Abstract
Biotechnology might contribute to solving food safety and security challenges. However, gene technology has been under public scrutiny, linked to the framing of the media and public discourse. The study aims to investigate people’s perceptions and acceptance of food biotechnology with focus on transgenic genetic modification versus genome editing. An online experiment was conducted with participants from the United Kingdom (n = 490) and Switzerland (n = 505). The participants were presented with the topic of food biotechnology and more specifically with experimentally varied vignettes on transgenic and genetic modification and genome editing (scientific uncertainty: high vs. low, media format: journalistic vs. user-generated blog). The results suggest that participants from both countries express higher levels of acceptance for genome editing compared to transgenic genetic modification. The general and personal acceptance of these technologies depend largely on whether the participants believe the application is beneficial, how they perceive scientific uncertainty, and the country they reside in. Our findings suggest that future communication about gene technology should focus more on discussing trade-offs between using an agricultural technologies and tangible and relevant benefits, instead of a unidimensional focus on risk and safety.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Producing safe and high-quality food, while simultaneously handling consumer aversion towards novel food technologies are among the challenges the food industry faces today (Augustin et al. 2016; Asioli et al. 2017). Food biotechnology, more specifically, gene technology, is under a significant amount of scrutiny and scepticism from the public (Connor and Siegrist 2010; Runge et al. 2017; Rose et al. 2019; Siegrist and Hartmann 2020). However, the variety of applications summarised under the term “gene technology” (or sometimes genetic engineering) vary in terms of targeted produce (e.g., plant vs. animal), novelty or regulation, and unsurprisingly, different applications are perceived in different ways by the public (Kronberger et al. 2013; Siegrist and Hartmann 2020; Busch et al. 2021). The possible technologies used in plant breeding range from traditional breeding and mutagenesis (i.e., mutation may occur spontaneously, through targeted cross-breeding or as a result of exposure to chemical or radiation) to cis- or transgenic gene modification (i.e., insertion of (foreign) gene material) and finally, genome editing (i.e., insertion, deletion, modification or replacing of gene material). In this article, we will use the term “genetic modification” for older technologies and the term “genome editing” for new plant breeding techniques (for an overview of technologies and terminology see Beghin and Gustafson 2021).
The limited existing data (Weisberg et al. 2017; Shew et al. 2018) suggests that the editing of genes to achieve desirable changes of a plant’s attributes seems (as yet) to be under less public scrutiny than breeding technologies summarised under the term of genetic modification (e.g., transgenics). Due to their political situation of taking regulatory decisions somewhat independently from the European Union (EU), Switzerland, and the United Kingdom (UK) are faced with the decision to either adhere to the EU’s existing precautionary regulatory framework or change the current regulation based on the new technologies. In Switzerland, an adjustment versus prolongation of the current restrictive regulation regarding gene technology was recently discussed, which led to a controversial prolongation of the moratorium in autumn 2021 (The Federal Council of Switzerland 2020; Swiss Parliament 2021a). However, a recent decision by the Swiss Council of States suggests that gene technology, which does not involve the insertion of foreign gene material, might eventually be exempt from this moratorium (Swiss Parliament 2021b). Post Brexit, the UK government exhibited a more open strategy towards genome editing by proposing that genome-edited crops are exempted from GMO regulations, provided the genetic changes could occur naturally or via existing conventional breeding techniques (Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology, 2022). To support production of abundant and healthy food with less negative impact on the environment, the UK Department for Environmental Food and Rural Affairs recently conducted a public consultation about the regulation of genetic technologies, with a particular focus on genome editing (Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs Press Office 2020; Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs 2021). Following this, a new legislation is on the way to enable scientists across England to undertake plant-based research and development using genome editing (Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs, 2022; Ledford, 2021) For all these decisions, it is vital to take into account the public’s view of associated uncertainties and benefits, as well as regulatory decisions (Helliwell et al. 2019). Thus, the present study aims to investigate people’s perceptions and acceptance of gene technology in these two countries with a particular focus on genome editing compared to genetic modification. For this, an interdisciplinary focus was chosen, combining psychology (public perception and acceptance) and communication science (communicating scientific uncertainty, role of information source).
Theoretical background and study aim
The public perception and acceptance of genetic modification and genome editing.
For decisions regarding the regulation of emerging applications of gene technology, it is vital to understand the public’s view, and learn from previous challenges that have for example led to the 1998 de facto moratorium that suspended approvals of new genetically modified organisms in the EU including UK (Frewer et al. 2011), and a moratorium in Switzerland, in place since 2005, that prohibits the use of genetically modified organisms in agriculture (Hansen et al. 2003; Wohlfender-Bühler et al. 2016). Food biotechnology denotes the use of gene technology in agriculture, namely its use in crops and livestock. For example it can be applied for reducing food waste, pest and disease control or improving nutritional profile of a particular crop (Acatech 2017). From a scientific standpoint, decisions leading to the development and implementation of a technology are accompanied by weighing of benefits, costs, and uncertainties. However, for the implementation, sustenance and finally the success of a technology, public perceptions and acceptance need to be properly managed as well (Winkler et al. 2019).
Due to limited capacity processing, the public makes use of a variety of analytical (e.g., available knowledge) and heuristic strategies (e.g., trust heuristic, affect heuristic, prior experience, and representativeness heuristic), to form an opinion regarding a new and potentially complex technology (Connor and Siegrist 2010; Runge et al. 2017; Rose et al. 2019). Predicting the public reaction to a specific technology is therefore not straightforward, but rather requires a good understanding of the mechanisms at play. For example, the spontaneous associations that the technology raises for people, might determine what affect is associated with the technology (Finucane et al. 2000; Slovic et al. 2004). This in turn might determine, whether a technology is accepted or not, and whether people would buy food produced with this technology (Connor and Siegrist 2011).
Recent studies suggest that people are more positively inclined towards genome editing than (transgenic) genetic modification (Weisberg et al. 2017; Shew et al. 2018; McCaughey et al. 2019; Brossard 2019; European Food Safety Authority 2019; Beghin and Gustafson 2021). A recently published study by Busch et al. (2021) showed that genome editing is met with higher public acceptance for medical and food protection applications compared to applications in animals. Kronberger et al. (2013) found that public concerns are higher when the boundaries of species are crossed in breeding (transgenics) than if the boundaries are not crossed and genes from similar or the same species are inserted (cisgenics). Moreover, editing of genes within a host leads to less negative associations than the insertion of foreign genes to the host, as this is associated with contamination and “Frankenstein food” (Delwaide et al. 2015; Edenbrandt et al. 2018). Another important factor is that genome editing is a more precise technology than traditional breeding, mutagenesis, and cis- or transgenic gene modification, and thus, it is associated with less (perceived) uncertainty (Shew et al. 2018; Brossard 2019). Lastly, the conceptualisation of genome editing in the media is more positive than the conceptualisation of genetic modification, and thus far, oppositional non-governmental organisations (NGOs) have not been particularly active against the technology (Zhang et al. 2018; Brossard 2019; McCaughey et al. 2019). The latter point might be particularly relevant, as in the digital information environment journalistic and user-generated media might act as an important communicator of uncertainties, risks, and benefits of a new technology.
The communication of scientific uncertainty
Generally, technological innovations such as gene technology, involve a degree of (scientific) uncertainty regarding opportunities, risks, and outcomes (Acatech 2017; Lang et al. 2019). A recent report by the European Food Safety Authority et al. (2019) recommended communicating scientific uncertaintyFootnote 1 to the public to increase perceived transparency and social trust in regulators. Social trust refers to the perception that institutions (e.g., regulation) are honest, credible, capable of managing a particular technology and share similar values (Siegrist 2008; Siegrist et al. 2000; Siegrist 2021). However, science communication, particularly communicating scientific uncertainty to lay-people is not a trivial task, and the literature has thus far not substantiated the claims that communicating uncertainty generally increases trust (Peters and Dunwoody 2016; Retzbach et al. 2016; Guenther et al. 2019). For example, it was suggested that the admission of uncertainty by experts (e.g., scientists, regulators) might also lead to a decrease in perceived competence, and thus, reduce the social trust needed for the acceptance of a technology (Siegrist 2019). However, Hendriks et al. (2016) found that if researchers as blog authors mentioned uncertainties themselves, epistemic trust remained stable.
Additionally, people differ in their awareness for scientific evidence and uncertainty, and even in their tolerance for (scientific) uncertainty (Kessler 2016; Retzbach et al. 2016; Lilleholt 2019). This will likely have an additional impact on the effect of uncertainty communication on their beliefs and acceptance (Kessler 2016). For example, people usually contextualise chemical substances as either safe or dangerous (Bearth et al. 2019; Saleh et al. 2019). This is rooted in people’s unfamiliarity with risk assessments, which rely on scientific methodology that introduce some degree of uncertainty (e.g., dose-response mechanisms, reliance on animal testing) (Kraus et al. 1992; Saleh et al. 2019). Therefore, people might not be willing to accept gene technology unless it is described as certainly safe for health and the environment. It is important to note though that, while the perception of the absence of a significant risk is certainly a precondition for acceptance, prior research clearly shows that it is not a guarantee for acceptance (Marris 2001; Stirling 2007).
The influence of journalistic media vs. user-generated media in public’s perception of communication about gene technology.
The public perception of and scepticism towards gene technology applied to food production has, among other sources, been linked to the media (Augoustinos et al. 2010; Bearth and Siegrist 2016; Runge et al. 2017). For example, a study about UK newspaper articles on genetically modified crops and food (Augostinos et al. 2000) showed that the topical focus was first, on genetic modification as risky, uncontrollable, and as an unnatural “Frankenstein” technology, and second, on the roles of different stakeholders (e.g., the opposed public, the government determined to introduce genetic modification despite opposition, inconclusive science, lobbying companies). Walker and Malson (2020) suggest that the public views genome editing in a slightly more positive light than genetic modification. The topics that dominated public discussions on Facebook regarding news posts on genome editing in agriculture are as follows: messing with nature or the natural order, pro-science arguments and focus on beneficial aspects, the conflation with genetic modification and referencing science fiction.
As shown by Walker and Malson (2020), digitalisation has contributed to a landscape of bi-directional public discourse, which means that people are no longer passive receivers of information but might even actively communicate via online blogs (Kwak et al. 2010). With at least 150 million professional and amateur blogs on the Internet, blogging offers a potentially powerful tool for engaging large and diverse audiences with science (Ranger and Bultitude 2014). In general, blogs have emerged as increasingly important news sources that might even influence the public discourse and societal decision making. The essential qualities of credibility and capturing public trust in the news sphere, however, often depends upon the established reputation of journalistic news (Gunter et al. 2000; Lofgren 2013). Bloggers are occasionally criticized by journalists and the public for not being able to master the professional rules and standards of message delivery as there is no clear or legitimate gatekeeping process, for having a highly personal and opinionated nature, for the fact that anyone can create a blog and publish their thoughts on any subject they like, regardless of whether they are qualified, and sometimes for spreading misinformation based on personal interests (Gunter et al. 2009).
Previous research showed ambivalent findings on the question of whether people trust in online newspapers more than blogs. For example, Gunter et al. (2009) point out that only a few blogs can reach the trust placed in traditional (online) news. However, the experimental study by Mackay and Lowrey (2007) shows that, information on blogs was judged to be more credible than the same information in an online newspaper. In addition, among experienced internet users, blogs are perceived as more credible or at least as credible as journalistic media such as newspapers or television (TV; Banning and Sweetser 2007; Johnson and Kayne 2009). Overall, it is largely unclear, how user-generated media (e.g., blogs) versus journalistic media (e.g., online newspaper articles) affect people’s perceptions of information on gene technology and their trust in these two sources.
Study aims and objectives
This study aimed to investigate people’s perceptions and acceptance of food biotechnology with a particular focus on transgenic genetic modification versus genome editing. It was conducted in the UK and Switzerland because the findings may help UK Government Agencies with their recent plans on post-Brexit regulation of plant breeding techniques including genome editing, as well as the Swiss government’s open questions regarding the regulation of genome editing (Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs Press Office 2020; Federal Office for the Environment 2020; The Federal Council of Switzerland 2020). Thus, the research questions of this study were as follows:
-
(1)
What kind of associations (e.g., words, images, thoughts) and affect do Swiss and UK citizens have regarding the term “food biotechnology”?
-
(2)
Is the acceptance of genome editing higher than the acceptance of transgenic genetic modification? Does the acceptance relate to the level of communicated uncertainty (high versus low) and the media format (journalistic versus user-generated)?
-
(3)
What role do individual factors play in people’s acceptance of transgenic genetic modification and genome editing in agriculture?
Methodology
Study design
Our online study comprised three parts: (1) people’s associations and affect towards food biotechnology, (2) an experiment on people’s views of the agricultural application of transgenic genetic modificationFootnote 2 and genome editing, and (3) individual variables (e.g., perceived uncertainty of scientific evidence, trust). As this study was part of a larger project, not all variables included in the questionnaire will be presented in this article (e.g., genetic literacy, objective and subjective knowledge about genetic modification versus genome editing)Footnote 3. The experimental part was a 2 (technology: genetically-modified food vs. genome-edited food) by 2 (uncertainty: high certainty vs. high uncertainty) by 2 (media: journalistic vs. user-generated blog) mixed design. Technology was a within-person variable, while uncertainty, media and country were between-person variables.
Study procedure
The questionnaire was originally developed in English and translated to German by a bilingual translator. The stimulus material and questionnaire in both languages were pretested and revised accordingly, prior to data collection. The samples were recruited and incentivised in collaboration with a market research company (respondi AG; Koeln, Germany). Quota sampling was applied based on gender, age, and education. Participants with a very short completion time were excluded (UK: n = 43; Switzerland: n = 25). For this, the cut-off point was a duration of the median divided by two (UK: 358.5 s; Switzerland: 404.0 s) as recommended in the literature (Greszki et al. 2014)Footnote 4.
Materials
First part: Associations and affect towards biotechnology
After providing informed consent, participants’ gender, age, and education were assessed. Participants were next asked to provide the words, images, and thoughts that come to their minds when hearing the term “food biotechnology” (associations of food biotechnology). The participants were asked to provide at least one association and were free to provide up to a total of three associations. Subsequently, they were presented with a slider (1 ‘very negative feelings,’ 5 ‘neutral feelings,’ to 11 ‘very positive feelings’) for each mentioned association (affect to associations of biotechnology). Next, the following introduction to ‘food biotechnology’ and its role in securing our food supply was provided, followed by another slider inquiring what kind of feelings were evoked by this description to measure their affect to biotechnology (1 ‘very negative feelings,’ to 6 ‘neutral feelings,’ to 11 ‘very positive feelings’):
In order to secure our food supply, the prolongation of shelf life and thus, the reduction of food waste, is an important goal that could be tackled by food biotechnology. Some developments in food biotechnology, such as the use of plastic wraps, may seem like simple advances in the world of food production and consumption. Others appear to be a lot more technological, such as the modification or editing of the genes of our food sources (e.g., maize, soya or tomatoes). These new species have desired properties to reduce food waste, such as pest resistance or longer shelf life.
Second part: Experimental section on a specific application in agriculture
For the experimental part, participants from each country were randomly split into four groups (uncertainty x media). Participants in each group were presented first a text on a genetically-modified tomato with prolonged shelf life followed by a text on a genome-edited tomato with prolonged shelf life. The texts differed between-person in the sentence regarding scientific uncertainty: ‘Scientists conclude with high certainty…’ for groups 1 and 3 and ‘Scientists conclude with high uncertainty…’ for groups 2 and 4. Additionally, the texts differed between-person in the presented media: Groups 1 and 2 were asked to imagine that the two texts originate from an online newspaper, while groups 3 and 4 were asked to imagine that the texts originate from an online food blog that they regularly follow. Figure 1 presents two example texts for genetically-modified and genome- edited food.
Acceptance was measured directly after presenting each text with three items comprising general acceptance (‘Based on the text, do you think genetic modification/genome editing should be used in the production of fruits and vegetables?’ on a slider from 1 ‘should not be used under any circumstances’ to 11 ‘should definitely be used.’) and personal acceptance in form of willingness to buy (WTB) and willingness to eat (WTE). WTB was measured as ‘How willing would you be to buy a genetically modified tomato/genome-edited tomato with extended shelf life?’ and WTE as ‘How willing would you be to eat a genetically modified tomato/genome-edited tomato with extended shelf life?’ on a slider from 1 ‘not willing at all’ to 11 ‘very willing.’ The three items resulted in a one-factor solution according to a Principal Component Analysis (PCA; for genetic modification: KMO = 0.7, Eigenvalue: 2.7, % of variance: 90.9%; for genome editing: KMO = 0.8, Eigenvalue: 2.8, % of variance: 93.9%) and exhibited an excellent internal consistency (for genetic modification: α = .95; for genome editing: α = .97).
Manipulation checks were implemented for the two between-person independent variables uncertainty and media. As a manipulation check for the variable uncertainty, the perceived uncertainty regarding the safety of genetically-modified and genome- edited food was measured directly after the experimental part with the following item: ‘Based on the text, how certain or uncertain are you that the risk assessments ensure the safety of the genetically modified tomato/genome-edited tomato?’ on a slider from 1 ‘certain that the safety is NOT ensured’ to 6 ‘uncertain’ to 11 ‘certain that the safety is ensured.’ For ease of interpretation, the scale was recoded into three categories (1 to 5 ‘certain that safety is NOT ensured,’ 6 ‘uncertain’ and 7 to 11 ‘certain that the safety is ensured’). As a manipulation check for the variable media, participants were asked to indicate what online newspaper or food blog they were imagining when reading the experimental text.
Third part: Individual variables related to the acceptance
All subsequently presented multi-item scales were subjected to a PCA (oblique rotation in case of multi-dimensionality) and reliability analysis (Cronbach’s Alpha). The scales were built by taking the mean over all respective items.
First, participants were asked to indicate their trust in different information sources. This item was based on prior literature and adapted to the current context (Costa-Font et al. 2008). A PCA with oblique rotation resulted in two subscales (cf. Table 1): Trust in institutions with government agencies, farmers, scientists, and the food industry (α = 0.72) and trust in the media with online blogs, journalistic, and social media (α = 0.82).
Second, a scale measuring the perceived certainty of scientific evidence (Marschall et al. 2011; Retzbach et al. 2016) was included (cf. Table 1). Compared to the original scale (Retzbach et al. 2016), solely the objective subscale was used in this article, where higher scores indicate higher perceived certainty of scientific evidence. The five items resulted in a one-factor solution according to a PCA with an excellent internal consistency (cf. Table 1, α = 0.91).
Third, relevance of prolonged shelf life was measured with the following self-developed item: “In general, how desirable do you find it that tomatoes have a longer shelf life?” slider from 1 ‘not desirable at all’ to 11 ‘very desirable’).
Fourth, overall text content and source credibility were assessed for the two experimental texts (Roberts 2010). The scale comprises 10 bipolar items ranging for instance from 1 to 5 (the source…: can/cannot be trusted, is inaccurate/accurate, is unfair/fair, does not tell the complete story/tells the complete story, is biased/is not biased; the text…: is unbelievable/believable, is inaccurate/accurate, is not trustworthy/is trustworthy, is biased/not biased, reflects part of the story/the whole story). The 10 items were combined into one scale by taking the mean over all items, measuring the credibility of the messenger and message (KMO = 0.9, Eigenvalue: 6.0, % of variance: 59.8%; α = 0.92).
Lastly, participants’ general risk aversion was measured with one self-developed item: “How do you describe yourself: How willing are you in general to take risks?” (1: “not willing to take risks at all” – 7: “very much willing to take risks.”).
Data analysis
For the associations regarding the term “food biotechnology,” a manual standardised content analysis was conducted, which resulted in 15 categories. The analysis was performed by three trained and independent coders with good intercoder reliability (Krippendorff`s Alpha = 0.81; Cohens Kappa = 0.81). For the final version, the first author reviewed and resolved all irregularities. Subsequently, correspondence analysis was applied for analysing the relationship between categorical data (in this case associations and country) and other variables (in this case affect). The descriptive and multivariate data analyses were conducted in SPSS 25 (IBM Corp. 2017). All included variables and scales were subjected to descriptive and an exploratory data analysis prior to the multivariate analyses. The experimental effects on people’s perceptions were assessed with a mixed Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) with three independent variables (technology, uncertainty, media) and the dependent variable acceptance. The mixed ANOVA were conducted separately for Switzerland and the UK. Lastly, the impact of individual variables on people’s acceptance of genetically-modified and genome- edited food was analysed in two separate linear regression analyses.
Results
Sample description
There were n = 505 participants (50.8%) from Switzerland and n = 490 participants (49.2%) from the UK. Table 2 presents an overview of the socio-demographics of the sample in total and separated by country. Education was recoded to approximate comparability with educational systems in Switzerland and the UK into low (n = 430, 43.2%) and high (n = 560, 56.3%). Based on the quota design, gender, age, and education distributions were representative for the respective populations in Switzerland and the UK above 18 years of age (United Nations 2019).
Food biotechnology: associations and affect
In total, participants provided 2415 usable associations, whereof 857 first associations, 806 s associations and 752 third associations were provided. Table 3 shows an overview of the 15 categories identified in the content analysis. The following three categories were most prevalent: “Science and research” (21.4%), “Specific food, eating and nutrition” (12.7%) and “Genes and genetic modification” (9.7%). Other prevalent associations were regarding industry, innovation, unnaturalness and chemicals. Moreover, a substantial number of participants reported generic positive and negative associations. The affective rating of the most prevalent associations (i.e., first association, mentioned more than 100 times) was positive for “Science and research” (M = 7.0, SD = 2.3) and for “Specific food, eating and nutrition” (M = 8.0, SD = 2.7), while “Genes and genetic modification” was associated with negative affect (M = 3.8, SD = 2.7). The overall affect reported for the mentioned associations was near the midpoint of the scale (Switzerland: M = 6.3, SD = 2.4, UK: M = 6.1, SD = 2.6) and did not differ significantly between countries, t(993) = 1.1, p = .249, d = 0.1. However, after reading the introductory text, participants from the UK (M = 6.5, SD = 2.8) reported more positive affect than participants from Switzerland (M = 6.0, SD = 2.6), t(985) = -2.7, p = .006, d = 0.2.
A correspondence analysis was conducted with the first associations that were mentioned at least 20 times, the valence of the affect related to the association (negative, neutral, or positive), and the country of the respondent. Correspondence analysis is a way to visualise large cross-tables. In this case, the cross-table was made up of 13 columns (the 13 associations) and 6 rows (negative, neutral, and positive affect in the two countries) that displays the observed frequency in the cells. The cross-table, which is the basis of this correspondence analysis, can be found in the Supplementary material (Table B). For the correspondence analysis, the following values were uncovered: χ2(60) = 413.5, p < .001, with an inertia of λG = 0.49. The first dimension explained 73% of variance and the second dimension explained 17%, which is why a two-factor solution was used in Fig. 2. Associations that are further from the centre (i.e., innovation, eco products, natural) are more discriminating than associations closer to the centre (i.e., transformation, industry, science, and research). This allows to draw conclusions on the relationship between association, affect, and country of respondent. “Eco products” (in down/left quadrant, far from centre) and “natural” (in down/left quadrant, far from centre) were mostly mentioned by Swiss participants and were associated with positive affect. As both associations are far from the centre, they discriminate well between Swiss and UK participants and the valence of the associated affect. “Chemical” (in bottom/right quadrant, rather close to the centre) was more frequently mentioned by Swiss than UK participants, and it was mostly associated with negative affect in both countries. “Genes and genetic modification” (in top/right quadrant, close to the axis of dimension 2) was mostly mentioned by UK participants, yet with varying affect. In another example, “innovation” (in top/left quadrant, far from the centre) was mostly associated with positive affect in the UK, while in Switzerland, it was mostly associated with neutral affect.
Acceptance of genetically-modified and genome-edited tomato
In this section, the results of the experimental section on acceptance of a specific application in agriculture are presented. Prior to the experimental effects, the manipulation checks regarding the independent variables uncertainty and media are presented. Regarding uncertainty, the expected effect was achieved: Significantly more participants in the ‘high uncertainty’ condition were certain that the safety is not ensured for genetically-modified tomato (61.7%, χ2(2) = 43.5, p < .001) and for genome-edited food (62.2%, χ2(2) = 62.1, p < .001) than participants in the ‘high certainty’ condition (38.3% and 37.8%). The manipulation check regarding media demonstrated that it was easier for participants to imagine an online newspaper than an online food blog, as 227 participants (46.3%) indicated not reading an online newspaper compared to 435 participants (86.1%) that indicated not reading food blogs. Participants named a variety of online newspapers in Switzerland (e.g., Tagesanzeiger, 20 Minuten, Neue Zuercher Zeitung) and the UK (e.g., The Telegraph, The Guardian, Daily Mail). However, for the blogs, many participants did not mention any food blog at all, but rather mentioned Facebook, companies, or recipe blogs (e.g., Nigella Lawson, Betty Bossy).
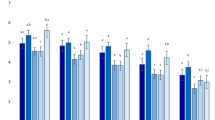
For acceptance, solely small effects of the experimental manipulation were observed (cf. Table 4). The mean values and 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) for each cell are presented in Table A of the Supplemental Material. Regarding acceptance, the significant main effect of technology exhibited the largest effect size. Participants from both countries exhibited slightly higher levels of acceptance for the genome-edited food (CH: M = 4.4, 95%CI[4.1, 4.7]; UK: M = 5.6, 95%CI[5.3, 5.9]) than for genetically-modified food (CH: M = 4.2, 95%CI[3.9, 4.4]; UK: M = 5.4, 95%CI[5.1, 5.6]). Smaller effects for an interaction between technology and uncertainty were found in both countries. Participants exhibited similarly low acceptance for the genetically-modified and genome-edited food in the ‘high uncertainty’ condition, but higher acceptance for the genome-edited food than the genetically-modified food in the ‘high certainty’ condition. In the UK, a main effect of uncertainty was uncovered, while this main effect was only marginally significant in Switzerland. Participants exhibited higher acceptance of the genetically-modified and genome-edited food in the ‘low uncertainty’ condition. In the UK, a significant interaction effect of technology and media suggests that acceptance was higher for genetically-modified food in the ‘user-generated condition,’ but not in the ‘journalistic condition.’ All other main and interaction effects were not significant.
The role of individual factors in the acceptance of genetically-modified vs. genome-edited food
To investigate participants’ acceptance of genetically-modified vs. genome- edited food further, two linear regression analyses were conducted but experimental manipulations were controlled. Table 5 presents the results of these two linear regression analyses. Similar amounts of variance in acceptance of genetically-modified vs. genome-edited food respectively could be explained by the suggested independent variables (roughly 60% for the acceptance of genetically-modified and genome- edited tomatoes). Similarly, almost the same variables were important for the acceptance of the two technologies, with three exceptions: Gender, country, and trust in institutions was only relevant for the acceptance of genetically-modified food. For these variables, acceptance of genetically-modified food was higher if participants were male, from the UK, and had higher trust in institutions. The most important variable was whether participants deemed it important that the shelf life of a tomato is prolonged. The more important participants thought this was, the higher their acceptance was for both genetically-modified and genome-edited food. The acceptance of both genetically-modified and genome-edited tomato was higher if (1) participants initially expressed more positive affect towards biotechnology, (2) they perceived the message and messenger to be more credible, and (3) they perceived more scientific certainty. Acceptance of genetically-modified and genome-edited food was lower if (1) participants expressed higher general risk aversion, and (2) participants were in the high uncertainty condition.
Discussion and implications for practice and future research
This study sheds light on Swiss and UK citizens’ perceptions of food biotechnology and their acceptance of the application of genetic modification and genome editing in agriculture.
It replicates previous findings (e.g., Gaskell et al. 2011; European Food Safety Authority 2019) that people in the UK are more supportive of biotechnology than people in Switzerland or other European countries. The continuously prolonged moratorium in Switzerland prohibiting the use of genetically-modified organisms (GMOs) in agriculture likely impacts people’s perceptions of biotechnology. The debate about this moratorium has been present in the public discourse and thus, shapes the public perception of biotechnology in Switzerland (Connor and Siegrist 2011). The differences in concern about biotechnology in Switzerland, compared to the UK, are also documented in the Eurobarometer survey from 2010, where participants from the UK exhibited the highest support for GMOs (44% compared to solely 20% in Switzerland) (Gaskell et al. 2011). This finding is also reflected in the most recent Eurobarometer survey, where the UK participants did not express particularly high concern regarding genetically modified food (European Food Safety Authority 2019). Aside from these cross-country and regulatory differences between the UK and Switzerland, our findings also explain some of the differences in acceptance of these technologies suggesting interesting starting points for future research.
First, it is possible that large interpersonal differences exist in people’s understanding of food biotechnology including both genetic modification and genome editing. Many participants in our study did not provide a single association, but rather three different associations suggesting a multi-dimensional conceptualisation of food biotechnology. Future research should be aware of the different aspects that people associate with food biotechnology. Swiss participants exhibited some misconceptions regarding what food biotechnology (“Lebensmittelbiotechnologie” in German) comprises because organic farming (“Biologische Landwirtschaft” in German) and eco products (“Bioprodukte” in German) were frequently mentioned. This might purely be based on the associations raised by the similarity in the wording. Moreover, Swiss people’s affective response towards biotechnology became more negative compared to UK participants after reading the definition. For UK participants, the term “food biotechnology” was more strongly associated with innovation. The findings of a previous Swiss study (Connor and Siegrist 2011) show some overlap (e.g., mention of science, manipulation, nutrition), as well as deviations that are likely be explained by changes in the public discourse over time and by the specific sample of the previous study (i.e., people living near protected sites in Switzerland).
Second, genome editing was more positively perceived and highly accepted than genetic modification in both samples (particularly, under conditions of low uncertainty). This might be explained partly by the fact that the former has been described as more precise compared to the latter in our vignette. The increased precision, compared to mutagenesis and genetic modification, is indeed one of the most relevant novelties of genome editing. Science communicators should discuss differences in technologies in terms of precision (e.g., mutagenesis, transgenic genetic modification) (cf. for a discussion of precision and genomic irregularities: Rosenbaum 2019; Kawall et al. 2020). A study on people’s acceptance of cisgenic and transgenic rice found that acceptance was higher for inserting genes from the plant’s own gene pool than for inserting genes from another plant (Delwaide et al. 2015). Therefore, it may be concluded that introducing “foreign” genes in a plant triggers the notion of contamination and thus, sparks rejection in consumers (Egolf et al. 2019; Siegrist and Hartmann 2020). This should potentially explain the higher acceptance of genome editing applications that do not require mixing of genes from different species. Improved precision and the notion of contamination are just two of the underlying factors that might explain differences in the perception of genetic modification and genome editing. Other factors may range from trust in science to ethical considerations to familiarity and terminology (Siegrist and Hartmann 2020; Beghin and Gustafson 2021).
Third, our results revealed that having tomatoes with longer shelf life is the most important predictor of UK and Swiss participants’ acceptance of genome-edited tomatoes. This suggests the importance of perceiving relevant personal or societal benefits on the acceptance of gene-edited foods. Prior research has also suggested that offering clear and tangible benefits positively impacts consumer acceptance of food innovations and technology (Frewer et al. 2011; Bearth and Siegrist 2016; Zahry and Besley 2019). Therefore, more personal benefits from genome-edited foods, such as the nutrient-enhanced golden rice or the non-browning artic apple might have even stronger impacts on people’s acceptance. Thus, further research is needed to examine the role of benefit perceptions in consumer acceptance of genome-edited foods.
Fourth, the experimental results for both genetic modification and genome editing suggest that people differentiate between levels of uncertainty regarding safety, and if high levels of uncertainty are communicated people are less willing to accept the technology. The effect of uncertainty perception on acceptance was small, whereas other factors, such as perceived benefit and the associations raised by the technology (i.e., increasing shelf life), were higher. Generally, research into people’s acceptance could benefit from focusing more strongly on benefit perception rather than perceived uncertainty regarding safety or risk perception. For example, genome editing can be suggested as a more sustainable alternative to conventional agriculture (e.g., the use of fungicides) to combat late blight in potato (Swiss Academies of Arts and Sciences 2018). Moreover, in this article, we focused on perceived uncertainty of safety, whereas uncertainty also relates to financial or social outcomes (Marris 2001). To conclude, showing the usefulness of gene technology might be a more successful strategy to improve people’s perceptions and acceptance than affirming that the risks are negligible (Kaptan et al. 2018).
Lastly, in this study, the source of this information (media) did not have a significant impact on Swiss and UK participants’ acceptance. This finding, however, should be interpreted with caution as the manipulation check suggested that journalistic sources were more easily available to the participants than user-generated blogs and that the provided scenario was hypothetical and the sources of information fictitious. Furthermore, people might have trusted in the information, regardless of the indicated source as the experiment was conducted on behalf of two universities. Future studies should attempt to deepen the understanding of the role that the new digital information landscape plays in the perception and acceptance of gene technology.
Limitations
This study has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results and designing future studies. First, the participants were recruited via a professional market research company. Its participants are likely composed of people that regularly fill out questionnaires. Despite data cleaning, it is possible that not all participants read the texts carefully. Second, it is challenging to measure education levels comparably, as Switzerland and the UK have different educational systems. Therefore, more UK participants were categorised into the high education group than Swiss participants, although this might not necessarily reflect different educational levels. However, it cannot entirely be ruled out that the participants from the two countries had different levels of scientific knowledge, which might explain some of the uncovered differences. Third, we measured self-reported acceptance for a hypothetical newspaper / blog story and are thus, not able to make predictions regarding actual decision making when confronted with a real article or blog, as well as real genetically-modified or genome-edited tomato sold in the shops. Fourth, the uncertainty manipulation and corresponding manipulation check focused rather simplistically on safety, while uncertainty might also relate to other aspects, such as economic or social outcomes of implementing genetic modification and genome editing in agriculture. These additional aspects that might relate to uncertainty should be covered in future experiments. Lastly, the results regarding genetic modification and genome editing might have turned out differently if we had not utilised a within-subjects design (i.e., shown the text of genome editing after genetic modification) or counterbalanced the order of presentation. Therefore, future studies should investigate the differences in the perception of older and newer breeder technologies in more depth.
Conclusions
To sum up, the following three main conclusions can be drawn from the findings. (1) genome editing might be met with more favourable perceptions than genetic modification in agriculture, (2) to improve people’s acceptance of gene technology, it is necessary to present tangible and relevant benefits (i.e., a higher perceived need for a tomato with a prolonged shelf-life implied higher acceptance), and (3) how scientific uncertainty is communicated has an impact on people’s perceptions and acceptance. Frequently, risk communication efforts are recommended to transparently broach the topic of uncertainty, despite the lack of broad knowledge about the effects of the communication of uncertainty, particularly in the field of innovative food technologies. Future research should attempt to clarify what types of uncertainty need to be communicated, and how these should be communicated regarding gene technology.
Notes
In this study, we focused on epistemic uncertainty of scientific claims, that is, claims based on scientific evidence or theories and/or claims communicated by scientists.
Subsequently called ‘genetic modification’ for reader friendliness.
Full questionnaire available upon request from the corresponding author.
Additionally, it was controlled how much time the participants spent on the sites with the texts on genetically-modified food (Median: 3.2 min) and genome-edited food (Median: 4.1 min), but no participants were excluded based on this.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of Variance.
- CH:
-
Switzerland.
- EU:
-
European Union.
- GMOs:
-
Genetically-Modified Organisms.
- NGO:
-
Non-Governmental Organisation.
- PCA:
-
Principal Component Analysis.
- TV:
-
Television.
- UK:
-
United Kingdom.
- WTB:
-
Willingness-To-Buy.
- WTE:
-
Willingness-To-Eat.
References
Acatech. 2017. Innovationspotenziale der Biotechnologie [Innovation potentials of biotechnology]. Munich, DE: Herbert Utz Verlag.
Asioli, D., J. Aschemann-Witzel, V. Caputo, R. Vecchio, A. Annunziata, T. Næs, and P. Varely. 2017. Making sense of the “clean label” trends: a review of consumer food choice behaviour and discussion of industry implications. Food Research International 1: 58–71.
Augoustinos, M., S. Crabb, and R. Shepherd. 2010. Genetically modified food in the news: media representations of the GM debate in the UK. Public Understanding of Science 19: 98–114.
Augustin, M. A., M. Riley, R. Stockmann, A. Bennett, T. Kahl, M. Lockett, P. Osmond, W. Sanguansri, W. Stonehouse, I. Zajac, and L. Cobiac. 2016. Role of food processing in food and nutrition security. Trends in Food Science & Technology 56: 115–125.
Banning, S. A., and K. D. Sweetser. 2007. How much do they think it affects them and whom do they believe? Comparing the third-person effect and credibility of blogs and traditional media. Communication Quarterly 55: 451–466.
Bearth, A., R. Saleh, and M. Siegrist. 2019. Lay-people’s knowledge about toxicology and its principles in eight European countries. Food and Chemical Toxicology 131: 110560.
Bearth, A., and M. Siegrist. 2016. Are risk or benefit perceptions more important for public acceptance of innovative food technologies: a meta-analysis. Trends in Food Science & Technology 49: 14–12.
Beghin, J. C., and C. R. Gustafson. 2021. Consumer Valuation of and attitudes towards novel foods produced with new plant engineering techniques: a review. Sustainability 13 (20): 11348.
Brossard, D. 2019. Biotechnology, communication and the public: keys to delve into the social perception of science. Mètode Revista De Difusió De La Investigació 9: 39–45.
Busch, G., E. Ryan, M. A. G. von Keyserlingk, and D. M. Weary. 2021. Citizen views on genome editing: effects of species and purpose. Agriculture and Human Values 1: 1–14.
Connor, M., and M. Siegrist. 2010. Factors influencing people’s acceptance of gene technology: the role of knowledge, health expectations, naturalness, and social trust. Science Communication 32: 514–538.
Connor, M., and M. Siegrist. 2011. The power of association: its impact on willingness to buy GM food. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: an international journal 17: 1142–1155.
Costa-Font, M., J. M. Gil, and W. B. Traill. 2008. Consumer acceptance, valuation of and attitudes towards genetically modified food: review and implications for food policy. Food Policy 33: 99–111.
Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs (DEFRA) Press Office. 2020. Agriculture Bill moves another step forwards. GOV.UK Blog. https://deframedia.blog.gov.uk/2020/07/29/agriculture-bill-moves-another-step-forward/. Accessed 7 February 2022.
Delwaide, A. C., L. L. Nalley, B. L. Dixon, D. M. Danforth, R. M. Nayga Jr., E. J. Van Loo, and W. Verbeke. 2015. Revisiting GMOs: Are There Differences in European Consumers’ Acceptance and Valuation for Cisgenically vs Transgenically Bred Rice? PLOS ONE 10: e0126060.
Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs (DEFRA). 2021. The regulation of genetic technologies. Gene editing consultation. https://consult.defra.gov.uk/agri-food-chain-directorate/the-regulation-of-genetic-technologies/. Accessed 7 February 2022.
Edenbrandt, A. K., L. A. House, Z. Gao, M. Olmstead, and D. Gray. 2018. Consumer acceptance of cisgenic food and the impact of information and status quo. Food Quality and Preference 69: 44–52.
Egolf, A., C. Hartmann, and M. Siegrist. 2019. When evolution works against the future: disgust’s contributions to the acceptance of new food technologies. Risk Analysis 39: 1546–1559.
European Food Safety Authority. 2019. Special Eurobarometer: food safety in the EU. Parma, IT: European Food Safety Authority.
Federal Office for the Environment. 2020. Neue Pflanzenzüchtungsverfahren: Grosse Diskussionen um einen kleinen Schnitt [New plant breeding methods: Big discussions about a small cut]. Federal Office for the Environment. https://www.bafu.admin.ch/bafu/de/home/themen/biotechnologie/dossiers/magazin2019-2-dossier/grosse-diskussionen-um-einen-kleinen-schnitt.html. Accessed 7 February 2022.
Finucane, M. L., A. Alhakami, P. Slovic, and S. M. Johnson. 2000. The affect heuristic in judgments of risks and benefits. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making 13: 1–17.
Frewer, L. J., K. Bergmann, M. Brennan, R. Lion, R. Meertens, G. Rowe, M. Siegrist, and C. Vereiijken. 2011. Consumer response to novel agri-food technologies: Implications for predicting consumer acceptance of emerging food technologies. Trends in Food Science & Technology 22: 442–456.
Gaskell, G., A. Allansdottir, N. Allum, P. Castro, Y. Esmer, C. Fischler, J. Jackson, N. Kronberger, J. Hampel, N. Mejlgaard, A. Quintanilha, A. Rammer, G. Revuelta, S. Stares, H. Torgersen, and W. Wager. 2011. The 2010 Eurobarometer on the life sciences. Nature Biotechnology 29: 113–114.
Greszki, R., M. Meyer, and H. Schoen. 2014. The impact of speeding on data quality in nonprobability and freshly recruited probability-based online panels. In Online Panel Research, eds. M. Callegaro, J. Baker, A. S. Bethlehem, J. A. Göritz, J. A. Krosnick, and P. J. Lavrakas, 238–262. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Guenther, L., J. Bischoff, A. Loewe, H. Marzinkowski, and M. Voigt. 2019. Scientific Evidence and Science Journalism. Journalism Studies 20: 40–59.
Gunter, B., V. Campbell, M. Touri, and R. K. Gibson. 2009. Blogs, news and credibility. Aslib Proceedings, 61: 185–204.
Hansen, J., L. Holm, L. J. Frewer, P. Robinson, and P. Sandøe. 2003. Beyond the knowledge deficit: recent research into lay and expert attitudes to food risks. Appetite 41: 111–121.
Helliwell, R., S. Hartley, and W. Pearce. 2019. NGO perspectives on the social and ethical dimensions of plant genome-editing. Agriculture and Human Values 36 (4): 779–791.
Hendriks, F., D. Kienhues, and R. Bromme. 2016. Evoking vigilance: would you (dis)trust a scientist who discusses ethical implications of research in a science blog? Public Understanding of Science 25: 992–1008.
IBM Corp. 2017. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows. Version 25.0. Armonk. NY: IBM Corp.
Johnson, T. J., and B. K. Kayne. 2009. In blog we trust? Deciphering credibility of components of the internet among politically interested internet users. Computers in Human Behavior 25: 175–182.
Kaptan, G., A. R. H. Fischer, and L. J. Frewer. 2018. Extrapoling understanding of food risk perceptions to emerging food safety cases. Journal of Risk Research 21: 996–1018.
Kawall, K., J. Cotter, and C. Then. 2020. Broadening the GMO risk assessment in the EU for genome editing technologies in agriculture. Environmental Sciences Europe 32: 1–24.
Kessler, S. H. 2016. Das ist doch evident! Eine Analyse dargestellter Evidenzframes und deren Wirkung am Beispiel von TV-Wissenschaftsbeiträgen [It’s evident! Identifying frames of evidence as used in science TV programs and testing their effects on beliefs]. Baden-Baden, DE: Nomos.
Kraus, N., T. Malmfors, and P. Slovic. 1992. Intuitive Toxicology: Expert and Lay Judgments of Chemical Risks. Risk Analysis 12: 215–232.
Kronberger, N., W. Wagner, and M. Nagata. 2013. How Natural Is “More Natural”? The Role of Method, Type of Transfer, and Familiarity for Public Perceptions of Cisgenic and Transgenic Modification. Science Communication 36: 106–130.
Kwak, D., Y. Kim, and M. H. Zimmerman. 2010. User- versus mainstream-media-generated content: media source, message valence, and team identification and sport consumers’ response. International Journal of Sport Communication 3: 402–421.
Lang, A., A. Spök, M. Gruber, D. Harrer, C. Hammer, F. Winkler, L. Kaelin, H. Hönigmayer, A. Sommer, M. Wuketich, M. Fuchs, and E. Griessler. 2019. Genome editing - Interdisziplinäre Technikfolgenabschätzung [Interdisciplinary technology assessment]. Zurich, CH: vdf Hochschulverlag.
Ledford, H. 2021. New rules will make UK gene-edited crop research easier. In New rules will make UK gene-edited crop research easier. Nature News. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-01572-0 Accessed 7 February 2022.
Lilleholt, L. 2019. Cognitive ability and risk aversion: A systematic review and meta analysis. Judgment and Decision Making 14: 234–279.
Lofgren, J. 2013. Food blogging and food-related media convergence. M/C Journal 16 (3): 1–2.
Mackay, J. B., and W. H. Lowrey. 2007. The credibility divide: reader trust of online newspapers and blogs. Annual Meeting of the International Communication Association. San Francisco, CA.
Marris, C. 2001. Public views on GMOs: deconstructing the myths. EMBO reports 2: 545–548.
Marschall, J., L. Otto, M. Rahnke, and M. Maier. 2011. Perceived uncertainty of scientific evidence. Landau, DE: Unpublished instrument.
McCaughey, T., D. M. Budden, P. G. Sanfilippo, G. E. Gooden, L. Fan, E. Fenwick, G. Rees, C. MacGregor, L. Si, C. Chen, H. H. Liang, A. Pebay, T. Baldwin, and A. W. Hewitt. 2019. A Need for Better Understanding Is the Major Determinant for Public Perceptions of Human Gene Editing. Human Gene Therapy 30: 36–43.
Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology. 2022. Postnote: Genome-Edited Food Crops. UK Parliament Post 663: 1–10.
Peters, H. P., and S. Dunwoody. 2016. Scientific uncertainty in media content: Introduction to this special issue. Public Understanding of Science 25: 893–908.
Ranger, M., and K. Bultitude. 2014. ‘The kind of mildly curious sort of science interested person like me’: Science bloggers’ practices relating to audience recruitement. Public Understanding of Science 25: 361–378.
Retzbach, J., L. Otto, and M. Maier. 2016. Measuring the perceived uncertainty of scientific evidence and its relationship to engagement with science. Public Understanding of Science 25: 638–655.
Roberts, C. 2010. Correlations among variables in message and messenger credibility scales. American Behavioral Scientist 54: 43–56.
Rose, K. M., E. L. Howell, L.Y.-F. Su, M. A. Xenos, D. Brossard, and D. A. Scheufele. 2019. Distinguishing scientific knowledge: The impact of different measures of knowledge on genetically modified food attitudes. Public Understanding of Science 28: 449–467.
Rosenbaum, L. 2019. The future of gene editing - toward scientific and social consensus. The New England Journal of Medicine 380: 971–975.
Runge, K. K., D. Brossard, D. A. Scheufele, K. M. Rose, and B. J. Larson. 2017. Attitudes about Food and Food-Related Biotechnology. Public Opinion Quarterly 81: 577–596.
Saleh, R., A. Bearth, and M. Siegrist. 2019. “Chemophobia” today: consumers’ knowledge and perceptions of chemicals. Risk Analysis 39: 2668–2682.
Shew, A. M., L. L. Nalley, H. A. Snell, R. M. Nayga, and B. L. Dion. 2018. CRISPR versus GMOs: public acceptance and valuation. Global Food Security 19: 71–80.
Siegrist, M. 2008. Factors influencing public acceptance of innovative food technologies and products. Trends in Food Science & Technology 19: 603–608.
Siegrist, M. 2019. Trust and risk perception: a critical review of the literature. Risk Analysis 41 (3): 480–490.
Siegrist, M., and C. Hartmann. 2020. Consumer acceptance of novel food technologies. Nature Food 1: 343–350.
Siegrist, M. 2021. Trust and risk perception: a critical review of the literature. Risk Analysis 41: 480–490.
Siegrist, M., G. Cvetkovich, and C. Roth. 2000. Salient value similarity, social trust, and risk/benefit perception. Risk Analysis 20: 353–362.
Slovic, P., M. L. Finucane, E. Peters, and D. G. MacGregor. 2004. Risk as analysis and risk as feelings: some thoughts about affect, reason, risk, and rationality. Risk Analysis 24: 311–322.
Stirling, A. 2007. Risk, precaution and science: towards a more constructive policy debate. EMBO reports 8: 309–315.
Swiss Academies of Arts and Sciences. 2018. Swiss Academies Factsheet 13: New approaches for protecting potatoes against late blight. Berne, CH: Swiss Academies of Arts and Sciences.
Swiss Parliament. 2021a. Nationalrat verlängert Gentech-Moratorium bis Ende 2025 [National Council extends GMO moratorium until the end of 2025]. Swiss Parliament. https://www.parlament.ch/de/services/news/Seiten/2021/20210923102414698194158159038_bsd058.aspx Accessed 7 February 2022.
Swiss Parliament. 2021b. Staenderat nimmt Genom-Editierung von Gentech-Moratorium aus [State Council exempts genome editing from GM moratorium]. Swiss Parliament. https://www.parlament.ch/de/services/news/Seiten/2021/20211202135625294194158159038_bsd110.aspx Accessed 8 February 2022.
The Federal Council of Switzerland. 2020. GVO-Anbau: Bundesrat verabschiedet Botschaft zur Verlängerung des Moratoriums [GMO cultivation: Federal Council decides on prolongation of the moratorium]. The Federal Council of Switzerland. https://www.admin.ch/gov/de/start/dokumentation/medienmitteilungen.msg-id-84232.html Accessed 7 February 2022.
United Nations. 2019. World Population Prospects. United Nations. https://population.un.org/wpp/ Accessed 7 February 2022.
Walker, B., and J. Malson. 2020. Science, God, and Nature: A Textual and Frequency Analysis of Facebook Comments on News Articles About Agricultural and Environmental Gene Editing. Environmental Communication 14 (7): 1004–1016.
Weisberg, S. M., D. Badgio, and A. Chatterjee. 2017. A CRISPR new world: attitudes in the public toward innovations in human genetic modification. Frontiers in Public Health 5: 1–9.
Winkler, F., H. Hoenigmayer, A. Lang, and E. Griessler. 2019. Ökonomische Implikationen von Genome Editing: eine explorative Unternehmensbefragung [Economic implications of genome editing: an explorative company survey]. In Genome Editing - Interdisziplinäre Technikfolgeabschätzung [Interdisciplinary technology assessment], 361–373. Zurich, CH: vdf Hochschulverlag: ed. TA-SWISS.
Wohlfender-Bühler, D., E. Feusthuber, R. Wäger, S. Mann, and S. J. Aubry. 2016. Genetically modified crops in Switzerland: implications for agrosystem sustainability evidenced by multi-criteria model. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 36 (33): 1–16.
Zahry, N. R., and J. C. Besley. 2019. Genetic engineering, genetic modification, or agricultural biotechnology: does the term matter? Journal of Risk Research 22: 16–31.
Zhang, Y., K. Massel, I. D. Godwin, and C. Gao. 2018. Applications and potential of genome editing in crop improvement. Genome Biology 19: 210.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Bearth, A., Kaptan, G. & Kessler, S.H. Genome-edited versus genetically-modified tomatoes: an experiment on people’s perceptions and acceptance of food biotechnology in the UK and Switzerland. Agric Hum Values 39, 1117–1131 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10460-022-10311-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10460-022-10311-8