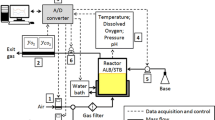
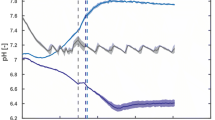
Abstract
A cultivation strategy combining the advantages of temperature-limited fed-batch and probing feeding control is presented. The technique was evaluated in fed-batch cultivations with E. coli BL21(DE3) producing xylanase in a 3 liter bioreactor. A 20% increase in cell mass was achieved and the usual decrease in specific enzyme activity normally observed during the late production phase was diminished with the new technique. The method was further tested by growing E. coli W3110 in a larger bioreactor (50 l). It is a suitable cultivation technique when the O2 transfer capacity of the reactor is reached and it is desired to continue to produce the recombinant protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Åkesson P Hagander JP Axelsson (2001) ArticleTitleAvoiding acetate accumulation in Escherichia coli cultures using feedback control of glucose feeding Biotechnol. Bioeng 73 223–230 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.1054 Occurrence Handle11257604
M Åkesson E Nordberg Karlsson P Hagander JP Axelsson A Tocaj (1999) ArticleTitleOnline detection of acetate formation in Escherichia coli cultures using dissolved oxygen responses to feed transients Biotechnol. Bioeng 64 590–598 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19990905)64:5<590::AID-BIT9>3.0.CO;2-T Occurrence Handle10404239
BJ Allison AJ Isaksson (1998) ArticleTitleDesign and performance of midranging controllers J. Process Contr 8 IssueID5 469–474 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0959-1524(98)00012-2
M Bailey P Biely K Poutanen (1992) ArticleTitleInterlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity J. Biotechnol 23 257–270 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-1656(92)90074-J
L Maré Particlede L Andersson P Hagander (2003) ArticleTitleProbing control of glucose feeding in Vibrio cholerae cultivations Bioprocess Biosystems Eng 25 221–228
T Holme S Arvidsson B Lindholm B Pavlu (1970) ArticleTitleEnzymes-laboratory scale production Process Biochem 5 62–66
K Konstantinov M Kishimoto T Seki Y Yoshida (1990) ArticleTitleA balanced DO-stat and its application to the control of acetic acid excretion by recombinant Escherichia coli Biotechnol. Bioeng 36 750–758 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.260360714
G Luli W Strohl (1990) ArticleTitleComparison of growth, acetate production and acetate inhibition of Escherichia coli strains in batch and fed-batch fermentations Appl. Environ. Microbiol 56 1004–1011 Occurrence Handle2187400
E Nordberg Karlsson L Dahlberg N Torto L Gorton O Holst (1998) ArticleTitleEnzymatic specicity and hydrolysis pattern of the catalytic domain of the xylanase xyn1 from Rhodothermus marinus J. Biotechnol 60 22–35 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1656(97)00178-8
JG Pan JS Rhee JM Lebeault (1987) ArticleTitlePhysiological constraints in increasing biomass concentration of Escherichia coli in fed-batch culture Biotechnol. Lett 9 89–94 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01032744
SO Ramchuran E Nordberg Karlsson S Velut L Maré Particlede P Hagander O Holst (2002) ArticleTitleProduction of heterologous thermostable glycoside hydrolases and the presence of host-cell proteases in substrate limited fed-batch cultures of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 60 IssueID4 408–416 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00253-002-1132-3 Occurrence Handle12466880
Rozkov A, (2001) Control of proteolysis of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. PhD thesis ISBN 917283160X. Stockholm, Sweden: Department of Biotechnology, Royal Institute of Technology
Silfversparre, G, Enfors S-O, Han L, Häggstöm L, Skogman H (2002) Method for growth of bacteria, minimising the release of endotoxins from the bacteria into the surrounding media. Patent: International publication number WO 02/36746
C Turner M Gregory M Turner (1994) ArticleTitleA study of the effect of specific growth rate and acetate on recombinant protein production of Escherichia coli JM107 Biotechnol. Lett 16 891–896 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00128620
Velut, S, de Maré L, Axelsson JP, Hagander P (2002) Evaluation of a probing feeding strategy in large scale cultivations. Technical Report ISRN LUTFD2TFRT-7601-SE. Lund, Sweden: Department of Automatic Control, Lund Institute of Technology. Legends
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Revisions requested 13 April 2005; Revisions received 6 May 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Maré, L., Velut, S., Ledung, E. et al. A cultivation technique for E. coli fed-batch cultivations operating close to the maximum oxygen transfer capacity of the reactor. Biotechnol Lett 27, 983–990 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-7844-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-7844-6