Abstract
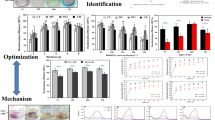
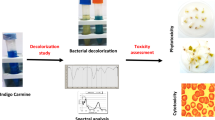
The textile industry is a leading contributor to water pollution. Therefore, there is a need for economic and environmental efforts to manage the textile industry’s wastewater. The present study used five bacterial strains, isolated from various Tunisian biotopes, to be characterized and screened for Congo Red (CR) decolorization, for the first time. Firstly, the isolated strains were subjected to standard cultural, microscopically, biochemical, antibiotic susceptibility and biofilm formation assays. The strain ST9 was partially identified as Bacillus spp. strain ST9. Secondly, the newly bacterial isolates crude filtrates were able to decolorize CR, generally recalcitrant to biodegradation due to its xenobiotic nature. Thus, only SM2 and ST9 strains prove their effectiveness for CR (150 mg L−1) total degradation. More than 5.5 mg L−1 h−1 of CR could be decolorized using ST9 filtrate under non-optimized conditions. UV–Visible and FT–IR analysis showed a decolorization and/or a transformation of CR, proving the role of the enzyme in dye decolorization. In fact, the azo dyes degradation was confirmed by the disparition of the characteristic peak at 499 nm and of the peaks located in the range 1610–1630 cm−1 and at 1600 cm−1 due to the azo bonds and the characteristic C=C band of the aromatic ring of CR, respectively. Combinning FTIR and UV–Vis spectra confirms the CR degradation using only SM2 and ST9 filtrates. The results showed CR has been degraded into nontoxic compounds evaluated by (1) phytotoxic assay on tomato, radish and watercress, and (2) cyto-toxicity assay in Vero cells. Furthermore, toxicity studies observed that the by-products from degradation by SM1 crude filtrate was not toxic to plants and less toxic to Vero cells as compared to pure CR. This work reported on the biodegradation of CR by bacterial crude filtrates, as green biocatalysts, which could be a potential candidate for the removal and detoxication of CR from textile wastewater.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benkhaya S, El Harfi S, El Harfi A (2017) Appl J Envir Eng Sci 3:311–320
Bruma A, Ramli I, Paz-Borbón LO et al (2013) Nanoscale 5:646–652
Ballay D, Blais JF (1998) Rev Sci Eau 77:86
Nevine KA (2008) Desalination 223:152–161
Rodriguez A, Garcia J, Ovejerog G et al (2009) J Hazard Mater 172:1311–1320
Talha AM, Goswami M, Giri BS et al (2018) Bioresour Technol 252:37–43
Lade H, Govindwar S, Paul D (2015) Int J Environ Res Pub Health 12:6894–6918
Shalini Y, Setty P (2019) Biochem Eng J 152:107368
Bharti V, Vikrant K, Goswami M et al (2019) Environ Res 171:356–364
Ben Younes S, Dallali C, Ellafi A et al (2020) Catal Lett 151:1248–1261
Fernanda M, Munari A, Tamara A et al (2008) World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1383–1392
Ajaz M, Shakeel S, Rehman A (2020) Int Microbiol 23:149–159
Bartholomew JW, Mittwer T (1952) Bacteriol. Rev Mar 16:1–29
Winker S, Woese CR (1991) Syst Appl Microbiol 14(1991):305–310
Hall TA (1999) Nucleic Acids Symposium Series. Information Retrieval Ltd., London, pp 95–98
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) Mol Biol Evol 38:3022–3027
Taieb I, Ben Younes S, Messai B et al (2021) Sustainability 13:10072–10090
Freeman DJ, Falkiner FR, Keane CT (1989) J Clin Pathol 42:872–874
Ben Abdallah F, Chaieb K, Zmantar T et al (2009) Braz J Microbiol 40:394–398
Chaieb K, Chehab O, Zmantar T et al (2007) Ann Microbiol 57:431–437
Sun Y, Wang W, Zheng F et al (2020) Chemosphere 251:126432
Huang WY, Lee MS, Lin LM et al (2020) Pediatr Neonatol 61:420–425
Ben Younes S, Bouallagui Z, Sayadi S (2012) J Mol Catal B Enzym 79:41–48
Ayandele AA, Oladipo EK, Oyebisi O et al (2020) Qatar Med J 2020:9–15
Dever LA, Dermody TS (1991) Arch Intern Med 151:886–895
Ophir T, Gutnick DL (1994) Appl Environ Microbiol 60:740–745
Milanov D, Lazi S, Vidi B et al (2010) Acta Veterinaria (Beograd) 60:217–226
Hamadi NK, Swaminathan S, Chen XD (2004) J Hazard Mater 112:133–141
Snoussi M, Noumi E, Cheriaa J et al (2008) New Microbiol 31:489–500
Donlan RM, Costerton JW (2002) Clin Microbiol Rev 15:167–193
Victor H, Ganda V, Kiranadi B, et al (2020) KnE Life Sciences 5:102–110
Rashmi M, Savitha K (2012) The IUP Journal of Genetics & Evolution 5:53–62
Ben Younes S, Cherif I, Dhouib A et al (2016) Catal Lett 146:204–211
Ben Mansour H, Boughzala O, Barillier D et al (2011) J Wat Sci 24:209–238
Abo-State MAM, Saleh YE, Hazaa HA (2017) J Eco Heal Env 5:41–48
Raj DS, Prabha RJ, Leena R (2012) J Ind Pollut Control 28:57–62
Sundarajoo A, Maniyam MN (2019) J Adv Res Design 62:1–9
Sundarajoo A, Maniyam MN, Azman HH et al (2022) Int J Environ Sci Technol 19:3305–3322
Al-Ansari MM, Li Z, Masood A et al (2022) Environ Res 205:112189–112198
Franciscon E, Zille A, Dias GF et al (2009) Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:280–288
Al-Thabaiti SA, Shafik Aazam E, Khan Z et al (2016) Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 156:28–35
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Chang JS et al (2009) J Hazard Mater 166:1421–1428
Bhoi YP, Pradhan SR, Behera C et al (2016) RSC Adv 6:35589–35601
Roy DC, Biswas SK, Sheam MM et al (2020) CRMICR 1:37–43
Franciscon E, Zille A, Dias GF et al (2009) Int Biodeter Biodegrad 63:280–288
Yamaki J, Takatsuji H, Kawamura T et al (2002) Solid State ion 148:241–245
Bartosova A, Blinova L, Sirotiak M et al (2017). Res Papers Faculty Mater Sci Technol Slovak Univ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1515/rput-2017-0012
Acemioglu B (2004) J Colloid Interf Sci 274:371–379
Gavril M, Hodson PV (2007) World J Microb Biot 23:103–124
Wesenberg D, Spiros IK, Agathos N (2003) Biotech Adv 22:161–187
Vignesh A, Manigundan K, Santhoshkumar J et al (2020) Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43:1457–1468
Singh PK, Singh RL (2017) Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 5:108–126
Brzozowska J, Hanower P (1976) Ann l’Univ d’Abidjan Sér C Sci Tome XII 1976:65–87
Ben Younes S, Karray F, Sayadi S (2011) Int Biodeter Biodegr 65:1104–1109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ellafi, A., Dali, A., Mnif, S. et al. Microbial Enzymatic Degradation, Spectral Analysis and Phytotoxicity Assessment of Congo Red Removal By Bacillus spp.. Catal Lett 153, 3620–3633 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-023-04272-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-023-04272-8