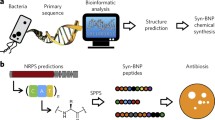
Abstract
Combinatorial biosynthesis of novel secondary metabolites derived from nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) has been in slow development for about a quarter of a century. Progress has been hampered by the complexity of the giant multimodular multienzymes. More recently, advances have been made on understanding the chemical and structural biology of these complex megaenzymes, and on learning the design rules for engineering functional hybrid enzymes. In this perspective, I address what has been learned about successful engineering of complex lipopeptides related to daptomycin, and discuss how synthetic biology and microbial genome mining can converge to broaden the scope and enhance the speed and robustness of combinatorial biosynthesis of NRPS-derived natural products for drug discovery.

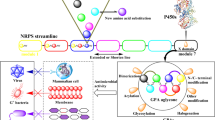
Modified from Nguyen et al. [67]

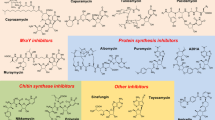
Modified from Baltz [7]

Reproduced from Baltz et al. [16]
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 February 2018
The original article can be found online at .
References
Ackerley DF (2016) Cracking the nonribosomal code. Cell Chem Biol 23:535–537
Alexander D, Rock J, He X, Miao V, Brian P, Baltz RH (2010) Development of a genetic system for lipopeptide combinatorial biosynthesis in Streptomyces fradiae and heterologous expression of the A54145 biosynthetic gene cluster. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6877–6887
Alexander D, Rock J, Gu JQ, Mascio C, Chu M, Brian P, Baltz RH (2011) Production of novel lipopeptide antibiotics related to A54145 by Streptomyces fradiae mutants blocked in biosynthesis of modified amino acids and assignment of lptJ, lptK and lptL gene functions. J Antibiot 64:79–87
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bachmann BO, Van Lanen SG, Baltz RH (2014) Microbial genome mining for accelerated natural products discovery: is a renaissance in the making? J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:175–184
Baltz RH (2008) Renaissance in antibacterial discovery from actinomycetes. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:557–563
Baltz RH (2008) Biosynthesis and genetic engineering of lipopeptide antibiotics related to daptomycin. Curr Top Med Chem 8:618–638
Baltz RH (2009) Daptomycin: mechanisms of action and resistance, and biosynthetic engineering. Curr Opin Chem Biol 13:144–151
Baltz RH (2010) Genomics and the ancient origins of the daptomycin biosynthetic gene cluster. J Antibiot 63:506–511
Baltz RH (2014) Combinatorial biosynthesis of cyclic lipopeptide antibiotics: a model for synthetic biology to accelerate the evolution of secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways. ACS Synth Biol 3:748–759
Baltz RH (2016) Genetic manipulation of secondary metabolite biosynthesis for improved production in Streptomyces and other actinomycetes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43:343–370
Baltz RH (2017) Gifted microbes for genome mining and natural product discovery. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44:573–588
Baltz RH (2017) Molecular beacons to identify gifted microbes for genome mining. J Antibiot 70:639–646
Baltz RH (2017) Microbial genome mining for natural product drug discovery. In: Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Grothaus PG (eds) Chemical biology of natural products. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 1–42
Baltz RH, McHenney MA, Hosted TJ (1997) Genetics of lipopeptide antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces fradiae A54145 and Streptomyces roseosporus A21978. Dev Ind Microbiol 34:93–98
Baltz RH, Miao V, Wrigley SK (2005) Natural products to drugs: daptomycin and related lipopeptide antibiotics. Nat Prod Rep 22:717–741
Bekker OB, Klimina KM, Vatlin AA, Zakharevich NV, Kasianov AS, Danilenko VN (2014) Draft genome sequence of Streptomyces fradiae ATCC 19609, a strain highly sensitive to antibiotics. Genome Announc 2:e01247-14
Blin K, Wolf T, Chevrette MG et al (2017) antiSMASH 4.0—improvements in chemistry prediction and gene cluster boundary identification. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W36–W41
Boeck LD, Papiska HR, Wetzel RW, Mynderse JS, Fukuda DS, Mertz FP, Berry DM (1990) A54145, a new lipopeptide antibiotic complex: discovery, taxonomy, fermentation and HPLC. J Antibiot 43:587–593
Butler MS, Robertson AA, Cooper MA (2014) Natural product and natural product derived drugs in clinical trials. Nat Prod Rep 31:1612–1661
Challis GL, Ravel J, Townsend CA (2000) Predictive, structure-based model of amino acid recognition by nonribosomal peptide synthetase adenylation domains. Chem Biol 7:211–224
Chen WH, Kunhua L, Guntaka S, Bruner SD (2016) Interdomain and intermodule organization in epimerization domain containing nonribosomal peptide synthetases. ACS Chem Biol 11:2293–2303
Chevrette MG, Aicheler F, Kohlbacher O, Currie CR, Medema MH (2017) SANDPUMA: ensemble predictions of nonribosomal peptide chemistry reveal biosynthetic diversity across Actinobacteria. Bioinformatics 33:3202–3210
Coëffet-Le Gal MF, Thurson L, Rich P, Miao V, Baltz RH (2006) Complementation of daptomycin dptA and dptD deletion mutations in-trans and production of hybrid lipopeptide antibiotics. Microbiology 152:2993–3001
Crüzemann M, Kohlhass C, Piel J (2013) Evolution-guided engineering of nonribosomal peptide synthetase adenylation domains. Chem Sci 4:1041–1045
Cundliffe E (2008) Control of tylosin biosynthesis in Streptomyces fradiae. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:1485–1491
Debono M, Abbott BJ, Molloy RM et al. (1988) Enzymatic and chemical modification of lipopeptide antibiotic A21978C: the synthesis and evaluation of daptomycin (LY146032). J Antibiot 41:1093–1105
Dehling E, Volkmann G, Matern JC, Dorner W, Alfermann J, Diecker J, Mootz HD (2016) Mapping the communication-mediating interface in nonribosomal peptide synthetases using a genetically encoded photocrosslinker supports an upside-down helix-hand motif. J Mol Biol 428:345–4360
Demain AL (2014) Importance of microbial natural products and the need to revitalize their discovery. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:185–201
Doekel S, Coëffet-Le Gal MF, Gu JQ, Chu M, Baltz RH, Brian P (2008) Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase module fusions to produce derivatives of daptomycin in Streptomyces roseosporus. Microbiology 154:2872–2880
Drake EJ, Miller BR, Shi C, Tarrash JT, Sundlov JA, Allen CL, Skiniotis G, Aldrich CC, Gulick AM (2016) Structures of two distinct conformations of holo-non-ribosomal peptide synthetases. Nature 529:235–238
Drake JW (2007) Mutations in clusters and showers. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:8203–8204
Drake JW, Baltz RH (1976) The biochemistry of mutagenesis. Annu Rev Biochem 45:11–37
Drake JW, Bebenek A, Kissling GE, Peddada S (2005) Clusters of mutations from transient hypermutability. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 102:12849–12854
Eisenstein BI, Oleson FB Jr, Baltz RH (2010) Daptomycin: from the mountain to the clinic with the essential help from Francis Tally, MD. Clin Inf Dis 50:S10–S15
Fischbach MA, Lai JR, Roche ED, Walsh CT, Liu DR (2007) Directed evolution can rapidly improve the activity of chimeric assembly-line enzymes. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:11951–11956
Giddings LA, Newman DJH (2013) Microbial natural products: molecular blueprints for antitumor drugs. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:1181–1210
Gomez-Escribano JP, Castro JF, Razmilic V, Chandra G, Andrews B, Bibb MJ (2016) The Streptomyces leeuwenhoekii genome: de novo sequencing and assembly in single contigs of the chromosome, circular plasmid pSLE1 and linear plasmid pSLE2. BMC Genomics 16:485
Gomez-Escribano JP, Alt S, Bibb MJ (2016) Next generation sequencing of actinobacteria for the discovery of novel natural products. Mar Drugs 14:78
Gu JQ, Alexander DC, Rock J, Brian P, Chu M, Baltz RH (2011) Structural characterization of a lipopeptide antibiotic A54145E(Asn3Asp9) produced by a genetically engineered strain of Streptomyces fradiae. J Antibiot 64:111–116
Gulick AM (2016) Structural insight into the necessary conformational changes of modular nonribosomal peptide synthetase. Curr Opin Chem Biol 35:89–96
Hill J, Siedlecki J, Parr I et al (2003) Synthesis and biological activity of N-acylated ornithine analogs of daptomycin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:4187–4191
Hosted TJ, Baltz RH (1996) Mutants of Streptomyces roseosporus that express enhanced recombination within partially homologous genes. Microbiology 142:2803–2813
Hojati Z, Milne C, Harvey B et al (2002) Structure, biosynthetic origin, and engineering biosynthesis of calcium-dependent antibiotics from Streptomyces coelicolor. Chem Biol 9:1175–1187
Hur GH, Vickery CR, Burkart MD (2012) Explorations of catalytic domains in non-ribosomal peptide synthetase enzymology. Nat Prod Rep 29:1074–1098
Jayapal KP, Lian W, Glod F, Sherman DH, Hu WS (2007) Comparative genomic hybridizations reveal absence of large Streptomyces coelicolor genomic islands in Streptomyces lividans. BMC Genomics 8:229
Katz L, Baltz RH (2016) Natural product discovery: past, present, and future. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43:155–176
Kim E, Moore BS, Yoon YJ (2015) Reinvigorating natural product combinatorial biosynthesis with synthetic biology. Nat Chem Biol 11:649–659
Ladner CC, Williams GJ (2016) Harnessing natural product assembly lines: structure, promiscuity, and engineering. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43:371–387
Marahiel MA (2016) A structural model for multimodular NRPS assembly lines. Nat Prod Rep 33:136–140
McHenney MA, Baltz RH (1996) Gene transfer and transposition mutagenesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: mapping insertions that influence daptomycin or pigment production. Microbiology 142:2363–2373
McHenney MA, Hosted TJ, Dehoff BS, Rosteck PR, Baltz RH (1998) Molecular cloning and physical mapping of the daptomycin gene cluster from Streptomyces roseosporus. J Bacteriol 180:143–151
Medema MH, Cimermancic P, Sali A, Takano E, Fischbach MA (2014) A systematic computational analysis of biosynthetic gene cluster evolution: lessons for engineering biosynthesis. PLoS Comput Biol 10:e1004016
Meyer S, Kehr JC, Mainz A, Dehm D, Petras D, Süssmuth RD, Dittmann E (2016) Biochemical dissection of the natural diversification of microcystin provides lessons for synthetic biology of NRPS. Cell Chem Biol 23:462–471
Miao V, Coëffet-Le Gal MF, Brian P et al (2005) Daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: cloning and analysis of the gene cluster and revision of peptide stereochemistry. Microbiology 151:1505–1523
Miao V, Brost R, Chapple J, She K, Coëffet-Le Gal MF, Baltz RH (2006) The lipopeptide antibiotic A54145 gene cluster from Streptomyces fradiae. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33:129–140
Miao V, Coëffet-Le Gal M-F, Nguyen K et al (2006) Genetic engineering of Streptomyces roseosporus to produce hybrid lipopeptide antibiotics. Chem Biol 13:269–276
Miller BR, Drake EJ, Shi C, Aldrich CC, Gulick AM (2016) Structures of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase module bound to MbtH-like proteins support a highly dynamic domain architecture. J Biol Chem 291:22559–22571
Miller BR, Gulick AM (2016) Structural biology of nonribosomal peptide synthetase. Methods Mol Biol 1401:3–29
Milne C, Powell A, Jim J, Nakeeb M, Smith CP, Micklefield J (2006) Biosynthesis of the (2S,3R)-3-methyl glutamate residue of nonribosomal peptides. J Am Chem Soc 128:11250–11259
Mukherjee S, Seshadri R, Varghese NJ et al (2017) 1003 reference genomes of bacterial and archaeal isolates expand coverage of the tree of life. Nat Biotechnol 35:676–683
Müller C, Nolden S, Gebhardt P et al (2007) Sequencing and analysis of the biosynthetic gene cluster of the lipopeptide antibiotic friulimicin in Actinoplanes friuliensis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:1028–1037
Nett M, Ikeda H, Moore B (2009) Genomic basis for natural product biosynthetic diversity in the actinomycetes. Nat Prod Rep 26:1362–1384
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2016) Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981–2014. J Nat Prod 79:629–661
Nguyen K, Kau D, Gu JQ, Brian P, Wrigley SK, Baltz RH, Miao V (2006) A glutamic acid 3-methyltransferase encoded by an accessory gene locus important for daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus. Mol Microbiol 61:1294–1307
Nguyen K, Ritz D, Gu JQ, Alexander D, Chu M, Miao V, Brian P, Baltz RH (2006) Combinatorial biosynthesis of lipopeptide antibiotics related to daptomycin. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 103:17462–17467
Nguyen KT, He X, Alexander D, Li C, Gu JQ, Mascio C, Van Praagh A, Mortin L, Chu M, Silverman JA, Brian P, Baltz RH (2010) Engineered hybrid lipopeptide antibiotics related to A54145 and daptomycin with improved properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:1404–1413
Owen JG, Calcutt MJ, Robins KJ, Ackerley DF (2016) Generating functional recombinant NRPS enzymes in the laboratory setting via peptidyl carrier protein engineering. Cell Chem Biol 23:1395–1406
Pan Y, Yang X, Li J, Zhang R, Hu Y, Zhou Y, Wang J, Zhu B (2011) Genome sequence of the spinosyns-producing bacterium Saccharopolyspora spinosa NRRL 18395. J Bacteriol 193:3150–3151
Pati A, Sikorski J, Nolan M et al (2009) Complete genome sequence of Saccharomonospora viridis type strain (P101). Stand Genomic Sci 1:141–149
Ren H, Hu P, Zhao H (2017) A plug-and-play pathway refactoring workflow for natural product research in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 114:1847–1854
Röttig M, Medema MH, Blin K, Weber T, Rausch C, Kohlbacher O (2011) NPRSpredictor2—a web server for predicting NRPS adenylation domain specificity. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W362–W367
Siedlecki J, Hill J, Parr I et al (2003) Array synthesis of novel lipodepsipeptides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:4245–4249
Smanski MJ, Zhou H, Claesen J, Shen B, Fischbach MA, Voigt CA (2016) Synthetic biology to access and expand nature’s chemical diversity. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:135–149
Solenberg PJ, Matsushima P, Stack DR, Wilkie SC, Thompson RC, Baltz RH (1997) Production of hybrid glycopeptide antibiotics in vitro and in Streptomyces toyocaensis. Chem Biol 4:195–202
Stachelhaus T, Mootz HD, Marahiel MA (1999) The specificity-conferring code of adenylation domains in nonribosomal peptide synthetases. Chem Biol 6:493–505
Strieker M, Tanović A, Marahiel MA (2010) Nonribosomal peptide synthetases: structure and dynamics. Curr Opin Struct Biol 20:234–240
Süssmuth RD, Mainz A (2017) Nonribosomal peptide synthesis—principle and prospects. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:3770–3823
Voigt CA (2012) Synthetic biology. ACS Synth Biol 1:1–2
Waldron C, Matsushima P, Rosteck PR et al (2001) Cloning and analysis of the spinosad biosynthetic gene cluster of Saccharopolyspora spinosa. Chem Biol 8:487–499
Wang Y, Chen Y, Shen Q, Yin X (2011) Molecular cloning and identification of the laspartomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces viridochromogenes. Gene 483:11–21
Weber T, Blin K, Duddela S et al (2015) antiSMASH 3.0—a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res 43:w237–w243
Weissman KJ (2015) The structural biology of biosynthetic megaenzymes. Nat Chem Biol 11:660–670
Winn M, Fyans JK, Zhuo Y, Mickelfield J (2016) Recent advances in engineering nonribosomal peptide assembly lines. Nat Prod Rep 33:317–347
Yamanaka K, Reynolds KA, Kersten RD et al (2014) Direct cloning and refactoring of a silent lipopeptide biosynthetic gene cluster yields the antibiotic taromycin A. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 111:1957–1962
Yuzawa S, Backman TW, Keasling JD, Katz L (2018) Synthetic biology of polyketide synthases: review and perspective. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2021-9
Acknowledgements
I thank my many colleagues at Eli Lilly and Company and Cubist Pharmaceuticals who carried out exceptional industrial research on genetic manipulation and combinatorial biosynthesis of daptomycin and A54145 BGCs. Special thanks go to Margaret McHenney, Pat Solenberg, Patti Matsushima, and Tom Hosted at Lilly; and Vivian Miao, Kien Nguyen, Dylan Alexander, Steve Wrigley, Julia Penn, Steve Martin, Marie Coëffet-Le Gal, Sasha Doekel, Jian-Qiao Gu, Min Chu, and Paul Brian at Cubist. I also thank Hans von Döhren who suggested developing combinatorial biosynthesis between the daptomycin and A54145 NRPSs, and who was a collaborator on the initial project at Lilly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baltz, R.H. Synthetic biology, genome mining, and combinatorial biosynthesis of NRPS-derived antibiotics: a perspective. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45, 635–649 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1999-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1999-8