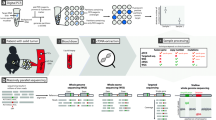
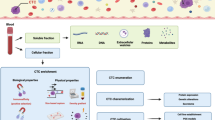
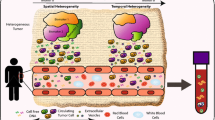
Abstract
Pediatric solid tumors have long been known to shed tumor cells, DNA, RNA, and proteins into the blood. Recent technological advances have allowed for improved capture and analysis of these typically scant circulating materials. Efforts are ongoing to develop “liquid biopsy” assays as minimally invasive tools to address diagnostic, prognostic, and disease monitoring needs in childhood cancer care. Applying these highly sensitive technologies to serial liquid biopsies is expected to advance understanding of tumor biology, heterogeneity, and evolution over the course of therapy, thus opening new avenues for personalized therapy. In this review, we outline the latest technologies available for liquid biopsies and describe the methods, pitfalls, and benefits of the assays that are being developed for children with extracranial solid tumors. We discuss what has been learned in several of the most common pediatric solid tumors including neuroblastoma, sarcoma, Wilms tumor, and hepatoblastoma and highlight promising future directions for the field.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tomasetti, C., Li, L., & Vogelstein, B. (2017). Stem cell divisions, somatic mutations, cancer etiology, and cancer prevention. Science, 355(6331), 1330–1334. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf9011.
Applebaum, M. A., Vaksman, Z., Lee, S. M., Hungate, E. A., Henderson, T. O., London, W. B., et al. (2017). Neuroblastoma survivors are at increased risk for second malignancies: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group Project. European Journal of Cancer, 72, 177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2016.11.022.
Ginsberg, J. P., Goodman, P., Leisenring, W., Ness, K. K., Meyers, P. A., Wolden, S. L., et al. (2010). Long-term survivors of childhood Ewing sarcoma: report from the childhood cancer survivor study. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 102(16), 1272–1283. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djq278.
Oeffinger, K. C., & Bhatia, S. (2009). Second primary cancers in survivors of childhood cancer. Lancet, 374(9700), 1484–1485. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61885-7.
Oeffinger, K. C., Mertens, A. C., Sklar, C. A., Kawashima, T., Hudson, M. M., Meadows, A. T., et al. (2006). Chronic health conditions in adult survivors of childhood cancer. The New England Journal of Medicine, 355(15), 1572–1582. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa060185.
Kirchhoff, A. C., Nipp, R., Warner, E. L., Kuhlthau, K., Leisenring, W. M., Donelan, K., et al. (2018). "Job Lock" Among Long-term Survivors of Childhood Cancer: a report from the childhood cancer survivor study. JAMA Oncology, 4(5), 707–711. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3372.
Nagarajan, R., Kamruzzaman, A., Ness, K. K., Marchese, V. G., Sklar, C., Mertens, A., et al. (2011). Twenty years of follow-up of survivors of childhood osteosarcoma: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Cancer, 117(3), 625–634. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25446.
Termuhlen, A. M., Tersak, J. M., Liu, Q., Yasui, Y., Stovall, M., Weathers, R., et al. (2011). Twenty-five year follow-up of childhood Wilms tumor: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 57(7), 1210–1216. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.23090.
Zheng, D. J., Krull, K. R., Chen, Y., Diller, L., Yasui, Y., Leisenring, W., et al. (2018). Long-term psychological and educational outcomes for survivors of neuroblastoma: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Cancer, 124(15), 3220–3230. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31379.
Cohn, S. L., Pearson, A. D., London, W. B., Monclair, T., Ambros, P. F., Brodeur, G. M., et al. (2009). The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) classification system: an INRG Task Force report. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(2), 289–297. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.16.6785.
Twist, C. J., Naranjo, A., Schmidt, M. L., Tenney, S. C., Cohn, S. L., Meany, H. J., et al. (2019). Defining Risk Factors for Chemotherapeutic Intervention in Infants With Stage 4S Neuroblastoma: a Report From Children's Oncology Group Study ANBL0531. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 37(2), 115–124. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.18.00419.
Dome, J. S., Perlman, E. J., & Graf, N. (2014). Risk stratification for wilms tumor: current approach and future directions. American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book, 215–223. https://doi.org/10.14694/EdBook_AM.2014.34.215.
Meyers, R. L., Maibach, R., Hiyama, E., Haberle, B., Krailo, M., Rangaswami, A., et al. (2017). Risk-stratified staging in paediatric hepatoblastoma: a unified analysis from the Children's Hepatic tumors International Collaboration. The Lancet Oncology, 18(1), 122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30598-8.
Harris, M. H., DuBois, S. G., Glade Bender, J. L., Kim, A., Crompton, B. D., Parker, E., et al. (2016). Multicenter Feasibility Study of Tumor Molecular Profiling to Inform Therapeutic Decisions in Advanced Pediatric Solid Tumors: the Individualized Cancer Therapy (iCat) Study. JAMA Oncology. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.5689.
Mody, R. J., Wu, Y. M., Lonigro, R. J., Cao, X., Roychowdhury, S., Vats, P., et al. (2015). Integrative Clinical Sequencing in the Management of Refractory or Relapsed Cancer in Youth. JAMA, 314(9), 913–925. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.10080.
Weiser, D. A., Kaste, S. C., Siegel, M. J., & Adamson, P. C. (2013). Imaging in childhood cancer: a Society for Pediatric Radiology and Children's Oncology Group Joint Task Force report. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 60(8), 1253–1260. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.24533.
Mandel, P., & Metais, P. (1948). Les acides nucleiques du plasma sanguin chez l'homme. Comptes Rendus des Seances de la Societe de Biologie et de Ses Filiales, 142(3-4), 241–243.
Wan, J. C. M., Massie, C., Garcia-Corbacho, J., Mouliere, F., Brenton, J. D., Caldas, C., et al. (2017). Liquid biopsies come of age: towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 17(4), 223–238. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.7.
Abbou, S. D., Shulman, D. S., DuBois, S. G., & Crompton, B. D. (2019). Assessment of circulating tumor DNA in pediatric solid tumors: the promise of liquid biopsies. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 66(5), e27595. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.27595.
Rossi, G., & Ignatiadis, M. (2019). Promises and Pitfalls of Using Liquid Biopsy for Precision Medicine. Cancer Research, 79(11), 2798–2804. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3402.
Grobner, S. N., Worst, B. C., Weischenfeldt, J., Buchhalter, I., Kleinheinz, K., Rudneva, V. A., et al. (2018). The landscape of genomic alterations across childhood cancers. Nature, 555(7696), 321–327. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25480.
Ashworth, T. R. (1869). A case of cancer in which cells similar to those in the tumours were seen in the blood after death. The Medical Journal of Australia, 14, 146–147.
Allard, W. J., Matera, J., Miller, M. C., Repollet, M., Connelly, M. C., Rao, C., et al. (2004). Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clinical Cancer Research, 10(20), 6897–6904. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0378.
Nagrath, S., Sequist, L. V., Maheswaran, S., Bell, D. W., Irimia, D., Ulkus, L., et al. (2007). Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature, 450(7173), 1235–1239. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06385.
Peterson, M. F., Otoc, N., Sethi, J. K., Gupta, A., & Antes, T. J. (2015). Integrated systems for exosome investigation. Methods, 87, 31–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.04.015.
Contreras-Naranjo, J. C., Wu, H. J., & Ugaz, V. M. (2017). Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: enabling liquid biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab on a Chip, 17(21), 3558–3577. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7lc00592j.
Jiang, N., Pan, J., Fang, S., Zhou, C., Han, Y., Chen, J., et al. (2019). Liquid biopsy: circulating exosomal long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Clinica Chimica Acta, 495, 331–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2019.04.082.
Whiteside, T. L. (2016). Tumor-Derived Exosomes and Their Role in Cancer Progression. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 74, 103–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acc.2015.12.005.
Kalluri, R. (2016). The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 126(4), 1208–1215. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI81135.
He, M., & Zeng, Y. (2016). Microfluidic Exosome Analysis toward Liquid Biopsy for Cancer. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 21(4), 599–608. https://doi.org/10.1177/2211068216651035.
Kowal, J., Tkach, M., & Thery, C. (2014). Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 29, 116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2014.05.004.
Melo, S. A., Luecke, L. B., Kahlert, C., Fernandez, A. F., Gammon, S. T., Kaye, J., et al. (2015). Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature, 523(7559), 177–182. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14581.
Esteller, M. (2007). Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modification maps. Nature Reviews. Genetics, 8(4), 286–298. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2005.
Wang, Z., Zang, C., Rosenfeld, J. A., Schones, D. E., Barski, A., Cuddapah, S., et al. (2008). Combinatorial patterns of histone acetylations and methylations in the human genome. Nature Genetics, 40(7), 897–903. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.154.
Xu, J., Zhang, X., Pelayo, R., Monestier, M., Ammollo, C. T., Semeraro, F., et al. (2009). Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nature Medicine, 15(11), 1318–1321. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2053.
Holdenrieder, S., Stieber, P., Bodenmuller, H., Busch, M., Fertig, G., Furst, H., et al. (2001). Nucleosomes in serum of patients with benign and malignant diseases. International Journal of Cancer, 95(2), 114–120. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0215(20010320)95:2<114::aid-ijc1020>3.0.co;2-q.
Kuroi, K., Tanaka, C., & Toi, M. (1999). Plasma Nucleosome Levels in Node-Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Breast Cancer, 6(4), 361–364.
Fahmueller, Y. N., Nagel, D., Hoffmann, R. T., Tatsch, K., Jakobs, T., Stieber, P., et al. (2012). Predictive and prognostic value of circulating nucleosomes and serum biomarkers in patients with metastasized colorectal cancer undergoing Selective Internal Radiation Therapy. BMC Cancer, 12, 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-12-5.
Schwarzenbach, H., Hoon, D. S., & Pantel, K. (2011). Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 11(6), 426–437. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3066.
Chen, X. Q., Stroun, M., Magnenat, J. L., Nicod, L. P., Kurt, A. M., Lyautey, J., et al. (1996). Microsatellite alterations in plasma DNA of small cell lung cancer patients. Nature Medicine, 2(9), 1033–1035. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0996-1033.
Nawroz, H., Koch, W., Anker, P., Stroun, M., & Sidransky, D. (1996). Microsatellite alterations in serum DNA of head and neck cancer patients. Nature Medicine, 2(9), 1035–1037. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0996-1035.
Lo, Y. M., Corbetta, N., Chamberlain, P. F., Rai, V., Sargent, I. L., Redman, C. W., et al. (1997). Presence of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum. Lancet, 350(9076), 485–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(97)02174-0.
Jahr, S., Hentze, H., Englisch, S., Hardt, D., Fackelmayer, F. O., Hesch, R. D., et al. (2001). DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Research, 61(4), 1659–1665.
Snyder, M. W., Kircher, M., Hill, A. J., Daza, R. M., & Shendure, J. (2016). Cell-free DNA Comprises an In Vivo Nucleosome Footprint that Informs Its Tissues-Of-Origin. Cell, 164(1-2), 57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.050.
Thierry, A. R., El Messaoudi, S., Gahan, P. B., Anker, P., & Stroun, M. (2016). Origins, structures, and functions of circulating DNA in oncology. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 35(3), 347–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-016-9629-x.
Diehl, F., Li, M., Dressman, D., He, Y., Shen, D., Szabo, S., et al. (2005). Detection and quantification of mutations in the plasma of patients with colorectal tumors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(45), 16368–16373. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507904102.
Stewart, C. M., & Tsui, D. W. Y. (2018). Circulating cell-free DNA for non-invasive cancer management. Cancer Genetics, 228-229, 169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cancergen.2018.02.005.
Diaz Jr., L. A., Williams, R. T., Wu, J., Kinde, I., Hecht, J. R., Berlin, J., et al. (2012). The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature, 486(7404), 537–540. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11219.
Murtaza, M., Dawson, S. J., Tsui, D. W., Gale, D., Forshew, T., Piskorz, A. M., et al. (2013). Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature, 497(7447), 108–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12065.
Kopreski, M. S., Benko, F. A., Kwak, L. W., & Gocke, C. D. (1999). Detection of tumor messenger RNA in the serum of patients with malignant melanoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 5(8), 1961–1965.
Reis, E. M., & Verjovski-Almeida, S. (2012). Perspectives of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer Diagnostics. Frontiers in Genetics, 3, 32. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2012.00032.
Qi, P., Zhou, X. Y., & Du, X. (2016). Circulating long non-coding RNAs in cancer: current status and future perspectives. Molecular Cancer, 15(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-016-0524-4.
Reid, G., Kirschner, M. B., & van Zandwijk, N. (2011). Circulating microRNAs: association with disease and potential use as biomarkers. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology, 80(2), 193–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2010.11.004.
Vickers, K. C., Palmisano, B. T., Shoucri, B. M., Shamburek, R. D., & Remaley, A. T. (2011). MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nature Cell Biology, 13(4), 423–433. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2210.
Arroyo, J. D., Chevillet, J. R., Kroh, E. M., Ruf, I. K., Pritchard, C. C., Gibson, D. F., et al. (2011). Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(12), 5003–5008. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1019055108.
Miller, M. C., Doyle, G. V., & Terstappen, L. W. (2010). Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells Detected by the CellSearch System in Patients with Metastatic Breast Colorectal and Prostate Cancer. Journal of Oncology, 2010, 617421. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/617421.
Alix-Panabieres, C. (2012). EPISPOT assay: detection of viable DTCs/CTCs in solid tumor patients. Recent Results in Cancer Research, 195, 69–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28160-0_6.
Ramskold, D., Luo, S., Wang, Y. C., Li, R., Deng, Q., Faridani, O. R., et al. (2012). Full-length mRNA-Seq from single-cell levels of RNA and individual circulating tumor cells. Nature Biotechnology, 30(8), 777–782. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2282.
Im, H., Shao, H., Park, Y. I., Peterson, V. M., Castro, C. M., Weissleder, R., et al. (2014). Label-free detection and molecular profiling of exosomes with a nano-plasmonic sensor. Nature Biotechnology, 32(5), 490–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2886.
Castellanos-Rizaldos, E., Grimm, D. G., Tadigotla, V., Hurley, J., Healy, J., Neal, P. L., et al. (2018). Exosome-Based Detection of EGFR T790M in Plasma from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Clinical Cancer Research, 24(12), 2944–2950. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3369.
McAnena, P., Brown, J. A., & Kerin, M. J. (2017). Circulating Nucleosomes and Nucleosome Modifications as Biomarkers in Cancer. Cancers (Basel), 9(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9010005.
Gale, D., Lawson, A. R. J., Howarth, K., Madi, M., Durham, B., Smalley, S., et al. (2018). Development of a highly sensitive liquid biopsy platform to detect clinically-relevant cancer mutations at low allele fractions in cell-free DNA. PLoS One, 13(3), e0194630. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194630.
Leary, R. J., Sausen, M., Kinde, I., Papadopoulos, N., Carpten, J. D., Craig, D., et al. (2012). Detection of chromosomal alterations in the circulation of cancer patients with whole-genome sequencing. Science Translational Medicine, 4(162), 162ra154. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3004742.
Wasserkort, R., Kalmar, A., Valcz, G., Spisak, S., Krispin, M., Toth, K., et al. (2013). Aberrant septin 9 DNA methylation in colorectal cancer is restricted to a single CpG island. BMC Cancer, 13, 398. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-398.
Li, W., Zhang, X., Lu, X., You, L., Song, Y., Luo, Z., et al. (2017). 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signatures in circulating cell-free DNA as diagnostic biomarkers for human cancers. Cell Research, 27(10), 1243–1257. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.121.
Song, C. X., Yin, S., Ma, L., Wheeler, A., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2017). 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signatures in cell-free DNA provide information about tumor types and stages. Cell Research, 27(10), 1231–1242. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.106.
Sanders, R., Mason, D. J., Foy, C. A., & Huggett, J. F. (2013). Evaluation of digital PCR for absolute RNA quantification. PLoS One, 8(9), e75296. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075296.
Giraldez, M. D., Spengler, R. M., Etheridge, A., Godoy, P. M., Barczak, A. J., Srinivasan, S., et al. (2018). Comprehensive multi-center assessment of small RNA-seq methods for quantitative miRNA profiling. Nature Biotechnology, 36(8), 746–757. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4183.
Lim, S. B., Di Lee, W., Vasudevan, J., Lim, W. T., & Lim, C. T. (2019). Liquid biopsy: one cell at a time. NPJ Precision Oncology, 3, 23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-019-0095-0.
Pantel, K., Brakenhoff, R. H., & Brandt, B. (2008). Detection, clinical relevance and specific biological properties of disseminating tumour cells. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 8(5), 329–340. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2375.
Bidard, F. C., Peeters, D. J., Fehm, T., Nole, F., Gisbert-Criado, R., Mavroudis, D., et al. (2014). Clinical validity of circulating tumour cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: a pooled analysis of individual patient data. The Lancet Oncology, 15(4), 406–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70069-5.
Bidard, F. C., Michiels, S., Riethdorf, S., Mueller, V., Esserman, L. J., Lucci, A., et al. (2018). Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer patients treated by neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a meta-analysis. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 110(6), 560–567. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djy018.
Adams, D. L., Stefansson, S., Haudenschild, C., Martin, S. S., Charpentier, M., Chumsri, S., et al. (2015). Cytometric characterization of circulating tumor cells captured by microfiltration and their correlation to the CellSearch((R)) CTC test. Cytometry. Part A, 87(2), 137–144. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.22613.
Lee, Y., Guan, G., & Bhagat, A. A. (2018). ClearCell(R) FX, a label-free microfluidics technology for enrichment of viable circulating tumor cells. Cytometry. Part A, 93(12), 1251–1254. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.23507.
Li, X., Corbett, A. L., Taatizadeh, E., Tasnim, N., Little, J. P., Garnis, C., et al. (2019). Challenges and opportunities in exosome research-Perspectives from biology, engineering, and cancer therapy. APL Bioengineering, 3(1), 011503. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5087122.
Fraga, M. F., Ballestar, E., Villar-Garea, A., Boix-Chornet, M., Espada, J., Schotta, G., et al. (2005). Loss of acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Nature Genetics, 37(4), 391–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1531.
Seligson, D. B., Horvath, S., Shi, T., Yu, H., Tze, S., Grunstein, M., et al. (2005). Global histone modification patterns predict risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Nature, 435(7046), 1262–1266. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03672.
Gezer, U., Yoruker, E. E., Keskin, M., Kulle, C. B., Dharuman, Y., & Holdenrieder, S. (2015). Histone Methylation Marks on Circulating Nucleosomes as Novel Blood-Based Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 29654–29662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226180.
Bauden, M., Pamart, D., Ansari, D., Herzog, M., Eccleston, M., Micallef, J., et al. (2015). Circulating nucleosomes as epigenetic biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. Clinical Epigenetics, 7, 106. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-015-0139-4.
Ulz, P., Thallinger, G. G., Auer, M., Graf, R., Kashofer, K., Jahn, S. W., et al. (2016). Inferring expressed genes by whole-genome sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature Genetics, 48(10), 1273–1278. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3648.
Vogelstein, B., & Kinzler, K. W. (1999). Digital PCR. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96(16), 9236–9241. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.16.9236.
Zhu, Z., Jenkins, G., Zhang, W., Zhang, M., Guan, Z., & Yang, C. J. (2012). Single-molecule emulsion PCR in microfluidic droplets. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 403(8), 2127–2143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5914-x.
Li, M., Diehl, F., Dressman, D., Vogelstein, B., & Kinzler, K. W. (2006). BEAMing up for detection and quantification of rare sequence variants. Nature Methods, 3(2), 95–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth850.
O'Leary, B., Hrebien, S., Beaney, M., Fribbens, C., Garcia-Murillas, I., Jiang, J., et al. (2019). Comparison of BEAMing and Droplet Digital PCR for Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis. Clinical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2019.305805.
Choi, M., Scholl, U. I., Ji, W., Liu, T., Tikhonova, I. R., Zumbo, P., et al. (2009). Genetic diagnosis by whole exome capture and massively parallel DNA sequencing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(45), 19096–19101. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910672106.
Forshew, T., Murtaza, M., Parkinson, C., Gale, D., Tsui, D. W., Kaper, F., et al. (2012). Noninvasive identification and monitoring of cancer mutations by targeted deep sequencing of plasma DNA. Science Translational Medicine, 4(136), 136ra168. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3003726.
Koeppel, F., Blanchard, S., Jovelet, C., Genin, B., Marcaillou, C., Martin, E., et al. (2017). Whole exome sequencing for determination of tumor mutation load in liquid biopsy from advanced cancer patients. PLoS One, 12(11), e0188174. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188174.
Nakagawa, H., Wardell, C. P., Furuta, M., Taniguchi, H., & Fujimoto, A. (2015). Cancer whole-genome sequencing: present and future. Oncogene, 34(49), 5943–5950. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.90.
Chan, K. C., Jiang, P., Zheng, Y. W., Liao, G. J., Sun, H., Wong, J., et al. (2013). Cancer genome scanning in plasma: detection of tumor-associated copy number aberrations, single-nucleotide variants, and tumoral heterogeneity by massively parallel sequencing. Clinical Chemistry, 59(1), 211–224. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2012.196014.
Pasaniuc, B., Rohland, N., McLaren, P. J., Garimella, K., Zaitlen, N., Li, H., et al. (2012). Extremely low-coverage sequencing and imputation increases power for genome-wide association studies. Nature Genetics, 44(6), 631–635. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2283.
Adalsteinsson, V. A., Ha, G., Freeman, S. S., Choudhury, A. D., Stover, D. G., Parsons, H. A., et al. (2017). Scalable whole-exome sequencing of cell-free DNA reveals high concordance with metastatic tumors. Nature Communications, 8(1), 1324. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00965-y.
Hovelson, D. H., Liu, C. J., Wang, Y., Kang, Q., Henderson, J., Gursky, A., et al. (2017). Rapid, ultra low coverage copy number profiling of cell-free DNA as a precision oncology screening strategy. Oncotarget, 8(52), 89848–89866. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21163.
Jaenisch, R., & Bird, A. (2003). Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nature Genetics, 33(Suppl), 245–254. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1089.
Bernstein, B. E., Meissner, A., & Lander, E. S. (2007). The mammalian epigenome. Cell, 128(4), 669–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.033.
Kustanovich, A., Schwartz, R., Peretz, T., & Grinshpun, A. (2019). Life and death of circulating cell-free DNA. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 20(8), 1057–1067. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2019.1598759.
Luo, C., Hajkova, P., & Ecker, J. R. (2018). Dynamic DNA methylation: in the right place at the right time. Science, 361(6409), 1336–1340. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat6806.
Ehrlich, M. (2006). Cancer-linked DNA hypomethylation and its relationship to hypermethylation. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, 310, 251–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-31181-5_12.
Ehrlich, M. (2009). DNA hypomethylation in cancer cells. Epigenomics, 1(2), 239–259. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi.09.33.
Melnikov, A. A., Gartenhaus, R. B., Levenson, A. S., Motchoulskaia, N. A., & Levenson Chernokhvostov, V. V. (2005). MSRE-PCR for analysis of gene-specific DNA methylation. Nucleic Acids Research, 33(10), e93. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gni092.
Sasaki, M., Anast, J., Bassett, W., Kawakami, T., Sakuragi, N., & Dahiya, R. (2003). Bisulfite conversion-specific and methylation-specific PCR: a sensitive technique for accurate evaluation of CpG methylation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 309(2), 305–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.08.005.
Brunner, A. L., Johnson, D. S., Kim, S. W., Valouev, A., Reddy, T. E., Neff, N. F., et al. (2009). Distinct DNA methylation patterns characterize differentiated human embryonic stem cells and developing human fetal liver. Genome Research, 19(6), 1044–1056. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.088773.108.
Maunakea, A. K., Nagarajan, R. P., Bilenky, M., Ballinger, T. J., D'Souza, C., Fouse, S. D., et al. (2010). Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in regulating alternative promoters. Nature, 466(7303), 253–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09165.
Taiwo, O., Wilson, G. A., Morris, T., Seisenberger, S., Reik, W., Pearce, D., et al. (2012). Methylome analysis using MeDIP-seq with low DNA concentrations. Nature Protocols, 7(4), 617–636. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.012.
Aberg, K. A., McClay, J. L., Nerella, S., Xie, L. Y., Clark, S. L., Hudson, A. D., et al. (2012). MBD-seq as a cost-effective approach for methylome-wide association studies: demonstration in 1500 case--control samples. Epigenomics, 4(6), 605–621. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi.12.59.
Zhang, L., Szulwach, K. E., Hon, G. C., Song, C. X., Park, B., Yu, M., et al. (2013). Tet-mediated covalent labelling of 5-methylcytosine for its genome-wide detection and sequencing. Nature Communications, 4, 1517. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2527.
Wang, Q., Gu, L., Adey, A., Radlwimmer, B., Wang, W., Hovestadt, V., et al. (2013). Tagmentation-based whole-genome bisulfite sequencing. Nature Protocols, 8(10), 2022–2032. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.118.
Chan, K. C., Jiang, P., Chan, C. W., Sun, K., Wong, J., Hui, E. P., et al. (2013). Noninvasive detection of cancer-associated genome-wide hypomethylation and copy number aberrations by plasma DNA bisulfite sequencing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(47), 18761–18768. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1313995110.
Lee, E. J., Luo, J., Wilson, J. M., & Shi, H. (2013). Analyzing the cancer methylome through targeted bisulfite sequencing. Cancer Letters, 340(2), 171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.040.
Shen, S. Y., Singhania, R., Fehringer, G., Chakravarthy, A., Roehrl, M. H. A., Chadwick, D., et al. (2018). Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes. Nature, 563(7732), 579–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0703-0.
Shen, S. Y., Burgener, J. M., Bratman, S. V., & De Carvalho, D. D. (2019). Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA. Nature Protocols, 14(10), 2749–2780. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0202-2.
Song, C. X., & He, C. (2013). Potential functional roles of DNA demethylation intermediates. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 38(10), 480–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2013.07.003.
Zeng, C., Stroup, E. K., Zhang, Z., Chiu, B. C., & Zhang, W. (2019). Towards precision medicine: advances in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine cancer biomarker discovery in liquid biopsy. Cancer Communications (Lond), 39(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-019-0356-x.
Pastor, W. A., Pape, U. J., Huang, Y., Henderson, H. R., Lister, R., Ko, M., et al. (2011). Genome-wide mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in embryonic stem cells. Nature, 473(7347), 394–397. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10102.
Song, C. X., Szulwach, K. E., Fu, Y., Dai, Q., Yi, C., Li, X., et al. (2011). Selective chemical labeling reveals the genome-wide distribution of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nature Biotechnology, 29(1), 68–72. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1732.
Yu, M., Hon, G. C., Szulwach, K. E., Song, C. X., Zhang, L., Kim, A., et al. (2012). Base-resolution analysis of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the mammalian genome. Cell, 149(6), 1368–1380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.027.
Petterson, A., Chung, T. H., Tan, D., Sun, X., & Jia, X. Y. (2014). RRHP: a tag-based approach for 5-hydroxymethylcytosine mapping at single-site resolution. Genome Biology, 15(9), 456. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0456-5.
Zeng, H., He, B., Xia, B., Bai, D., Lu, X., Cai, J., et al. (2018). Bisulfite-Free, Nanoscale Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single Base Resolution. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 140(41), 13190–13194. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b08297.
Hu, L., Liu, Y., Han, S., Yang, L., Cui, X., Gao, Y., et al. (2019). Jump-seq: genome-Wide Capture and Amplification of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Sites. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 141(22), 8694–8697. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b02512.
Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, F., Chen, Z., & Zhou, X. (2019). Bisulfite-free, single base-resolution analysis of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in genomic DNA by chemical-mediated mismatch. Chemical Science, 10(2), 447–452. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8sc04272a.
Han, D., Lu, X., Shih, A. H., Nie, J., You, Q., Xu, M. M., et al. (2016). A Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for Genome-wide 5hmC Profiling of Rare Cell Populations. Molecular Cell, 63(4), 711–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.028.
Cai, J., Chen, L., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X., Lu, X., Liu, W., et al. (2019). Genome-wide mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosines in circulating cell-free DNA as a non-invasive approach for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318882.
Chiu, B. C., Zhang, Z., You, Q., Zeng, C., Stepniak, E., Bracci, P. M., et al. (2019). Prognostic implications of 5-hydroxymethylcytosines from circulating cell-free DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Advances, 3(19), 2790–2799. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000175.
Gao, P., Lin, S., Cai, M., Zhu, Y., Song, Y., Sui, Y., et al. (2019). 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine profiling from genomic and cell-free DNA for colorectal cancers patients. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 23(5), 3530–3537. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14252.
Zhang, J., Han, X., Gao, C., Xing, Y., Qi, Z., Liu, R., et al. (2018). 5-Hydroxymethylome in Circulating Cell-free DNA as A Potential Biomarker for Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 16(3), 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2018.06.002.
Tian, X., Sun, B., Chen, C., Gao, C., Zhang, J., Lu, X., et al. (2018). Circulating tumor DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine as a novel diagnostic biomarker for esophageal cancer. Cell Research, 28(5), 597–600. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0014-x.
Del Re, M., Marconcini, R., Pasquini, G., Rofi, E., Vivaldi, C., Bloise, F., et al. (2018). PD-L1 mRNA expression in plasma-derived exosomes is associated with response to anti-PD-1 antibodies in melanoma and NSCLC. British Journal of Cancer, 118(6), 820–824. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2018.9.
David, L., Huber, W., Granovskaia, M., Toedling, J., Palm, C. J., Bofkin, L., et al. (2006). A high-resolution map of transcription in the yeast genome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(14), 5320–5325. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601091103.
Wang, Z., Gerstein, M., & Snyder, M. (2009). RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nature Reviews. Genetics, 10(1), 57–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2484.
Buschmann, D., Haberberger, A., Kirchner, B., Spornraft, M., Riedmaier, I., Schelling, G., et al. (2016). Toward reliable biomarker signatures in the age of liquid biopsies - how to standardize the small RNA-Seq workflow. Nucleic Acids Research, 44(13), 5995–6018. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw545.
Giraldez, M. D., Spengler, R. M., Etheridge, A., Goicochea, A. J., Tuck, M., Choi, S. W., et al. (2019). Phospho-RNA-seq: a modified small RNA-seq method that reveals circulating mRNA and lncRNA fragments as potential biomarkers in human plasma. The EMBO Journal, 38(11). https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2019101695.
Yuan, T., Huang, X., Woodcock, M., Du, M., Dittmar, R., Wang, Y., et al. (2016). Plasma extracellular RNA profiles in healthy and cancer patients. Scientific Reports, 6, 19413. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19413.
Pinto, N. R., Applebaum, M. A., Volchenboum, S. L., Matthay, K. K., London, W. B., Ambros, P. F., et al. (2015). Advances in Risk Classification and Treatment Strategies for Neuroblastoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 33(27), 3008–3017. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.59.4648.
Park, J. R., Kreissman, S. G., London, W. B., Naranjo, A., Cohn, S. L., Hogarty, M. D., et al. (2019). Effect of Tandem Autologous Stem Cell Transplant vs Single Transplant on Event-Free Survival in Patients With High-Risk Neuroblastoma: a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA, 322(8), 746–755. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.11642.
Tsuchida, Y., Honna, T., Iwanaka, T., Saeki, M., Taguchi, N., Kaneko, T., et al. (1987). Serial determination of serum neuron-specific enolase in patients with neuroblastoma and other pediatric tumors. Journal of Pediatric Surgery, 22(5), 419–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3468(87)80261-0.
Zeltzer, P. M., Marangos, P. J., Evans, A. E., & Schneider, S. L. (1986). Serum neuron-specific enolase in children with neuroblastoma. Relationship to stage and disease course. Cancer, 57(6), 1230–1234. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19860315)57:6<1230::aid-cncr2820570628>3.0.co;2-#.
Kogner, P., Bjork, O., & Theodorsson, E. (1993). Neuropeptide Y in neuroblastoma: increased concentration in metastasis, release during surgery, and characterization of plasma and tumor extracts. Medical and Pediatric Oncology, 21(5), 317–322. https://doi.org/10.1002/mpo.2950210502.
Kogner, P., Theodorsson, E., & Bjork, O. (1991). Plasma neuropeptide Y (NPY): a novel marker of neuroblastoma. Progress in Clinical and Biological Research, 366, 367–373.
Kogner, P., Bjork, O., & Theodorsson, E. (1990). Neuropeptide Y as a marker in pediatric neuroblastoma. Pediatric Pathology, 10(1-2), 207–216. https://doi.org/10.3109/15513819009067108.
Valentino, L., Moss, T., Olson, E., Wang, H. J., Elashoff, R., & Ladisch, S. (1990). Shed tumor gangliosides and progression of human neuroblastoma. Blood, 75(7), 1564–1567.
Moss, T. J., & Sanders, D. G. (1990). Detection of neuroblastoma cells in blood. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 8(4), 736–740. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1990.8.4.736.
Mattano Jr., L. A., Moss, T. J., & Emerson, S. G. (1992). Sensitive detection of rare circulating neuroblastoma cells by the reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Research, 52(17), 4701–4705.
Seeger, R. C., Reynolds, C. P., Gallego, R., Stram, D. O., Gerbing, R. B., & Matthay, K. K. (2000). Quantitative tumor cell content of bone marrow and blood as a predictor of outcome in stage IV neuroblastoma: a Children's Cancer Group Study. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 18(24), 4067–4076. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2000.18.24.4067.
Burchill, S. A., Lewis, I. J., Abrams, K. R., Riley, R., Imeson, J., Pearson, A. D., et al. (2001). Circulating neuroblastoma cells detected by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA are an independent poor prognostic indicator in stage 4 neuroblastoma in children over 1 year. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 19(6), 1795–1801. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2001.19.6.1795.
Viprey, V. F., Gregory, W. M., Corrias, M. V., Tchirkov, A., Swerts, K., Vicha, A., et al. (2014). Neuroblastoma mRNAs predict outcome in children with stage 4 neuroblastoma: a European HR-NBL1/SIOPEN study. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 32(10), 1074–1083. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.53.3604.
Stutterheim, J., Gerritsen, A., Zappeij-Kannegieter, L., Yalcin, B., Dee, R., van Noesel, M. M., et al. (2009). Detecting minimal residual disease in neuroblastoma: the superiority of a panel of real-time quantitative PCR markers. Clinical Chemistry, 55(7), 1316–1326. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.117945.
Marachelian, A., Villablanca, J. G., Liu, C. W., Liu, B., Goodarzian, F., Lai, H. A., et al. (2017). Expression of Five Neuroblastoma Genes in Bone Marrow or Blood of Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Neuroblastoma Provides a New Biomarker for Disease and Prognosis. Clinical Cancer Research, 23(18), 5374–5383. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2647.
Yanez, Y., Grau, E., Oltra, S., Canete, A., Martinez, F., Orellana, C., et al. (2011). Minimal disease detection in peripheral blood and bone marrow from patients with non-metastatic neuroblastoma. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 137(8), 1263–1272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-011-0997-x.
Zeka, F., Decock, A., Van Goethem, A., Vanderheyden, K., Demuynck, F., Lammens, T., et al. (2018). Circulating microRNA biomarkers for metastatic disease in neuroblastoma patients. JCI Insight, 3(23). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.97021.
Morini, M., Cangelosi, D., Segalerba, D., Marimpietri, D., Raggi, F., Castellano, A., et al. (2019). Exosomal microRNAs from Longitudinal Liquid Biopsies for the Prediction of Response to Induction Chemotherapy in High-Risk Neuroblastoma Patients: a Proof of Concept SIOPEN Study. Cancers (Basel), 11(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101476.
Chicard, M., Boyault, S., Colmet Daage, L., Richer, W., Gentien, D., Pierron, G., et al. (2016). Genomic Copy Number Profiling Using Circulating Free Tumor DNA Highlights Heterogeneity in Neuroblastoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 22(22), 5564–5573. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0500.
Van Roy, N., Van Der Linden, M., Menten, B., Dheedene, A., Vandeputte, C., Van Dorpe, J., et al. (2017). Shallow Whole Genome Sequencing on Circulating Cell-Free DNA Allows Reliable Noninvasive Copy-Number Profiling in Neuroblastoma Patients. Clinical Cancer Research, 23(20), 6305–6314. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0675.
Chicard, M., Colmet-Daage, L., Clement, N., Danzon, A., Bohec, M., Bernard, V., et al. (2018). Whole-Exome Sequencing of Cell-Free DNA Reveals Temporo-spatial Heterogeneity and Identifies Treatment-Resistant Clones in Neuroblastoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 24(4), 939–949. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1586.
Klega, K., Imamovic-Tuco, A., Ha, G., Clapp, A. N., Meyer, S., Ward, A., et al. (2018). Detection of Somatic Structural Variants Enables Quantification and Characterization of Circulating Tumor DNA in Children With Solid Tumors. JCO Precision Oncology, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO.17.00285.
Kojima, M., Hiyama, E., Fukuba, I., Yamaoka, E., Ueda, Y., Onitake, Y., et al. (2013). Detection of MYCN amplification using blood plasma: noninvasive therapy evaluation and prediction of prognosis in neuroblastoma. Pediatric Surgery International, 29(11), 1139–1145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3374-9.
Combaret, V., Hogarty, M. D., London, W. B., McGrady, P., Iacono, I., Brejon, S., et al. (2009). Influence of neuroblastoma stage on serum-based detection of MYCN amplification. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 53(3), 329–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.22009.
Gotoh, T., Hosoi, H., Iehara, T., Kuwahara, Y., Osone, S., Tsuchiya, K., et al. (2005). Prediction of MYCN amplification in neuroblastoma using serum DNA and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 23(22), 5205–5210. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.02.014.
Combaret, V., Bergeron, C., Noguera, R., Iacono, I., & Puisieux, A. (2005). Circulating MYCN DNA predicts MYCN-amplification in neuroblastoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 23(34), 8919–8920; author reply 8920. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.04.0170.
Combaret, V., Audoynaud, C., Iacono, I., Favrot, M. C., Schell, M., Bergeron, C., et al. (2002). Circulating MYCN DNA as a tumor-specific marker in neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Research, 62(13), 3646–3648.
Lodrini, M., Sprussel, A., Astrahantseff, K., Tiburtius, D., Konschak, R., Lode, H. N., et al. (2017). Using droplet digital PCR to analyze MYCN and ALK copy number in plasma from patients with neuroblastoma. Oncotarget, 8(49), 85234–85251. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19076.
Combaret, V., Brejon, S., Iacono, I., Schleiermacher, G., Pierron, G., Ribeiro, A., et al. (2011). Determination of 17q gain in patients with neuroblastoma by analysis of circulating DNA. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 56(5), 757–761. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.22816.
Yagyu, S., Iehara, T., Gotoh, T., Miyachi, M., Katsumi, Y., Kikuchi, K., et al. (2011). Preoperative analysis of 11q loss using circulating tumor-released DNA in serum: a novel diagnostic tool for therapy stratification of neuroblastoma. Cancer Letters, 309(2), 185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2011.05.032.
Misawa, A., Tanaka, S., Yagyu, S., Tsuchiya, K., Iehara, T., Sugimoto, T., et al. (2009). RASSF1A hypermethylation in pretreatment serum DNA of neuroblastoma patients: a prognostic marker. British Journal of Cancer, 100(2), 399–404. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6604887.
Yagyu, S., Gotoh, T., Iehara, T., Miyachi, M., Katsumi, Y., Tsubai-Shimizu, S., et al. (2008). Circulating methylated-DCR2 gene in serum as an indicator of prognosis and therapeutic efficacy in patients with MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 14(21), 7011–7019. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1249.
Hayashi, M., Zhu, P., McCarty, G., Meyer, C. F., Pratilas, C. A., Levin, A., et al. (2017). Size-based detection of sarcoma circulating tumor cells and cell clusters. Oncotarget, 8(45), 78965–78977. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20697.
Barris, D. M., Weiner, S. B., Dubin, R. A., Fremed, M., Zhang, X., Piperdi, S., et al. (2018). Detection of circulating tumor DNA in patients with osteosarcoma. Oncotarget, 9(16), 12695–12704. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.24268.
Shulman, D. S., Klega, K., Imamovic-Tuco, A., Clapp, A., Nag, A., Thorner, A. R., et al. (2018). Detection of circulating tumour DNA is associated with inferior outcomes in Ewing sarcoma and osteosarcoma: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. British Journal of Cancer, 119(5), 615–621. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0212-9.
Allen-Rhoades, W., Kurenbekova, L., Satterfield, L., Parikh, N., Fuja, D., Shuck, R. L., et al. (2015). Cross-species identification of a plasma microRNA signature for detection, therapeutic monitoring, and prognosis in osteosarcoma. Cancer Medicine, 4(7), 977–988. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.438.
Ma, W., Zhang, X., Chai, J., Chen, P., Ren, P., & Gong, M. (2014). Circulating miR-148a is a significant diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with osteosarcoma. Tumour Biology, 35(12), 12467–12472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2565-x.
Schleiermacher, G., Peter, M., Oberlin, O., Philip, T., Rubie, H., Mechinaud, F., et al. (2003). Increased risk of systemic relapses associated with bone marrow micrometastasis and circulating tumor cells in localized ewing tumor. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 21(1), 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2003.03.006.
Hayashi, M., Chu, D., Meyer, C. F., Llosa, N. J., McCarty, G., Morris, C. D., et al. (2016). Highly personalized detection of minimal Ewing sarcoma disease burden from plasma tumor DNA. Cancer, 122(19), 3015–3023. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30144.
Krumbholz, M., Hellberg, J., Steif, B., Bauerle, T., Gillmann, C., Fritscher, T., et al. (2016). Genomic EWSR1 Fusion Sequence as Highly Sensitive and Dynamic Plasma Tumor Marker in Ewing Sarcoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 22(17), 4356–4365. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-3028.
Allegretti, M., Casini, B., Mandoj, C., Benini, S., Alberti, L., Novello, M., et al. (2018). Precision diagnostics of Ewing's sarcoma by liquid biopsy: circulating EWS-FLI1 fusion transcripts. Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology, 10, 1758835918774337. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835918774337.
Eguchi-Ishimae, M., Tezuka, M., Kokeguchi, T., Nagai, K., Moritani, K., Yonezawa, S., et al. (2019). Early detection of the PAX3-FOXO1 fusion gene in circulating tumor-derived DNA in a case of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer, 58(8), 521–529. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22734.
Miyachi, M., Tsuchiya, K., Yoshida, H., Yagyu, S., Kikuchi, K., Misawa, A., et al. (2010). Circulating muscle-specific microRNA, miR-206, as a potential diagnostic marker for rhabdomyosarcoma. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 400(1), 89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.08.015.
Jimenez, I., Chicard, M., Colmet-Daage, L., Clement, N., Danzon, A., Lapouble, E., et al. (2019). Circulating tumor DNA analysis enables molecular characterization of pediatric renal tumors at diagnosis. International Journal of Cancer, 144(1), 68–79. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31620.
Murray, M. J., Raby, K. L., Saini, H. K., Bailey, S., Wool, S. V., Tunnacliffe, J. M., et al. (2015). Solid tumors of childhood display specific serum microRNA profiles. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 24(2), 350–360. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0669.
Ludwig, N., Nourkami-Tutdibi, N., Backes, C., Lenhof, H. P., Graf, N., Keller, A., et al. (2015). Circulating serum miRNAs as potential biomarkers for nephroblastoma. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 62(8), 1360–1367. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.25481.
Schmitt, J., Backes, C., Nourkami-Tutdibi, N., Leidinger, P., Deutscher, S., Beier, M., et al. (2012). Treatment-independent miRNA signature in blood of Wilms tumor patients. BMC Genomics, 13, 379. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-379.
Treger, T. D., Chagtai, T., Butcher, R., Cresswell, G. D., Al-Saadi, R., Brok, J., et al. (2018). Somatic TP53 Mutations Are Detectable in Circulating Tumor DNA from Children with Anaplastic Wilms Tumors. Translational Oncology, 11(6), 1301–1306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2018.08.006.
Charlton, J., Williams, R. D., Weeks, M., Sebire, N. J., Popov, S., Vujanic, G., et al. (2014). Methylome analysis identifies a Wilms tumor epigenetic biomarker detectable in blood. Genome Biology, 15(8), 434. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0434-y.
Liu, W., Chen, S., & Liu, B. (2016). Diagnostic and prognostic values of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in children with hepatoblastoma: a Chinese population-based study. Pediatric Surgery International, 32(11), 1059–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3960-8.
Jiao, C., Jiao, X., Zhu, A., Ge, J., & Xu, X. (2017). Exosomal miR-34s panel as potential novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in patients with hepatoblastoma. Journal of Pediatric Surgery, 52(4), 618–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.09.070.
Gerson, J. M., Schlesinger, H. R., Sereni, P., Moorhead, P. S., & Hummeler, K. (1977). Isolation and characterization of a neuroblastoma cell line from peripheral blood in a patient with disseminated disease. Cancer, 39(6), 2508–2512. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(197706)39:6<2508::aid-cncr2820390630>3.0.co;2-x.
Pelkey, T. J., Frierson Jr., H. F., & Bruns, D. E. (1996). Molecular and immunological detection of circulating tumor cells and micrometastases from solid tumors. Clinical Chemistry, 42(9), 1369–1381.
Kreissman, S. G., Seeger, R. C., Matthay, K. K., London, W. B., Sposto, R., Grupp, S. A., et al. (2013). Purged versus non-purged peripheral blood stem-cell transplantation for high-risk neuroblastoma (COG A3973): a randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology, 14(10), 999–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70309-7.
Miyajima, Y., Kato, K., Numata, S., Kudo, K., & Horibe, K. (1995). Detection of neuroblastoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood at diagnosis by the reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. Cancer, 75(11), 2757–2761. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19950601)75:11<2757::aid-cncr2820751120>3.0.co;2-s.
Miyajima, Y., Horibe, K., Fukuda, M., Matsumoto, K., Numata, S., Mori, H., et al. (1996). Sequential detection of tumor cells in the peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with stage IV neuroblastoma by the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. Cancer, 77(6), 1214–1219. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19960315)77:6<1214::aid-cncr31>3.0.co;2-2.
Uemura, S., Ishida, T., Thwin, K. K. M., Yamamoto, N., Tamura, A., Kishimoto, K., et al. (2019). Dynamics of Minimal Residual Disease in Neuroblastoma Patients. Frontiers in Oncology, 9, 455. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00455.
Viprey, V. F., Corrias, M. V., Kagedal, B., Oltra, S., Swerts, K., Vicha, A., et al. (2007). Standardisation of operating procedures for the detection of minimal disease by QRT-PCR in children with neuroblastoma: quality assurance on behalf of SIOPEN-R-NET. European Journal of Cancer, 43(2), 341–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2006.08.007.
Schleiermacher, G., Mosseri, V., London, W. B., Maris, J. M., Brodeur, G. M., Attiyeh, E., et al. (2012). Segmental chromosomal alterations have prognostic impact in neuroblastoma: a report from the INRG project. British Journal of Cancer, 107(8), 1418–1422. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.375.
Pinto, N., Mayfield, J. R., Raca, G., Applebaum, M. A., Chlenski, A., Sukhanova, M., et al. (2016). Segmental Chromosomal Aberrations in Localized Neuroblastoma Can be Detected in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Samples and Are Associated With Recurrence. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 63(6), 1019–1023. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.25934.
Brodeur, G. M., Seeger, R. C., Schwab, M., Varmus, H. E., & Bishop, J. M. (1984). Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science, 224(4653), 1121–1124.
Pugh, T. J., Morozova, O., Attiyeh, E. F., Asgharzadeh, S., Wei, J. S., Auclair, D., et al. (2013). The genetic landscape of high-risk neuroblastoma. Nature Genetics, 45(3), 279–284. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2529.
Durinck, K., & Speleman, F. (2018). Epigenetic regulation of neuroblastoma development. Cell and Tissue Research, 372(2), 309–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2773-y.
Brodeur, G. M., & Bagatell, R. (2014). Mechanisms of neuroblastoma regression. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 11(12), 704–713. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.168.
Applebaum, M. A., Barr, E. K., Karpus, J., Nie, J., Zhang, Z., Armstrong, A. E., et al. (2019). 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiles Are Prognostic of Outcome in Neuroblastoma and Reveal Transcriptional Networks That Correlate With Tumor Phenotype. JCO Precision Oncology, (3), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO.18.00402.
van Groningen, T., Koster, J., Valentijn, L. J., Zwijnenburg, D. A., Akogul, N., Hasselt, N. E., et al. (2017). Neuroblastoma is composed of two super-enhancer-associated differentiation states. Nature Genetics, 49(8), 1261–1266. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3899.
Ostler, K. R., Yang, Q., Looney, T. J., Zhang, L., Vasanthakumar, A., Tian, Y., et al. (2012). Truncated DNMT3B isoform DNMT3B7 suppresses growth, induces differentiation, and alters DNA methylation in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Research, 72(18), 4714–4723. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0886.
Yang, Q., Kiernan, C. M., Tian, Y., Salwen, H. R., Chlenski, A., Brumback, B. A., et al. (2007). Methylation of CASP8, DCR2, and HIN-1 in neuroblastoma is associated with poor outcome. Clinical Cancer Research, 13(11), 3191–3197. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2846.
Lu, Z., Tian, Y., Salwen, H. R., Chlenski, A., Godley, L. A., Raj, J. U., et al. (2013). Histone-lysine methyltransferase EHMT2 is involved in proliferation, apoptosis, cell invasion, and DNA methylation of human neuroblastoma cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs, 24(5), 484–493. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0b013e32835ffdbb.
Decock, A., Ongenaert, M., Van Criekinge, W., Speleman, F., & Vandesompele, J. (2016). DNA methylation profiling of primary neuroblastoma tumors using methyl-CpG-binding domain sequencing. Scientific Data, 3, 160004. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.4.
Olsson, M., Beck, S., Kogner, P., Martinsson, T., & Caren, H. (2016). Genome-wide methylation profiling identifies novel methylated genes in neuroblastoma tumors. Epigenetics, 11(1), 74–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2016.1138195.
Decock, A., Ongenaert, M., Cannoodt, R., Verniers, K., De Wilde, B., Laureys, G., et al. (2016). Methyl-CpG-binding domain sequencing reveals a prognostic methylation signature in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget, 7(2), 1960–1972. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6477.
Applebaum, M., Barr, E., Karpus, J., West-Szymanski, D., Zhang, W., Salwen, H., et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5HMC) Profiles of Cell-Free DNA (CFDNA): novel Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers for Children with Neuroblastoma. In Pediatric blood & cancer, 2019 (Vol. 66, pp. S318–S318). Hoboken: Wiley.
Burningham, Z., Hashibe, M., Spector, L., & Schiffman, J. D. (2012). The epidemiology of sarcoma. Clinical Sarcoma Research, 2(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3329-2-14.
Reed, D. R., Hayashi, M., Wagner, L., Binitie, O., Steppan, D. A., Brohl, A. S., et al. (2017). Treatment pathway of bone sarcoma in children, adolescents, and young adults. Cancer, 123(12), 2206–2218. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30589.
McBride, D. J., Orpana, A. K., Sotiriou, C., Joensuu, H., Stephens, P. J., Mudie, L. J., et al. (2010). Use of cancer-specific genomic rearrangements to quantify disease burden in plasma from patients with solid tumors. Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer, 49(11), 1062–1069. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.20815.
Vo, K. T., Edwards, J. V., Epling, C. L., Sinclair, E., Hawkins, D. S., Grier, H. E., et al. (2016). Impact of Two Measures of Micrometastatic Disease on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Ewing Sarcoma: a Report from the Children's Oncology Group. Clinical Cancer Research, 22(14), 3643–3650. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2516.
Irtan, S., Ehrlich, P. F., & Pritchard-Jones, K. (2016). Wilms tumor: "State-of-the-art" update, 2016. Seminars in Pediatric Surgery, 25(5), 250–256. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2016.09.003.
Brioude, F., Lacoste, A., Netchine, I., Vazquez, M. P., Auber, F., Audry, G., et al. (2013). Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: growth pattern and tumor risk according to molecular mechanism, and guidelines for tumor surveillance. Hormone Research in Pædiatrics, 80(6), 457–465. https://doi.org/10.1159/000355544.
Bisogno, G., De Salvo, G. L., Bergeron, C., Gallego Melcon, S., Merks, J. H., Kelsey, A., et al. (2019). Vinorelbine and continuous low-dose cyclophosphamide as maintenance chemotherapy in patients with high-risk rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS 2005): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology, 20(11), 1566–1575. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30617-5.
Parikh, A. R., Leshchiner, I., Elagina, L., Goyal, L., Levovitz, C., Siravegna, G., et al. (2019). Liquid versus tissue biopsy for detecting acquired resistance and tumor heterogeneity in gastrointestinal cancers. Nature Medicine, 25(9), 1415–1421. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0561-9.
Funding
MAA is supported by the NIH Grant Number and K08CA226237. The contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
CH is a shareholder of Shanghai Epican Genetech Co. Ltd. that licensed 5hmC-Seal from The University of Chicago. CH is a scientific founder and scientific advisory board member of Accent Therapeutics, Inc.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Daniel A. Weiser, Diana C. West-Szymanski and Ellen Fraint Denotes co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiser, D.A., West-Szymanski, D.C., Fraint, E. et al. Progress toward liquid biopsies in pediatric solid tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev 38, 553–571 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-019-09825-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-019-09825-1