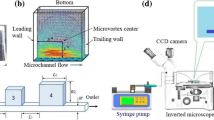
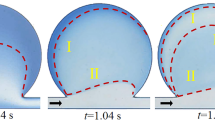
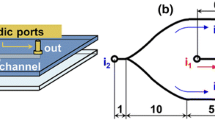
Abstract
Fluid flows in microchannels with microcavities at low Reynolds number are increasingly used in microfluidic applications such as trapping and sorting of cells and particles. For optimizing the microcavity configuration and better controlling the microenvironment in the microcavities, it is important to thoroughly understand the flow behaviors in the microcavities. Hence, using microparticle image velocimetry (μPIV), we investigated quantitatively the flow characteristics of rectangular microcavities with a wide range of aspect ratio (λ = 0.25–3) and Reynolds numbers (Re = 0–100). Depending on the control parameters (Re and λ), a flow regime map in microcavities has been constructed, including three different flow patterns: attached flow, separated flow, and transitional flow. The critical parameters for the transform of flow patterns were determined. Only a single central microvortex appears in the microcavities, and the evolution and characteristics of the microvortex were investigated in detail. The results revealing the flow mechanism of different flow patterns in the rectangular microcavities can provide useful design guidelines of microfluidic-based devices, as well as a map to help microfluidic users in their design of application-driven microcavities.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourdon CJ, Olsen MG, Gorby AD (2006) The depth of correlation in micro-PIV for high numerical aperture and immersion objectives. J Fluids Eng 128:883–886
Chiang TP, Sheu WH, Hwang RR (1996) Finite volume analysis of spiral motion in a rectangular lid-driven cavity. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 23:325–346
Chiu D (2007) Cellular manipulations in microvortices. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:17–20
Cioffi M, Moretti M, Manbachi A, Chung BG, Khademhosseini A, Dubini G (2010) A computational and experimental study inside microfluidic systems: the role of shear stress and flow recirculation in cell docking. Biomed Microdevices 12:619–626
Duffy DC, McDonald JC, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70:4974–4984
Fan LL, He XK, Han Y, Du L, Zhao L, Zhe J (2014) Continuous size-based separation of microparticles in a microchannel with symmetric sharp corner structures. Biomicrofluidics 8(2):024108
Fishler R, Mulligan MK, Sznitman J (2013) Mapping low-Reynolds-number microcavity flows using microfluidic screening devices. Microfluid Nanofluidics 15:491–500
He K, Retterer ST, Srijanto BR, Conrad JC, Krishnamoorti R (2014) Transport and dispersion of nanoparticles in periodic nanopost arrays. ACS Nano 8:4221–4227
Heaton CJ (2008) On the appearance of moffatt eddies in viscous cavity flow as the aspect ratio varies. Phys Fluids 20:103102–103111
Hur SC, Tse HTK, Di Carlo D (2010) Sheathless inertial cell ordering for extreme throughput flow cytometry. Lab Chip 10:274–280
Hur SC, Mach AJ, Di Carlo D (2011) High-throughput size-based rare cell enrichment using microscale vortices. Biomicrofluidics 5:022206
Jang YH, Kwon CH, Kim SB, Selimović Š, Sim WY, Bae H, Khademhosseini A (2011) Deep wells integrated with microfluidic valves for stable docking and storage of cells. Biotechnol J 6(2):156–164
Karimi A, Yazdi S, Ardekani AM (2013) Hydrodynamic mechanisms of cell and particle trapping in microfluidics. Biomicrofluidics 7:021501
Khabiry M, Chung B, Hancock M, Soundararajan H, Du Y, Cropek D, Lee W, Khademhosseini A (2009) Cell docking in double grooves in a microfluidic channel. Small 5:1186–1194
Lima R, Wada S, Tanaka S, Takeda M, Ishikawa T, Tsubota K, Imai Y, Yamaguchi T (2008) In vitro blood flow in a rectangular PDMS microchannel: experimental observations using a confocal micro-PIV system. Biomed Microdevices 10:153–167
Lindken R, Rossi M, Große S, Westerweel J (2009) Micro-particle image velocimetry (μPIV): recent developments, applications, and guidelines. Lab Chip 9:2551–2567
Lindström S, Andersson-Svahn H (2010) Overview of single-cell analyses: microdevices and applications. Lab Chip 10:3363–3372
Liu K, Pitchimani R, Dang D, Bayer K, Harrington T, Pappas D (2008) Cell culture chip using low-shear mass transport. Langmuir 24:5955–5960
Liu K, Tian Y, Burrows SM, Reif RD, Pappas D (2009) Mapping vortex-like hydrodynamic flow in microfluidic networks using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta 651:85–90
Luo CX, Li H et al (2007) The combination of optical tweezers and microwell array for cell manipulation and cultivation in microfluidic device. Biomed Microdevices 9:573–578
Mach AJ, Kim JH, Arshi A, Hur SC, Di Carlo D (2011) Automated cellular sample preparation using a Centrifuge-on-a-Chip. Lab Chip 11:2827–2834
Manbachi A, Shrivastava S et al (2008) Microcirculation within grooved substrates regulates cell positioning and cell docking inside microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 8:747–754
Meinhart CD, Wereley ST, Santiago JG (1999) PIV measurements of a microchannel flow. Exp Fluids 27:414–419
Moffatt HK (1964) Viscous and resistive eddies near a sharp corner. J Fluid Mech 18:1–18
Mu X, Zheng WF, Sun JS, Zhang W, Jiang XY (2013) Microfluidics for manipulating cells. Small 9(1):9–21
Nguyen N, Wereley S (2002) Fundamentals and applications of microfluidics. Artech House Inc, Norwood
Nilsson J, Evander M, Hammarström B, Laurell T (2009) Review of cell and particle trapping in microfluidic systems. Anal Chim Acta 649(2):141–157
O’Brien V (1972) Closed streamlines associated with channel flow over a cavity. Phys Fluids 15:2089–2097
Park JS, Song SH, Jung HI (2009) Continuous focusing of microparticles using inertial lift force and vorticity via multi-orifice microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 9:939–948
Park JY, Morgan M, Sachs AN, Samorezov J, Teller R, Shen Y, Pienta KJ, Takayama S (2010) Single cell trapping in larger microwells capable of supporting cell spreading and proliferation. Microfluid Nanofluidics 8:263–268
Raffel M, Willert CE, Wereley ST, Kompenhans J (2007) Particle image velocimetry-a practical guide, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Sackmann EK, Fulton AL, Beebe DJ (2014) The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 507(7491):181–189
Santiago JG, Wereley ST, Meinhart CD, Beebe DJ, Adrian RJ (1998) A particle image velocimetry system for microfluidics. Exp Fluids 25:316–319
Shah RK, London AL (1978) Laminar flow forced convection in ducts. Academic Press, New York
Shankar PN (1997) Three-dimensional eddy structure in a cylindrical container. J Fluids Mech 342:97–118
Shankar PN, Deshpande MD (2000) Fluid mechanics in the driven cavity. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 32:93–136
Shelby JP, Lim DSW, Kuo JS, Chiu DT (2003) Microfluidic systems: high radial acceleration in microvortices. Nature 425:38
Shen C, Floryan JM (1985) Low Reynolds number flow over cavities. Phys Fluids 28:3191–3202
Shen F, Li XJ, Li PCH (2014) Study of flow behaviors on single-cell manipulation and shear stress reduction in microfluidic chips using computational fluid dynamics simulations. Biomicrofluidics 8:014109
Skelley AM, Kirak O, Suh H, Jaenisch R, Voldman J (2009) Microfluidic control of cell pairing and fusion. Nat Methods 6:147–152
Stone SW, Meinhart CD, Wereley ST (2002) A microfluidic-based nanoscope. Exp Fluids 33:613–619
Tanyeri M, Schroeder CM (2013) Manipulation and confinement of single particles using fluid flow. Nano Lett 13:2357–2364
Wereley ST, Meinhart CD (2010) Recent advances in micro-particle image velocimetry. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 42:557–576
Willert C, Raffel M, Kompenhans J, Stasicki B, Kahler C (1996) Recent applications of particle image velocimetry in aerodynamic research. Flow Meas Instrum 7:247–256
Williams SJ, Park C, Wereley ST (2010) Advances and applications on microfluidic velocimetry techniques. Microfluid Nanofluidics 8:709–726
Yew AG, Pinero D, Hsieh AH, Atencia J (2013) Low peclet number mass and momentum transport in microcavities. Appl Phys Lett 102:084108
Yu ZTF, Lee YK, Wong M, Zohar Y (2005) Fluid flows in microchannels with cavities. J Microelectromech Syst 14:1386–1398
Yun H, Kim K, Lee WG (2013) Cell manipulation in microfluidics. Biofabrication 5:022001
Zhou J, Kasper S, Papautsky I (2013) Enhanced size-dependent trapping of particles using microvortices. Microfluid Nanofluidics 15:611–623
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11002007 and 11072011), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7152012), and Training Plan of New Talent of Beijing University of Technology (2015-RX-L02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, F., Xiao, P. & Liu, Z. Microparticle image velocimetry (μPIV) study of microcavity flow at low Reynolds number. Microfluid Nanofluid 19, 403–417 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1575-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1575-3