Abstract
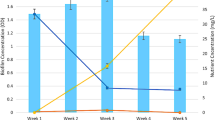
Pentachlorophenol (PCP) has been widely used as a pesticide in paddy fields and has imposed negative ecological effect on agricultural soil systems, which are in typically anaerobic conditions. In this study, we investigated the effect of repeated additions of PCP to paddy soil on the microbial communities under anoxic conditions. Acetate was added as the carbon source to induce and accelerate cycles of the PCP degradation. A maximum degradation rate occurred at the 11th cycle, which completely transformed 32.3 μM (8.6 mg L−1) PCP in 5 days. Illumina high throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA gene was used to profile the diversity and abundance of microbial communities at each interval and the results showed that the phyla of Bacteroidates, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Euryarchaeota had a dominant presence in the PCP-dechlorinating cultures. Methanosarcina, Syntrophobotulus, Anaeromusa, Zoogloea, Treponema, W22 (family of Cloacamonaceae), and unclassified Cloacamonales were found to be the dominant genera during PCP dechlorination with acetate. The microbial community structure became relatively stable as cycles increased. Treponema, W22, and unclassified Cloacamonales were firstly observed to be associated with PCP dechlorination in the present study. Methanosarcina that have been isolated or identified in PCP dechlorination cultures previously was apparently enriched in the PCP dechlorination cultures. Additionally, the iron-cycling bacteria Syntrophobotulus, Anaeromusa, and Zoogloea were enriched in the PCP dechlorination cultures indicated they were likely to play an important role in PCP dechlorination. These findings increase our understanding for the microbial and geochemical interactions inherent in the transformation of organic contaminants from iron rich soil, and further extend our knowledge of the PCP-transforming microbial communities in anaerobic soil conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaens P, Chang P, Barkovskii A (1996) Dechlorination of PCDD/F by organic and inorganic electron transfer molecules in reduced environments. Chemosphere 32:433–441
Augustijn-Beckers P, Hornsby A, Wauchope R (1994) The SCS/ARS/CES pesticide properties database for environmental decision-making. II. Additional compounds, reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer, New York, pp 1–82
Bae HS, Rash BA, Rainey FA, Nobre MF, Tiago I, Costa MS, Moe WM (2007) Description of Azospira restricta sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from groundwater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1521–1526
Bouchard B, Beaudet R, Villemur R, McSween G, Lepine F, Bisaillon JG (1996) Isolation and characterization of Desulfitobacterium frappieri sp. nov., an anaerobic bacterium which reductively dechlorinates pentachlorophenol to 3-chlorophenol. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 46:1010–1015
Brahushi F, Dörfler U, Schroll R, Munch JC (2004) Stimulation of reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene in soil by inducing the native microbial activity. Chemosphere 55:1477–1484
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:4516–4522
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, Owens SM, Betley J, Fraser L, Bauer M (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 6:1621–1624
Chang BV, Zheng JX, Yuan SY (1996) Effects of alternative electron donors, acceptors and inhibitors on pentachlorophenol dechlorination in soil. Chemosphere 33:313–320
Chen M, Shih K, Hu M, Li F, Liu C, Wu W, Tong H (2012) Biostimulation of indigenous microbial communities for anaerobic transformation of pentachlorophenol in paddy soils of southern China. J Agric Food Chem 60:2967–2975
Chen M, Tao L, Li F, Lan Q (2014) Reductions of Fe(III) and pentachlorophenol linked with geochemical properties of soils from Pearl River Delta. Geoderma 217–218:201–211
Chen Y, Tao L, Wu K, Wang Y (2016) Shifts in indigenous microbial communities during the anaerobic degradation of pentachlorophenol in upland and paddy soils from southern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:23184–23194
Chouari R, Le Paslier D, Dauga C, Daegelen P, Weissenbach J, Sghir A (2005) Novel major bacterial candidate division within a municipal anaerobic sludge digester. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2145–2153
Christiansen N, Ahring BK (1996) Desulfitobacterium hafniense sp. nov., an anaerobic, reductively dechlorinating bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:442–448
Coby AJ, Picardal F, Shelobolina E, Xu H, Roden EE (2011) Repeated anaerobic microbial redox cycling of iron. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6036–6042
Cutter LA, Watts JE, Sowers KR, May HD (2001) Identification of a microorganism that links its growth to the reductive dechlorination of 2,3,5,6-chlorobiphenyl. Environ Microbiol 3:699–709
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Keller K, Brodie EL, Larsen N, Piceno YM, Phan R, Andersen GL (2006) NAST: a multiple sequence alignment server for comparative analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W394–W399
Duhamel M, Edwards EA (2007) Growth and yields of dechlorinators, acetogens, and methanogens during reductive dechlorination of chlorinated ethenes and dihaloelimination of 1,2-dichloroethane. Environ Sci Technol 41:2303–2310
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2008) Microbial degradation of chlorinated phenols. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7:211–241
Fredrickson JK, Gorby YA (1996) Environmental processes mediated by iron-reducing bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 7:287–294
Graber JR, Leadbetter JR, Breznak JA (2004) Description of Treponema azotonutricium sp. nov. and Treponema primitia sp. nov., the first spirochetes isolated from termite guts. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1315–1320
Guan X, Liu F, Xie Y, Zhu L, Han B (2013) Microbiota associated with the migration and transformation of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons in groundwater. Environ Geochem Health 35:535–549
He J, Sung Y, Dollhopf ME, Fathepure BZ, Tiedje JM, Löffler FE (2002) Acetate versus hydrogen as direct electron donors to stimulate the microbial reductive dechlorination process at chloroethene-contaminated sites. Environ Sci Technol 36:3945–3952
Heimann AC, Batstone DJ, Jakobsen R (2006) Methanosarcina spp. drive vinyl chloride dechlorination via interspecies hydrogen transfer. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2942–2949
Holliger CH, Harmsen H, Ludwig W, Schumacher W, Tindall B, Vazquez F, Weiss N, Zehnder AJB (1998) Dehalobacter restrictus gen. nov. and sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic bacterium that reductively dechlorinates tetra- and trichloroethene in an anaerobic respiration. Arch Microbiol 169:313–321
Hori T, Muller A, Igarashi Y, Conrad R, Friendrich MW (2010) Identification of iron-reducing microorganisms in anoxic rice paddy soil by 13C-acetate probing. ISME J 4:267–278
Keith L, Telliard W (1979) ES&T special report: priority pollutants: Ia perspective view. Environ Sci Technol 13:416–423
Kennes C, Wu WM, Bhatnagar L, Zeikus J (1996) Anaerobic dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by methanogenic pentachlorophenol-degrading granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44:801–806
Khodadoust AP, Suidan MT, Acheson CM, Brenner RC (1999) Solvent extraction of pentachlorophenol from contaminated soils using water-ethanol mixtures. Chemosphere 38:2681–2693
Kittelmann S, Friedrich MW (2008) Identification of novel perchloroethene-respiring microorganisms in anoxic river sediment by RNA-based stable isotope probing. Environ Microbiol 10:31–46
Kotik M, Davidová A, Voříšková J, Baldrian P (2013) Bacterial communities in tetrachloroethene-polluted groundwaters: a case study. Sci Total Environ 454:517–527
Kranzioch-Seipel I, Beckert U, Shen C, Yin D, Tiehm A (2016) Microbial dechlorination of HCB, PCP, PCB180, HCH and PCE in a Yangtze Three Gorges Reservoir enrichment culture, China. Environ Earth Sci 75(10):1–9
Kuwatsuka S, Igarashi M (1975) Degradation of PCP in soils: II. The relationship between the degradation of PCP and the properties of soils, and the identification of the degradation products of PCP. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:405–414
Lendvay J, Löffler FE, Dollhopf M, Aiello M, Daniels G, Fathepure B, Gebhard M, Heine R, Helton R, Shi J (2003) Bioreactive barriers: a comparison of bioaugmentation and biostimulation for chlorinated solvent remediation. Environ Sci Technol 37:1422–1431
Li P, Wang X, Stagnitti F, Li L, Gong Z, Zhang H, Xiong X, Austin C (2005) Degradation of phenanthrene and pyrene in soil slurry reactors with immobilized bacteria Zoogloea sp. Environ Eng Sci 22:390–399
Li H, Peng J, Weber KA, Zhu Y (2011) Phylogenetic diversity of Fe(III)-reducing microorganisms in rice paddy soil: enrichment cultures with different short-chain fatty acids as electron donors. J Soils Sediment 11:1234–1242
Li Z, Inoue Y, Suzuki D, Ye L, Katayama A (2013) Long-term anaerobic mineralization of pentachlorophenol in a continuous-flow system using only lactate as an external nutrient. Environ Sci Technol 47:1534–1541
Li X, Zhang W, Liu T, Chen L, Chen P, Li F (2016) Changes in the composition and diversity of microbial communities during anaerobic nitrate reduction and Fe(II) oxidation at circumneutral pH in paddy soil. Soil Biol Biochem 94:70–79
Lucas R, Kuchenbuch A, Fetzer I, Harms H, Kleinsteuber S (2015) Long-term monitoring reveals stable and remarkably similar microbial communities in parallel full-scale biogas reactors digesting energy crops. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91:fiv004
Männistö MK, Tiirola MA, Salkinoja-Salonen MS, Kulomaa MS, Puhakka JA (1999) Diversity of chlorophenol-degrading bacteria isolated from contaminated boreal groundwater. Arch Microbiol 171:189–197
McCormick ML, Adriaens P (2004) Carbon tetrachloride transformation on the surface of nanoscale biogenic magnetite particles. Environ Sci Technol 38:1045–1053
Miura T, Yamazoe A, Ito M, Ohji S, Hosoyama A, Takahata Y, Fujita N (2015) The impact of injections of different nutrients on the bacterial community and its dechlorination activity in chloroethene-contaminated groundwater. Microbes Environ 30:164
Montenegro MA, Araujo JC, Vazoller RF (2003) Microbial community evaluation of anaerobic granular sludge from a hybrid reactor treating pentachlorophenol by using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Water Sci Technol 48:65–73
Narihiro T, Sekiguchi Y (2007) Microbial communities in anaerobic digestion processes for waste and wastewater treatment: a microbiological update. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:273–278
Pansu M, Gautheyrou J (2007) Handbook of soil analysis: mineralogical, organic and inorganic methods. Springer, Berlin, pp 289–367
Payne RB, May HD, Sowers KR (2011) Enhanced reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyl impacted sediment by bioaugmentation with a dehalorespiring bacterium. Environ Sci Technol 45:8772–8779
Riviere D, Desvignes V, Pelletier E, Chaussonnerie S, Guermazi S, Weissenbach J, Li T, Camacho P, Sghir A (2009) Towards the definition of a core of microorganisms involved in anaerobic digestion of sludge. ISME J 3:700–714
Ruckdeschel G, Renner G, Schwarz K (1987) Effects of pentachlorophenol and some of its known and possible metabolites on different species of bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2689–2692
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Shao Y, Chung BS, Lee SS, Park W, Lee SS, Jeon CO (2009) Zoogloea caeni sp. nov., a floc-forming bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:526–530
Soil Survey Staff (2014) Keys to soil Taxonomy. In: 12th USDA, p 179
Sponza DT, Cigal C (2008) Relationships between anaerobic consortia and removal efficiencies in an UASB reactor degrading 2,4 dichlorophenol (DCP). J Environ Manag 87:177–192
Stuart S, Woods S, Lemmon T, Ingle J (1999) The effect of redox potential changes on reductive dechlorination of pentachlorophenol and the degradation of acetate by a mixed, methanogenic culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 63:69–78
Tartakovsky B, Manuel MF, Beaumier D, Greer C, Guiot S (2001) Enhanced selection of an anaerobic pentachlorophenol-degrading consortium. Biotechnol Bioeng 73:476–483
Tong H, Hu M, Li F, Liu C, Chen M (2014) Biochar enhances the microbial and chemical transformation of pentachlorophenol in paddy soil. Soil Biol Biochem 70:142–150
Tong H, Liu C, Li F, Luo C, Chen M, Hu M (2015) The key microorganisms for anaerobic degradation of pentachlorophenol in paddy soil as revealed by stable isotope probing. J Hazard Mater 298:252–260
Utkin I, Dalton DD, Wiegel J (1995) Specificity of reductive dehalogenation of substituted ortho-chlorophenols by Desulfitobacterium dehalogenans JW/IU-DC1. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:346–351
Wang CC, Lee CM, Lu CJ, Chuang MS, Huang CZ (2000) Biodegradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in the presence of primary substrate by immobilized pure culture bacteria. Chemosphere 41:1873–1879
Xu Y, He Y, Zhang Q, Xu J, Crowley D (2015) Coupling between pentachlorophenol dechlorination and soil redox as revealed by stable carbon isotope, microbial community structure, and biogeochemical data. Environ Sci Technol 49:5425–5433
Yoshida N, Yoshida Y, Handa Y, Kim HK, Ichihara S, Katayama A (2007) Polyphasic characterization of a PCP-to-phenol dechlorinating microbial community enriched from paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 381:233–242
Zhang C, Katayama A (2012) Humin as an electron mediator for microbial reductive dehalogenation. Environ Sci Technol 46:6575–6583
Zhang H, Zivel M, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2010) Effect of dechlorination and sulfate reduction on the microbial community structure in denitrifying membrane-biofilm reactors. Environ Sci Technol 44:5159–5164
Zhang C, Zhang D, Li Z, Akatsuka T, Yang S, Suzuki D, Katayama A (2014) Insoluble Fe-humic acid complex as a solid-phase electron mediator for microbial reductive dechlorination. Environ Sci Technol 48:6318–6325
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41603127, 41420104007, and 41673135), the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation of China (2016A030313780, 2016B020242006 and S2013050014266), Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (201503107-4), the Scientific Platform and Innovation Capability Construction Program of GDAS (2016GDASPT-0212), and One Hundred Talents Programme of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, H., Chen, M., Li, F. et al. Changes in the microbial community during repeated anaerobic microbial dechlorination of pentachlorophenol. Biodegradation 28, 219–230 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9791-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9791-z