Abstract
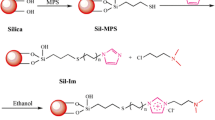
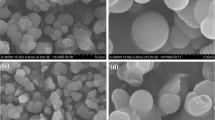
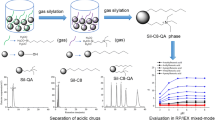
In this study, octylbenzimidazolium-modified silica (BeImC8-Sil) was prepared by covalent attachment of 1-octylbenzimidazole to γ-chloropropyl silica. The synthesized materials were characterized by the elemental analysis, IR spectrum, and thermogravimetric analysis. Due to the introduction of phenyl and octyl groups on the quaternary imidazolium, the developed BeImC8-Sil column can function via both reversed-phase and anion-exchange retention mechanisms. The chromatographic properties of the synthesized material were investigated by the separations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, mono-substituted derivatives of benzene, anilines, and phenols, revealing the existence of multiple interactions, including hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking, electrostatic forces, and hydrophobic interactions in reversed-phase mode; inorganic and organic anions were also separated mainly through anion-exchange interaction. The proposed BeImC8-Sil is a promising mixed-mode stationary phase for the separation of complex samples in high-performance liquid chromatography.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snyder LR, Kirkland JJ, Dolan JW (2010) Introduction to modern liquid chromatography. Wiley, New Jersey
Fekete S, Oláh E, Fekete J (2012) Fast liquid chromatography: the domination of core-shell and very fine particles. J Chromatogr A 1228:57–71
Yang Y, Geng X (2011) Mixed-mode chromatography and its applications to biopolymers. J Chromatogr A 1218:8813–8825
Mansour FR, Danielson ND (2013) Multimodal liquid chromatography of small molecules. Anal Methods 5:4955–4972
Apfelthaler E, Bicker W, Lämmerhofer M, Sulyok M, Krska R, Lindner W, Schuhmacher R (2008) Retention pattern profiling of fungal metabolites on mixed-mode reversed-phase/weak anion exchange stationary phases in comparison to reversed-phase and weak anion exchange separation materials by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1191:171–181
Bicker W, Lämmerhofer M, Lindner W (2008) Mixed-mode stationary phases as a complementary selectivity concept in liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry-based bioanalytical assays. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:263–266
Dietrich MA, Adamek M, Bilińska B, Hejmej A, Steinhagen D, Ciereszko A (2011) Multi-modal applicability of a reversed-phase/weak-anion exchange material in reversed-phase, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, hydrophilic interaction and hydrophobic interaction chromatography modes. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:2517–2530
Kiseleva MG, Nesterenko PN (2000) Phenylaminopropyl silica—a new specific stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography of phenols. J Chromatogr A 898:23–34
Kiseleva MG, Radchenko LV, Nesterenko PN (2001) Ion-exchange properties of hypercrosslinked polystyrene impregnated with methyl orange. J Chromatogr A 920:79–85
Takeuchi T, Kawasaki T, Lim LW (2010) Separation of inorganic anions on a pyridine stationary phase in ion chromatography. Anal Sci 26:511–514
Auler LMLA, Silva CR, Collins KE, Collins CH (2005) New stationary phase for anion-exchange chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1073:147–153
Auler L, Silva CR, Bottoli C, Collins CH (2011) Anion separations for liquid chromatography using propylpyridinium silica as the stationary phase. Talanta 84:1174–1179
Sun M, Feng J, Liu S, Xiong C (2011) Polydopamine supported preparation method for solid-phase microextraction coatings on stainless steel wire. J Chromatogr A 1218:3601–3607
Muenter MM, Stokes KC, Obie RT, Jezorek JR (1999) Simultaneous separation of inorganic ions and neutral organics on ion-exchange stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 844:39–51
Zhang M, Liang X, Jiang S, Qiu H (2014) Preparation and applications of surface-confined ionic-liquid stationary phases for liquid chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 53:60–72
Qiu H, Jiang S, Liu X, Zhao L (2006) Novel imidazolium stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1116:46–50
Bi W, Zhou J, Row KH (2010) Separation of xylose and glucose on different silica-confined ionic liquid stationary phases. Anal Chim Acta 677:162–168
Qian W, Baker GA, Baker SN, Colón LA (2006) Surface confined ionic liquid as a stationary phase for HPLC. Analyst 131:1000–1005
Qiu H, Jiang Q, Wei Z, Wang X, Liu X, Jiang S (2007) Preparation and evaluation of a silica-based 1-alkyl-3-(propyl-3-sulfonate) imidazolium zwitterionic stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1163:63–69
Qiu H, Jiang Q, Liu X, Jiang S (2008) Comparison of anion-exchange and hydrophobic interactions between two new silica-based long-chain alkylimidazolium stationary phases for LC. Chromatographia 68(3–4):167–171
Sun Y, Cabovska B, Evans CE, Ridgway TH, Stalcup AM (2005) Retention characteristics of a new butylimidazolium-based stationary phase. Anal Bioanal Chem 382:728–734
Chitta KR, Meter DSV, Stalcup AM (2009) Separation of peptides by HPLC using a surface-confined ionic liquid stationary phase. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:775–781
Meter DSV, Oliver NJ, Carle AB, Dehm S, Ridgway TH, Stalcup AM (2009) Characterization of surface-confined ionic liquid stationary phases: impact of cation and anion identity on retention. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:283–294
Sun M, Feng J, Luo C, Liu X, Jiang S (2013) Benzimidazole modified silica as a novel reversed-phase and anion-exchange mixed-mode stationary phase for HPLC. Talanta 105:135–141
Qiu H, Mallik AK, Takafuji M, Liu X, Jiang S, Ihara H (2012) A new imidazolium-embedded C18 stationary phase with enhanced performance in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 738:95–101
Qiao X, Ye M, Xiang C, Wang Q, Liu CF, Miao WJ (2012) Analytical strategy to reveal the in vivo process of multi-component herbal medicine: a pharmacokinetic study of licorice using liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1258:84–93
Shannon MS, Hindman MS, Danielsen SPO, Tedstone JM, Gilmore RD, Bara JE (2012) Properties of alkylbenzimidazoles for CO2 and SO2 capture and comparisons to ionic liquids. Sci China Chem 55:1638–1647
Kimata K, Iwaguchi K, Onishi S, Jinno K, Eksteen R, Hosoya K, Araki M, Tanaka N (1989) Chromatographic characterization of silica C18 packing materials. Correlation between a preparation method and retention behavior. of stationary phase. J Chromatogr Sci 27:721–728
Tanaka N, Tokuda Y, Iwaguchi K, Araki M (1982) Effect of stationary phase structure on retention and selectivity in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 239:761–772
Horak J, Maier NM, Lindner W (2004) Investigations on the chromatographic behavior of hybrid reversed-phase materials containing electron donor-acceptor systems II. Contribution of π–π aromatic interactions. J Chromatogr A 1045:43–58
Zhao Q, Wei F, Xiao N, Yu Q-W, Yuan B-F, Feng Y-Q (2012) Dispersive microextraction based on water-coated Fe3O4 followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for determination of 3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol in edible oils. J Chromatogr A 1240:45–51
Acknowledgments
The authors express their thanks to the support of the “Hundred Talents Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21275133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Q., Zhao, W., Qiu, H. et al. Silica-Based Phenyl and Octyl Bifunctional Imidazolium as a New Mixed-Mode Stationary Phase for Reversed-Phase and Anion-Exchange Chromatography. Chromatographia 79, 1437–1443 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3166-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3166-1