Abstract
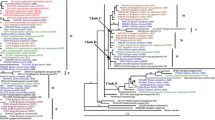
The trnS/psbC region of chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) was sequenced for 18 Elymus polyploid species, Hordelymus europaeus and their putative diploid ancestors. The objective was to determine the maternal origin and evolutionary relationships of these polyploid taxa. Phylogenetic analysis showed that Elymus and Pseudoroegneria species formed a highly supported monophyletic group (100 % bootstrap values), suggesting that Pseudoroegneria is the maternal genome donor to polyploid Elymus species studied here. The phylogenetic tree based on cpDNA sequence data indicates that E. submuticus contains a St-genome. Taking into consideration of our previously published RPB2 data, we can conclude that hexaploid E. submuticus contains at least one copy of St and Y genomes. Our Neighor-joining analysis of cpDNA data put Psathyrostachys juncea, Hordeum bogdanii and Hordelymus europaeus into one group, suggesting a close relationship among them.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cpDNA:
-
chloroplast DNA
- E. :
-
Elymus
- H. :
-
Hordeum
- Hor. :
-
Hordelymus
- Lop. :
-
Lophopyrum
- P :
-
Pseudoroegneria
- Psa :
-
Psathyrostachys
- RAPD:
-
random amplified polymorphic DNA
- T. :
-
Taeniatherum
- Th :
-
Thinopyrum
References
Demesure, B., Sodzi, N., Petit, R.J.: A set of universal primers for amplification of polymorphic non-coding regions of mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA in plants. — Mol. Ecol. 4: 129–131, 1995.
Dewey, D.R.: The genomic system of classification as a guide to intergeneric hybridization within the perennial Triticeae. — In: Gustafsen, J.P.(ed.): Gene Manipulation in Plant Improvement. Pp 209–279. Plenum Press, New York 1984.
Ellneskog-Staam, P., Taketa, S., Salomon, B., Anamthawat-Jónsson, K., Von Bothmer, R.: Identifying the genome of wood barley Hordelymus europaeus (Poaceae: Triticeae). — Hereditas 143: 103–112, 2006.
Felsenstein, J.: Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. — Evolution 39: 783–791, 1985.
Helfgott, D.M., Mason-Gamer, R.J.: The evolution of North American Elymus (Triticeae, Poaceae) allotetraploids: evidence from phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene sequences. — Syst. Bot. 29: 850–861, 2004.
Hsiao, C., Chatterton, N.J., Asay, K.H., Jensen, K.B.: Phylogenetic relationships of the monogenomic species of the wheat tribe, Triticeae (Poaceae), inferred from nuclear rDNA (internal transcribed spacer) sequences. — Genome 38: 221–223, 1995.
Jensen, K.B., Wang, R.R.-C.: Cytological and molecular evidence for transferring Elymus coreanus from the genus Elymus to Leymus and molecular evidence for Elymus californicus (Poaceae: Triticeae). — Int. J. Plant Sci. 158: 872–877, 1997.
Jones, T.A., Redinbaugh, M.G., Zhang, Y.: The western wheatgrass chloroplast genome originates in Pseudoroegneria. Crop Sci. 40: 43–47, 2000.
Junghans, H., Metzlaff, M.: A simple and rapid method for the preparation of total plant DNA. — Biotechniques 8: 176, 1990.
Kellogg, E.A., Appels, R., Mason-Gamer, R.J.: When genes tell different stories: the diploid genera of Triticeae (Gramineae). — Syst. Bot. 21: 1–17, 1996.
Liu, Q., Ge, S., Tang, H., Zhang, X., Zhu, G., Lu, B.R.: Phylogenetic relationships in Elymus (Poaceae: Triticeae) based on the nuclear ribosomal transcribed spacer and chloroplast trnL-F sequences. — New Phytol. 170: 411–420, 2006.
Löve, A.: Conspectus of the Triticeae. — Feddes Rep. 95: 425–521, 1984.
Lu, B.R.: Biosystematic Investigations of Asiatic wheatgrasses — Elymus L. (Triticeae: Poaceae) — Dissertation, The Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Svalöve 1993.
Mason-Gamer, R.J.: Origin of North America Elymus (Poaceae: Triticeae) allotetraploids based on granule-bound starch synthase gene sequences. — Syst. Bot. 26: 757–758, 2001.
Mason-Gamer, R.J., Orme, N.L., Anderson, C.M.: Phylogenetic analysis of North American Elymus and the monogenomic Triticeae (Poaceae) using three chloroplast DNA data sets. — Genome 45: 991–1002, 2002.
McMillan, E., Sun, G.L.: Genetic relationships of tetraploid Elymus species and their genomic donor species inferred from polymerase chain reaction-restriction length polymorphism analysis of chloroplast gene regions. — Theor. appl. Genet. 108: 535–542, 2004.
Pelger, S.: Prolamin variation and evolution in Triticeae as recognized by monoclonal antibodies. — Genome 36: 1042–1048, 1993.
Petersen, G., Seberg, O.: Phylogenetic relationships of allotetraploid Hordelymus europaeus (L.) Harz (Poaceae: Triticeae). — Plant Syst. Evol. 273: 87–95, 2008.
Redinbaugh, M.G., Jones, T.A., Zhang, Y.: Ubiquity of the St chloroplast genome in St-containing Triticeae polyploids. — Genome 43: 846–852, 2000.
Soltis, D.E., Soltis, P.S.: Molecular data and the dynamic nature of polyploidy. — Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 12: 243–273, 1993.
Sun, G..L., Ni, Y., Daley, T.: Molecular phylogeny of RPB2 gene reveals multiple origins, geographic differentiation of H genome, and the relationship of the Y genome to other genomes in Elymus species. — Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 46: 897–907, 2008.
Svitashev, S., Bryngelsson, T., Li, X., Wang, R.R.C.: Genomespecific repetitive DNA and RAPD markers for genome identification in Elymus and Hordelymus. — Genome 41: 120–128, 1998.
Swofford, D.L.: PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony, Version 4 beta 10 win. — Sinauer Press, Sunderland 2003.
Tajima, F., Nei, M.: Estimation of evolutionary distance between nucleotide sequences. — Mol. Biol. Evol. 1: 269–285, 1984.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmouguin, F., Higgins, D.G.: The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tool. — Nucl. Acids Res. 25: 4876–4882, 1997.
Von Bothmer, R., Jacobsen, N.: Intergeneric hybridization between Hordeum and Hordelymus (Poaceae). Nordic J. Bot. 9: 113–117, 1989.
Von Bothmer, R., Lu, B.R., Linde-Laursen, I.B.: Intergeneric hybridization and C-banding patterns in Hordelymus (Triticeae, Poaceae). — Plant Syst. Evol. 189: 259–266, 1994.
Wang, G..Z., Miyashita, N.T., Kiochiro, T.: Plasmon analyses of Triticum (wheat) and Aegilops: PCR-single-strand conformational polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) analyses of organellar DNAs. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 14570–14577, 1997.
Wang, R.R.C., Dewey, D.R., Hisao, C.: Intergeneric hybrids of Agropyron and Pseudoroegneria. — Bot. Gaz. 146: 268–274, 1985.
Wang, R.R.-C., Von Bothmer, R., Dvorak, J., Fedak, G., Linde-Laursen, I., Muramatsu, M.: Genome symbols in the Triticeae. -In: Wang, R.R.C., Jensen, K.B., Jaussi, C. (ed.): Proceeding of the 2nd International Triticeae Symposium. Pp. 29–34. Logan 1994.
Xu, D.H., Ban, T.: Phylogenetic and evolutionary relationships between Elymus humidus and other Elymus species based on sequencing of non-coding regions of cpDNA and AFLP of unclear DNA. — Theor. appl. Genet. 108: 1443–1448, 2004.
Zeng, J., Zhang, L., Fan, X., Zhang, H.Q., Yang, R.W., Zhou, Y.H: Phylogenetic analysis of Kengyilia species based on nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences. — Biol. Plant. 52: 231–236, 2008.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported with grants from NSERC, a Senate Research Grant at Saint Mary’s University. Thanks go to Dr. Björn Salomon at the Swedish University of Agricultural Science, Regional Plant Introduction Station, USDA, Nordic Genetic Resource Center and Plant Gene Resources of Canada for kindly supplying the seeds used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Y., Asamoah-Odei, N. & Sun, G. Maternal origin, genome constitution and evolutionary relationships of polyploid Elymus species and Hordelymus europaeus . Biol Plant 55, 68–74 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-011-0009-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-011-0009-7