Abstract
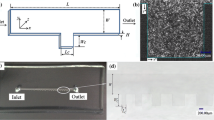
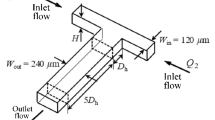
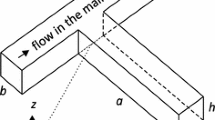
The paper is concerned with the experimental and numerical investigations of the vortex formation and flow focusing inside a cross-shaped microchannel domain. The local hydrodynamics in the junction area, upstream of the focusing region, is analyzed with the aim to characterize the onset and the evolution of the vortical structures, in correlation with the operating parameters. The numerical simulations based on a finite-volume approach are validated by direct flow visualizations using epifluorescence and confocal microscopy. The main result of the study is a flow pattern map, providing comprehensive information on the flow dynamics inside the microchannel junction as a function of the input flow rates and the corresponding Reynolds numbers. The flow pattern map identifies the limits of the flow focusing regime and the critical values of the parameters at which the vortical structures are formed. Beyond the breakdown of the classical flow focusing scenario with one focused output stream, flow patterns with two and four output streams are identified.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JD, Degroote J, Degrez G, Dick E, Grundmann R, Vierendeels J (2009) Computational fluid dynamics. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-85056-4
Bǎlan CM, Broboanǎ D, Bǎlan C (2012) Investigations of vortex formation in microbifurcations. Microfluid Nanofluid 13:819–833. doi:10.1007/s10404-012-1005-8
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Papautsky I (2008) Inertial microfluidics for continuous particle filtration and extraction. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:217–226. doi:10.1007/s10404-008-0377-2
Bothe D, Stemich C, Warnecke HJ (2006) Fluid mixing in a T-shaped micro-mixer. Chem Eng Sci 61:2950–2958. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2005.10.060
Bothe D, Lojewski A, Warnecke HJ (2011) Fully resolved numerical simulation of reactive mixing in a T-shaped micromixer using parabolized species equations. Chem Eng Sci 66:6424–6440. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2011.08.045
Brennich ME, Köster S (2013) Tracking reactions in microflow. Microfluid Nanofluid 16:39–45. doi:10.1007/s10404-013-1212-y
Carlotto S, Fortunati I, Ferrante C, Schwille P, Polimeno A (2010) Time correlated fluorescence characterization of an asymmetrically focused flow in a microfluidic device. Microfluid Nanofluid 10:551–561. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0689-x
Engler M, Kockmann N, Kiefer T, Woias P (2004) Convective mixing and its applications to micro reactors. In: Proceedings of ICMM2004-2412. pp 781–788. doi: 10.1115/ICMM2004-2412
Fan L-L, Han Y, He X-K, Zhao L, Zhe J (2014) High-throughput, single-stream microparticle focusing using a microchannel with asymmetric sharp corners. Microfluid Nanofluid 17:639–646. doi:10.1007/s10404-014-1344-8
Ferziger JH, Peric M (2002) Computational methods for fluid dynamics. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-56026-2
FLUENT6.3 Doc. User’s Manual, 2006 Fluent Incorporated, Lebanon, New Hampshire
Fu T, Wu Y, Ma Y, Li HZ (2012) Droplet formation and breakup dynamics in microfluidic flow-focusing devices: from dripping to jetting. Chem Eng Sci 84:207–217. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2012.08.039
Golden JP, Justin GA, Nasir M, Ligler FS (2012) Hydrodynamic focusing-a versatile tool. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:325–335. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5415-3
Ha BH, Lee KS, Jung JH, Sung HJ (2014) Three-dimensional hydrodynamic flow and particle focusing using four vortices Dean flow. Microfluid Nanofluid. doi:10.1007/s10404-014-1346-6
Haward SJ, Poole RJ, Alves MA, Oliviera PJ, Goldenfeld N, Shen AQ (2016) Tricritical spiral vortex instability in cross-slot flow. Phys Rev E 93:031101(R). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.93.031101
Hoffmann M, Schlüter M, Räbiger N (2006) Experimental investigation of liquid-liquid mixing in T-shaped micro-mixers using μ-LIF and μ-PIV. Chem Eng Sci 61:2968–2976. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2005.11.029
Hong JS, Stavis SM, Depaoli Lacerda SH, Locascio LE, Raghavan SR, Gaitan M (2010) Microfluidic directed self-assembly of liposome-hydrogel hybrid nanoparticles. Langmuir 26:11581–11588. doi:10.1021/la100879p
Hsu WL, Inglis DW, Jeong H, Dunstan DE, Davidson MR, Goldys EM, Harvie DJE (2014) Stationary chemical gradients for concentration gradient-based separation and focusing in nanofluidic channels. Langmuir 30:5337–5348. doi:10.1021/la500206b
Iliescu C, Mărculescu C, Venkataraman S, Languille B, Yu H, Tresset G (2014) On-Chip Controlled Surfactant–DNA Coil-Globule Transition by Rapid Solvent Exchange Using Hydrodynamic Flow Focusing. Langmuir 30:13125–13136. doi:10.1021/la5035382
Jahn A, Vreeland WN, Devoe DL, Locascio LE, Gaitan M (2007) Microfluidic directed formation of liposomes of controlled size. Langmuir 23:6289–6293. doi:10.1021/la070051a
Jahn A, Lucas F, Wepf RA, Dittrich PS (2013) Freezing continuous-flow self-Assembly in a microfluidic device: toward imaging of liposome formation. Langmuir 29:1717–1723. doi:10.1021/la303675g
Kennedy MJ, Stelick SJ, Perkins SL, Cao L, Batt CA (2009) Hydrodynamic focusing with a microlithographic manifold: controlling the vertical position of a focused sample. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:569–578. doi:10.1007/s10404-009-0417-6
Kockmann N, Kiefer T, Engler M, Woias P (2006) Convective mixing and chemical reactions in microchannels with high flow rates. Sens Actuators B Chem 117:495–508. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2006.01.004
Kockmann N, Dreher S, Woias P (2007) Unsteady laminar flow regimes and mixing in T-shaped micromixers. In: ASME 5th international conference on nanochannels, microchannels, minichannels. pp 671–678. doi: 10.1115/ICNMM2007-30041
Kunstmann-Olsen C, Hoyland JD, Rubahn H-G (2011) Influence of geometry on hydrodynamic focusing and long-range fluid behavior in PDMS microfluidic chips. Microfluid Nanofluid 12:795–803. doi:10.1007/s10404-011-0923-1
Lee MG, Choi S, Park J-K (2009) Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing with a single sheath flow in a single-layer microfluidic device. Lab Chip 9:3155–3160. doi:10.1039/b910712f
Lin S-C, Yen P-W, Peng C-C, Tung Y-C (2012) Single channel layer, single sheath-flow inlet microfluidic flow cytometer with three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing. Lab Chip 12:3135. doi:10.1039/c2lc40246g
Maenaka H, Yamada M, Yasuda M, Seki M (2008) Continuous and size-dependent sorting of emulsion droplets using hydrodynamics in pinched microchannels. Langmuir 24:4405–4410. doi:10.1021/la703581j
Mijajlovic M, Wright D, Zivkovic V, Bi JX, Biggs MJ (2013) Microfluidic hydrodynamic focusing based synthesis of POPC liposomes for model biological systems. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 104:276–281. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.12.020
Nasir M, Mott DR, Kennedy MJ, Golden JP, Ligler FS (2011) Parameters affecting the shape of a hydrodynamically focused stream. Microfluid Nanofluid 11:119–128. doi:10.1007/s10404-011-0778-5
Oliveira MSN, Pinho FT, Alves MA (2012) Divergent streamlines and free vortices in Newtonian fluid flows in microfluidic flow-focusing devices. J Fluid Mech 711:171–191. doi:10.1017/jfm.2012.386
Rodriguez-Trujillo R, Mills CA, Samitier J, Gomila G (2006) Low cost micro-Coulter counter with hydrodynamic focusing. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:171–176. doi:10.1007/s10404-006-0113-8
Rondeau E, Cooper-White JJ (2008) Biopolymer microparticle and nanoparticle formation within a microfluidic device. Langmuir 24:6937–6945. doi:10.1021/la703339u
Schabas G, Yusuf H, Moffitt MG, Sinton D (2008) Controlled self-assembly of quantum dots and block copolymers in a microfluidic device. Langmuir. doi:10.1021/la703297q
Soleymani A, Kolehmainen E, Turunen I (2008) Numerical and experimental investigations of liquid mixing in T-type micromixers. Chem Eng J 135:219–228. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2007.07.048
Spielman G, Goren SL (1968) Improving Resolution in Coulter Counting by Hydrodynamic Focusing. J Colloids Interface Sci 26:175–182
Ushikubo FY, Birribilli FS, Oliveira DRB, Cunha RL (2014) Y- and T-junction microfluidic devices: effect of fluids and interface properties and operating conditions. Microfluid Nanofluid 17:711–720. doi:10.1007/s10404-014-1348-4
Wang WH, Zhang ZL, Xie YN, Wang L, Yi S, Liu K, Liu J, Pang DW, Zhao XZ (2007) Flow-focusing generation of monodisperse water droplets wrapped by ionic liquid on microfluidic chips: from plug to sphere. Langmuir 23:11924–11931. doi:10.1021/la701170s
Wesseling P (2001) Principles of computational fluid dynamics. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-05146-3
Wong SH, Ward MCL, Wharton CW (2004) Micro T-mixer as a rapid mixing micromixer. Sens Actuators B Chem 100:359–379. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2004.02.008
Xuan X, Zhu J, Church C (2010) Particle focusing in microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 9:1–16. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0602-7
Zhang Z, Zhao P, Xiao G, Lin M, Cao X (2008) Focusing-enhanced mixing in microfluidic channels. Biomicrofluidics 2:1–9. doi:10.1063/1.2894313
Zhou J, Kasper S, Papautsky I (2013) Enhanced size-dependent trapping of particles using microvortices. Microfluid Nanofluid 15:611–623. doi:10.1007/s10404-013-1176-y
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. eng. Catalin Marculescu for his assistance in fabrication of the microchannels and also the financial support received from the grant UEFISCDI, projects PN-II-ID-PCE-2012-4-0245/2013 and PN-II-PT-PCCA-2011-3.1-0052. The work of Iulia Rodica Damian was funded by the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development 2007–2013 of the Ministry of European Funds through the Financial Agreement POSDRU/159/1.5/S/132397.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damian, I.R., Hardt, S. & Balan, C. From flow focusing to vortex formation in crossing microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 21, 142 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1975-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1975-7