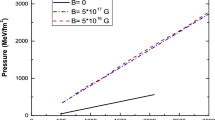
In this paper, we investigated the thermodynamic properties of strange quark matter using the Nambu-Jona-Lasinio (NJL) model at finite temperatures where we considered the dynamical mass as the effective interaction between quarks. By considering the pressure of strange quark matter (SQM) at finite temperatures, we showed that the equation of state of this system gets stiffer with increasing temperature. In addition, we investigated the energy conditions and stability of the equation of state and showed that the equation of state of SQM satisfies the conditions of stability. Finally, we computed the structure properties of hot strange quark stars (SQS) including the gravitational mass, radius, Schwarzschild radius, average density, compactness, and gravitational redshift. Our calculations showed that in this model, the maximum mass and radius of SQS increase with increasing temperature. Furthermore it was shown that the average density of SQS is greater than the normal nuclear density, and it is an increasing function of temperature. We also discussed the temperature dependence of the maximum gravitational mass calculated by different methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Gell-Mann, Phys. Lett., 8, 214, 1964.
G. Zweig, Cern-Reports, TH-401, TH-412, 1964.
R. L. Jaffe, Phys. Rev. Lett., 38, 195, 617E, 1977.
S. A. Chin and A. K. Kerman, Phys. Rev. Lett., 43, 1292, 1979.
E. Witten, Phys. Rev., D30, 272, 1984.
N. Itoh, Prog. Theor. Phys., 44, 291, 1970.
A. R. Bodmer, Phys. Rev., D4, 1601, 1971.
K. Sato and H. Suzuki, Phys. Rev. Lett., 58, 2722, 1987.
H. Suzuki and K. Sato, Perprint, UTAP, 53/87, 1987.
T. Hatsuda, Mod. Phys. Lett., A2, 805, 1987.
M. Prakash, J. M. Lattimer, A. W. Steiner et al., Nucl. Phys., A715, 835, 2003.
H. W. Yu, R. X. Xu, Res. Astron. Astrophys., 11, 471, 2010.
J. D. Carroll, D. B. Leinweber, A. W. Thomas et al., Phys. Rev., C79, 045810, 2009.
A. Chodos, R. L. Jaffe, K. Johnson et al., Phys. Rev., D9, 3471, 1974.
M. Alford, M. Braby, M. Paris et al., Astrophys. J., 626, 969, 2005.
B. Freedman and L. Mclerran, Phys. Rev., D16, 1130, 1977.
G. H. Bordbar and A. Peivand, Res. Astron. Astrophys., 11, 851, 2011.
G.H.Bordbar, A.Poostforush, A.Zamani, Astrophysics, 54, 277, 2011.
G. H. Bordbar, H. Bahri, and F. Kayanikhoo, Res. Astron. Astrophys., 12, 1280, 2012.
G. H. Bordbar, F. Kayanikhoo, and H. Bahri, Iran. J. Sci. Tech., A37, 165, 2013.
G. H. Bordbar, and Z. Alizadeh, Astrophysics, 57, 130, 2014.
G. H. Bordbar, M. Bigdeli, and T. Yazdizadeh, Int. J. Mod. Phys., A21, 5991, 2006.
T. Yazdizadeh and G. H. Bordbar, Res. Astron. Astrophys., 11, 471, 2011.
G. H. Bordbar and B. Ziaei, Res. Astron. Astrophys., 12, 540, 2012.
Y. Nambu and G. Jona-Lasinio, Phys. Rev., 122, 345, 1961.
S. P. Klevanski, Rev. Mod. Phys., 64, 3, 1992.
U. Vogl and W. Weise, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys., 27, 195, 1991.
M. Buballa, Phys. Rep., 407, 205, 2005.
K. Schertler, S. Leupold, and J. Schaffner-Bielich, Phys. Rev., C60, 025801, 1999.
G. X. Peng, H. C. Chiang, J. J. Yang et al., Phys. Rev., C61, 015201, 1999.
G. Y. Shao, M. Di Toro, B. Liu et al., Phys. Rev., D83, 094033, 2011.
M. R. Pennington, J. Phys. Conf. Ser., 18, 1, 2005.
S. Raha, AIP Conference Proceedings, 508, 226, 2000.
S. B. Ruster, V. Werth, M. Buballa et al., Phys. Rev., D73, 034025, 2006.
K. Nakazato, K. Sumiyosh, and S. Yamada, Phys. Rev., D77, 103006, 2008.
K. Nakazato, K. Sumiyosh, and S. Yamada, Astrophys. J., 721, 1284, 2010.
K. Nakazato, K. Sumiyosh, and S. Yamada, Astron. Astrophys., A50, 558, 2013.
J. R. Oppenheimer and G. M. Volkoff, Phys. Rev., 55, 374, 1939.
P. Chu, X. Li, B. Wang et al., Eur. Phys. J., C77, 512, 2017.
P. Haensel, A. Y. Potekhin, and D. G. Yakovlev, Neutron stars 1: Equation of state and structure, Springer, 2007.
A. Burrows and J. P. Ostriker, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci., 111, 2409, 2014.
A. G. Alaverdyan and G. S. Hajyan, J. Phys. Conf. Ser., 496, 012005, 2014.
M. Bagchi, S. Ray, M. Dey et al., Astron. Astrophys., 450, 431, 2006.
V. Dexheimer, J. R. Torres, and D. P. Menezes, Eur. Phys. J., C73, 2569, 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Astrofizika, Vol. 62, No. 2, pp. 313-328 (June 2019).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bordbar, G.H., Hosseini, R., Kayanikhoo, F. et al. Structure of Hot Strange Quark Stars: an NJL Model Approach at Finite Temperature. Astrophysics 62, 276–290 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10511-019-09580-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10511-019-09580-9