanism of silver particle formation during photoreduction using in situ time-resolved SAXS analysis. Langmuir 26(23):17896–17905. https://doi.org/10.1021/la102705h
He J, Kunitake T, Nakao A (2003) Facile in situ synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles in porous cellulose fibers. Chem Mater 15(23):4401–4406. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm034720r
Hebeish A, El-Rafie M, Abdel-Mohdy F, Abdel-Halim E, Emam H (2010) Carboxymethyl cellulose for green synthesis and stabilization of silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 82:933–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.06.020
Hebeish A, Farag S, Sharaf S, Shaheen TI (2015) Nanosized carbamoylethylated cellulose as novel precursor for preparation of metal nanoparticles. Fibers Polym 16(2):276–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-015-0276-6
Henglein A, Giersing M (1999) Formation of colloidal silver nanoparticles: capping action of citrate. J Phys Chem B 103:9533–9539. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9925334
Herreros-López A, Hadad C, Yate L, Alshatwi AA, Vicentini N, Carofiglio T, Prato M (2016) Synthesis and catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles supported on dendrimeric nanocellulose hybrids. Eur J Org Chem 19:3186–3192. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201600148
Hu H, Wu X, Wang H, Wang H, Zhou J (2019) Photo-reduction of Ag nanoparticles by using cellulose-based micelles as soft templates: catalytic and antimicrobial activities. Carbohydr Polym 213:419–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.062
Huang J, Dufresne A, Lin N (2019) Nanocellulose: from fundamentals to advanced materials. Wiley, Hobken
Ifuku S, Tsuji M, Morimoto M, Saimoto H, Yano H (2009) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles templated by TEMPO-mediated oxidized bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Biomacromol 10(9):2714–2717. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm9006979
Jacob J, Haponiuk JT, Thomas S, Gopi S (2018) Biopolymer based nanomaterials in drug delivery systems: a review. Mater Today Chem 9:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2018.05.002
Jeong L, Park WH (2014) Preparation and characterization of gelatin nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 15:6857–6879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046857
Jiao L, Li Q, Deng J, Okosi N, Xia J, Su M (2018) Nanocellulose templated growth of ultra-small bismuth nanoparticles for enhanced radiation therapy. Nanoscale 10:6751–6757. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR06462D
Kargarzadeh H, Mariano M, Gopakumar D, Ahmad I, Thomas S, Dufresne A, Huang J, Lin N (2018) Advances in cellulose nanomaterials. Cellulose 25(4):2151–2189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1723-5
Kaushik M, Moores A (2016) Review: nanocelluloses as versatile supports for metal nanoparticles and their applications in catalysis. Green Chem 18(3):622–637. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC02500A
Kitahama Y, Ikemachi T, Suzuki T, Miura T, Ozaki Y (2014) Plasmonic properties of triangle-shaped silver trimers selectively fabricated by near-field photo-reduction using an apertured cantilever for an atomic force microscope. Chem Commun 50:9693–9696. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC04230A
Kumar S, Mukherjee A, Dutta J (2020) Chitosan based nanocomposite films and coatings: emerging antimicrobial food packaging alternatives. Trends Food Sci Technol 97:196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.002
Leung ACW, Hrapovic S, Lam E, Liu Y, Male KB, Mahmoud KA, Luong JHT (2011) Characteristics and properties of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals prepared from a novel one-step procedure. Small 7(3):302–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201001715
Li R, He M, Li T, Zhang L (2015) Preparation and properties of cellulose/silver nanocomposite fibers. Carbohydr Polym 115:269–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.046
Mariano M, El Kissi N, Dufresne A (2014) Cellulose nanocrystals and related nanocomposites: review of some properties and challenges. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 52(12):791–806. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.23490
Martínez-Castañón GA, Niño-Martínez N, Martínez-Gutierrez F, Martínez-Mendoza JR, Ruiz F (2008) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J Nanopart Res 10(8):1343–1348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9428-6
Matar MJ, Ostrosky-Zeichner L, Paetznick VL, Rodriguez JR, Chen E, Rex JH (2003) Correlation between E-test, disk diffusion, and microdilution methods for antifungal susceptibility testing of fluconazole and voriconazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:1647–1651. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.47.5.1647-1651.2003
Mohandas A, Raja SD, Jayakumar BR (2018) Chitosan based metallic nanocomposite scaffolds as antimicrobial wound dressings. Bioact Mater 3(3):267–277
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00108B
Pal S, Nisi R, Stoppa M, Licciulli A (2017) Silver-functionalized bacterial cellulose as antibacterial membrane for wound-healing applications. ACS Omega 2(7):3632–3639. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b00442
Rehan M, Mashaly HM, Mowafi S, Bou E-KA, Emam HE (2015) Multi-functional textile design using in situ Ag NPs incorporation into natural fabric matrix. Dyes Pigment 118:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2015.02.021
Rehan M, Barhoum A, Van Assche G, Dufresne A, Gatjen L, Wilken R (2017) Towards multifunctional cellulosic fabric: UV photo reduction and in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles into cellulosic fabrics. Int J Biol Macromol 98:877–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.02.058
Ruparelia JP, Chatterjee AK, Duttagupta SP, Mukherji S (2008) Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomater 4:707–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2007.11.006
Sakai H, Kanada T, Shibata H, Ohkubo T, Abe M (2006) Preparation of highly dispersed core/shell-type titania nanocapsules containing a single Ag nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 128:4944–4945. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja058083c
Sangeetha J, Thangadurai D, Hospet R, Purushotham P, Manowade KR, Mujeeb MA, Mundaragi AC, Jogaiah S, David M, Thimmappa SC, Prasad R, Harish ER (2017) Production of bionanomaterials from agricultural wastes. In: Prasad R, Kumar M, Kumar V (eds) Nanotechnology. Springer, Singapore, pp 33–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4573-8_3
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE Jr, Conrad CMC (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Shaheen TI, Fouda A (2018) Green approach for one-pot synthesys of silver nanorods using cellulose nanocrystal and their cytoxicity and antibacterial assessment. Int J Biol Macromol 106:784–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.070
Shankar S, Rhim JW (2016) Preparation of nanocellulose from micro-crystalline cellulose: the effect on the performance and properties of agar-based composite films. Carbohydr Polym 135:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.08.082
Shankar S, Oun AA, Rhim J-W (2018) Preparation of antimicrobial hybrid nano-materials using regenerated cellulose and metallic nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 107:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.129
Sharma VK, Yngard RA, Lin Y (2009) Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 145(1):283–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2008.09.002
Suber L, Imperatori P, Pilloni L, Caschera D, Angelini N, Mezzi A, Kaciulis S, Iadecola A, Joseph B, Campi G (2018) Nanocluster superstructures or nanoparticles? The self-consuming scaffold decides. Nanoscale 10:7472–7483. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr09520a
Tang J, Sisler J, Grishkewich N, Tam KC (2017) Functionalization of cellulose nanocystals for advanced applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 494:397–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.077
Toro RG, Diab M, de Caro T, Al-Shemy M, Adel A, Caschera D (2020) Study of the effect of titanium dioxide hydrosol on the photocatalytic and mechanical properties of paper sheets. Materials 13:1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061326
Van Hyning D, Klemperer W, Zucoski C (2001) Silver nanoparticles formation: prediction and verification of the aggregative growth model. Langmuir 17:3128–3135. https://doi.org/10.1021/la000856h
Vu ND, Tran HT, Bui ND, Vu CD, Nguyen HV (2017) Lignin and cellulose extraction from Vietnam’s rice straw using ultrasound-assisted alkaline treatment method. Int J Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1063695
Xiong R, Grant AM, Ma R, Zhang S, Tsukruk VV (2018) Naturally-derived biopolymer nanocomposites: interfacial design, properties and emerging applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 125:1–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2018.01.002
Xu Q, Jin L, Wang Y, Chen H, Qin M (2019) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dialdehyde cellulose nanocrystal as a multi-functional agent and application to antibacterial paper. Cellulose 26:1309–1321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2118-3
Xue Y, Mou Z, Xiao H (2017) Nanocellulose as a sustainable biomass material: structure, properties, present status and future prospects in biomedical applications. Nanoscale 9:14758–14781. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR04994C
Yang G, Yao Y, Wang C (2017) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles impregnated bacterial cellulose-alginate composite film with improved properties. Mater Lett 209:11–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.07.097
Yu H-Y, Qin Z-Y, Sun B, Feng Yan C, Yao J-M (2014) One-pot green fabrication and antibacterial activity of thermally stable corn-like CNC/Ag nanocomposites. J Nanopart Res 16:2202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2202-4
Zhang X, Sun H, Tan S, Gao J, Fu Y, Liu Z (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis of Ag nanoparticles on the nanocellulose and their antibacterial study. Inorg Chem Commun 100:44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2018.12.012
Zinge C, Kandasubramanian B (2020) Nanocellulose based biodegradable polymers. Eur Polymer J 133:109758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109758
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. Luciana Cerri for her technical assistance in AFM analysis, Marianna Barbalinardo for SEM measurements and Mr. Claudio Veroli for the XRD measurements. The activities have been performed in the framework of the Joint Bilateral Agreement CNR/NRC (Italy/Egypt), Biennial Programme 2018–2019, for the project “Improvement of mechanical and barrier properties of biopolymer nano-composites for packaging applications”.
Funding
The activities have been performed in the framework of the Joint Bilateral Agreement CNR/NRC (Italy/Egypt), Biennial Programme 2018–2019, for the project “Improvement of mechanical and barrier properties of biopolymer nano-composites for packaging applications”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DC: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing-original draft, visualization, funding acquisition. AMA: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing-review and editing, funding acquisition. RGT: investigation, validation, writing-review and editing. TC: investigation, validation. FF: investigation. RM: investigation, validation. MTA: methodology, investigation, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of inertest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caschera, D., Toro, R.G., Federici, F. et al. Green approach for the fabrication of silver-oxidized cellulose nanocomposite with antibacterial properties. Cellulose 27, 8059–8073 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03364-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03364-7