Abstract
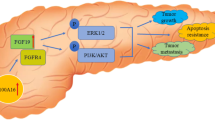
Pancreatic cancer remains the common cancer with the worst prognosis because of its late diagnosis and extensive metastasis. This study aimed to investigate the effects of GABRP on pancreatic cancer metastasis and the molecular mechanism. The expression of GABRP was measured using the quantitative real-time PCR and western blot. The biological behaviors of cancer cells were assessed using the cell counting kit-8, Transwell assay, and western blot. The regulation of GABRP on the MEK/ERK pathway was detected by western blot. The results indicated that GABRP was overexpressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and cells. Knockdown of GABRP suppressed cell viability, invasion, migration, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), whereas GABRP overexpression facilitated these biological behaviors. Inactivation of the MEK/ERK pathway reversed the effects on cellular processes induced by GABRP. Moreover, silencing of GABRP inhibited tumor growth. In conclusion, GABRP promoted the progression of pancreatic cancer by facilitating cell metastasis and tumor growth via activating the MEK/ERK pathway. The findings suggest that GABRP has the potential to be a therapeutic target for the metastatic pancreatic cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available upon reasonable request from corresponding author.
References
Bhattacharya A, Santhoshkumar A, Kurahara H, Harihar S (2021) Metastasis suppressor genes in pancreatic cancer: an update. Pancreas 50(7):923–932. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001853
Chen Y, Liu P, Shen D, Liu H, Xu L, Wang J, Shen D, Sun H, Wu H (2020) FAM172A inhibits EMT in pancreatic cancer via ERK-MAPK signaling. Biol Open. https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.048462
Diep CH, Munoz RM, Choudhary A, Von Hoff DD, Han H (2011) Synergistic effect between erlotinib and MEK inhibitors in KRAS wild-type human pancreatic cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 17(9):2744–2756. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2214
Du YX, Liu ZW, You L, Wu WM, Zhao YP (2016) Advances in understanding the molecular mechanism of pancreatic cancer metastasis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 15(4):361–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1499-3872(15)60033-9
Griesmann H, Mühl S, Riedel J, Theuerkorn K, Sipos B, Esposito I, Vanden Heuvel GB, Michl P (2021) CUX1 enhances pancreatic cancer formation by synergizing with KRAS and inducing MEK/ERK-dependent proliferation. Cancers (basel) 13(10):2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102462
Hu JX, Zhao CF, Chen WB, Liu QC, Li QW, Lin YY, Gao F (2021) Pancreatic cancer: a review of epidemiology, trend, and risk factors. World J Gastroenterol 27(27):4298–4321. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i27.4298
Jiang SH, Zhu LL, Zhang M, Li RK, Yang Q, Yan JY, Zhang C, Yang JY, Dong FY, Dai M, Hu LP, Li J, Li Q, Wang YH, Yang XM, Zhang YL, Nie HZ, Zhu L, Zhang XL, Tian GA, Zhang XX, Cao XY, Tao LY, Huang S, Jiang YS, Hua R, Qian Luo K, Gu JR, Sun YW, Hou S, Zhang ZG (2019) GABRP regulates chemokine signalling, macrophage recruitment and tumour progression in pancreatic cancer through tuning KCNN4-mediated Ca2+ signalling in a GABA-independent manner. Gut 68(11):1994–2006. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317479
Keleg S, Büchler P, Ludwig R, Büchler MW, Friess H (2003) Invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 2:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-2-14
Kim EK, Choi EJ (2010) Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.12.009
Klein AP (2021) Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(7):493–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00457-x
Lee S, Rauch J, Kolch W (2020) Targeting MAPK signaling in cancer: mechanisms of drug resistance and sensitivity. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031102
Li Y, Huang Y, Zhou C, Jiang PC, Pan W (2020) MiR-320c prevents the malignant development of cervical cancer by regulating GABRP level. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(17):8731–8739. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202009_22810
Loveday BPT, Lipton L, Thomson BN (2019) Pancreatic cancer: an update on diagnosis and management. Aust J Gen Pract 48(12):826–831. https://doi.org/10.31128/AJGP-06-19-4957
Ma J, Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhao T, Ji P, Song J, Zhang H, Luo W (2016) Proliferative effects of gamma-amino butyric acid on oral squamous cell carcinoma cells are associated with mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med 38(1):305–311. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2597
Ren B, Cui M, Yang G, Wang H, Feng M, You L, Zhao Y (2018) Tumor microenvironment participates in metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 17(1):108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0858-1
Sizemore GM, Sizemore ST, Seachrist DD, Keri RA (2014) GABA(A) receptor pi (GABRP) stimulates basal-like breast cancer cell migration through activation of extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). J Biol Chem 289(35):24102–24113. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.593582
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N, Zhou HF (2015) Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 35(6):600–604. https://doi.org/10.3109/10799893.2015.1030412
Sung HY, Yang SD, Ju W, Ahn JH (2017) Aberrant epigenetic regulation of GABRP associates with aggressive phenotype of ovarian cancer. Exp Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2017.62
Takehara A, Hosokawa M, Eguchi H, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O, Nakamura Y, Nakagawa H (2007) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) stimulates pancreatic cancer growth through overexpressing GABAA receptor pi subunit. Cancer Res 67(20):9704–9712. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2099
Wang J, Guo X, Xie C, Jiang J (2017) KIF15 promotes pancreatic cancer proliferation via the MEK-ERK signalling pathway. Br J Cancer 117(2):245–255. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.165
Wang SS, Xu J, Ji KY, Hwang CI (2021) Epigenetic alterations in pancreatic cancer metastasis. Biomolecules 11(8):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081082
Xu B, Sai N, Gilliham M (2021) The emerging role of GABA as a transport regulator and physiological signal. Plant Physiol 187(4):2005–2016. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab347
Yan L, Tu B, Yao J, Gong J, Carugo A, Bristow CA, Wang Q, Zhu C, Dai B, Kang Y, Han L, Feng N, Jin Y, Fleming J, Heffernan TP, Yao W, Ying H (2021) Targeting glucose metabolism sensitizes pancreatic cancer to MEK inhibition. Cancer Res 81(15):4054–4065. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3792
Yang Y, Ren L, Li S, Zheng X, Liu J, Li W, Fu W, Wang J, Du G (2022) GABRP is a potential prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltration and tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. Transl Cancer Res 11(4):649–668. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr-21-2021
Zeng S, Pöttler M, Lan B, Grützmann R, Pilarsky C, Yang H (2019) Chemoresistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 20(18):4504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184504
Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, Scheible M, Kaye J, Sugimoto H, Wu CC, LeBleu VS, Kalluri R (2015) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature 527(7579):525–530. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16064
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by YM, SG, WC, WJ, ZL, JH, and ZX. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YM and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics Approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The animal study was performed in line with the Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. The human and animal approvals were granted by the Ethics Committee of Xi’an No.3 Hospital.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Consent to Publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Fig. 1C.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Y., Li, R., Geng, S. et al. GABRP Promotes the Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer by Activation of the MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway. Biochem Genet 62, 242–253 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10410-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10410-z