Abstract
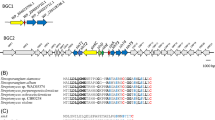
Ca2+-dependent cyclic lipodepsipeptides are an emerging class of antibiotics for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive pathogens. These compounds are synthesized by nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) complexes encoded by large gene clusters. The gene cluster encoding biosynthetic pathway enzymes for the Streptomyces fradiae A54145 NRP was cloned from a cosmid library and characterized. Four NRPS-encoding genes, responsible for subunits of the synthetase, as well as genes for accessory functions such as acylation, methylation and hydroxylation, were identified by sequence analysis in a 127 kb region of DNA that appears to be located subterminally in the bacterial chromosome. Deduced epimerase domain-encoding sequences within the NRPS genes indicated a d-stereochemistry for Glu, Lys and Asn residues, as observed for positionally analogous residues in two related compounds, daptomycin, and the calcium-dependent antibiotic (CDA) produced by Streptomyces roseosporus and Streptomyces coelicolor, respectively. A comparison of the structure and the biosynthetic gene cluster of A54145 with those of the related peptides showed many similarities. This information may contribute to the design of experiments to address both fundamental and applied questions in lipopeptide biosynthesis, engineering and drug development.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Baltz RH (1997) Lipopeptide antibiotics produced by Streptomyces roseosporus and Streptomyces fradiae. In: Strohl WR (ed) Biotechnology of antibiotics. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 415–435
Baltz RH (1998) Genetic manipulation of antibiotic-producing Streptomyces. Trends Microbiol 6:76–83
Baltz RH, McHenney MA, Hosted TJ (1997) Genetics of lipopeptide antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces fradiae A54145 and Streptomyces roseosporus A21978C. In: Baltz RH, Hegeman GD, Skatrud PL (eds) Developments in industrial microbiology. Society for Industrial Microbiology, Fairfax, VA, pp 93–98
Boeck LD, Papiska HR, Wetzel RW, Mynderse JS, Fukuda DS, Mertz FP, Berry DM (1990) A54145, a new lipopeptide antibiotic complex: discovery, taxonomy, fermentation and HPLC. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 43:587–593
Boeck LD, Wetzel RW (1990) A54145, a new lipopeptide antibiotic complex: factor control through precursor directed biosynthesis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 43:607–615
Bruner SD, Weber T, Kohli RM, Schwarzer D, Marahiel MA, Walsh CT, Stubbs MT (2002) Structural basis for the cyclization of the lipopeptide antibiotic surfactin by the thioesterase domain SrfTE. Structure (Camb) 10:301–310
Butler AR, Bate N, Cundliffe E (1999) Impact of thioesterase activity on tylosin biosynthesis in Streptomyces fradiae. Chem Biol 6:287–292
Challis GL, Ravel J, Townsend CA (2000) Predictive, structure-based model of amino acid recognition by nonribosomal peptide synthetase adenylation domains. Chem Biol 7:211–224
Chen H, Hubbard BK, O’Connor SE, Walsh CT (2002) Formation of beta-hydroxy histidine in the biosynthesis of nikkomycin antibiotics. Chem Biol 9:103–112
Clugston SL, Sieber SA, Marahiel MA, Walsh CT (2003) Chirality of peptide bond-forming condensation domains in nonribosomal peptide synthetases: the C5 domain of tyrocidine synthetase is a (D)C(L) catalyst. Biochemistry 42:12095–12104
Counter FT, Allen NE, Fukuda DS, Hobbs JN, Ott J, Ensminger PW, Mynderse JS, Preston DA, Wu CY (1990) A54145, a new lipopeptide antibiotic complex: microbiological evaluation. J Antibiot 43:616–622
Debono M, Barnhart M, Carrell CB, Hoffmann JA, Occolowitz JL, Abbott BJ, Fukuda DS, Hamill RL, Biemann K, Herlihy WC (1987) A21978C, a complex of new acidic peptide antibiotics: isolation, chemistry, and mass spectral structure elucidation. J Antibiot 40:761–777
Fukuda DS, Debono M, Molloy RM, Mynderse JS (1990) A54145, a new lipopeptide antibiotic complex: microbial and chemical modification. J Antibiot 43:601–606
Fukuda DS, Du Bus RH, Baker PJ, Berry DM, Mynderse JS (1990) A54145, a new lipopeptide antibiotic complex: isolation and characterization. J Antibiot 43:594–600
Hojati Z, Milne C, Harvey B, Gordon L, Borg M, Flett F, Wilkinson B, Sidebottom PJ, Rudd BA, Hayes MA, Smith CP, Micklefield J (2002) Structure, biosynthetic origin, and engineered biosynthesis of calcium-dependent antibiotics from Streptomyces coelicolor. Chem Biol 9:1175–1187
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M, Õmura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol 21:526–531
Kempter C, Kaiser D, Haag S, Nicholson G, Gnau V, Walk T, Gierling KH, Decker H, Zähner H, Jung G, Metzger JW (1997) CDA: calcium-dependent peptide antibiotics from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) containing unusual residues. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 36:498–501
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kohli RM, Walsh CT (2003) Enzymology of acyl chain macrocyclization in natural product biosynthesis. Chem Commun (Camb) 3:297–307
Kuhstoss S, Rao RN (1991) Analysis of the integration function of the streptomycete bacteriophage phi C31. J Mol Biol 222:897–908
Lakey JH, Lea EJ, Rudd BA, Wright HM, Hopwood DA (1983) A new channel-forming antibiotic from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) which requires calcium for its activity. J Gen Microbiol 129:3565–3573
Lauer B, Russwurm R, Schwarz W, Kalmanczhelyi A, Bruntner C, Rosemeier A, Bormann C (2001) Molecular characterization of co-transcribed genes from Streptomyces tendae Tu901 involved in the biosynthesis of the peptidyl moiety and assembly of the peptidyl nucleoside antibiotic nikkomycin. Mol Gen Genet 264:662–673
Leskiw BK, Bibb MJ, Chater KF (1991) The use of a rare codon specifically during development? Mol Microbiol 5:2861–2867
Marahiel MA, Stachelhaus T, Mootz HD (1997) Modular peptide synthetases involved in nonribosomal peptide synthesis. Chem Rev 97:2651–2674
Mendez C, Salas JA (1998) ABC transporters in antibiotic-producing actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 158:1–8
Miao V, Coeffet-Legal MF, Brian P, Brost R, Penn J, Whiting A, Martin S, Ford R, Parr IB, Bouchard M, Silva CJ, Wrigley SK, Baltz RH (2005) Daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: cloning and analysis of the gene cluster and revision of peptide stereochemistry. Microbiology 151(Pt 5):1507–1523
Motamedi H, Shafiee A, Cai SJ, Streicher SL, Arison BH, Miller RR (1996) Characterization of methyltransferase and hydroxylase genes involved in the biosynthesis of the immunosuppressants FK506 and FK520. J Bacteriol 178:5243–5248
Ryding NJ, Anderson TB, Champness WC (2002) Regulation of the Streptomyces coelicolor calcium-dependent antibiotic by absA, encoding a cluster-linked two-component system. J Bacteriol 184:794–805
Schwarzer D, Finking R, Marahiel MA (2003) Nonribosomal peptides: from genes to products. Nat Prod Rep 20:275–287
Seno E, Baltz RH (1989) Structural organization and regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis and resistance genes in actinomycetes. In: Shipiro S (ed) Regulation of secondary metabolism in actinomycetes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 1–48
Spatz K, Kohn H, Redenbach M (2002) Characterization of the Streptomyces violaceoruber SANK95570 plasmids pSV1 and pSV2. FEMS Microbiol Lett 213:87–92
Stachelhaus T, Mootz HD, Marahiel MA (1999) The specificity-conferring code of adenylation domains in nonribosomal peptide synthetases. Chem Biol 6:493–505
Uguru GC, Milne C, Borg M, Flett F, Smith CP, Micklefield J (2004) Active-site modifications of adenylation domains lead to hydrolysis of upstream nonribosomal peptidyl thioester intermediates. J Am Chem Soc 126:5032–5033
Wessels P, von Döhren H, Kleinkauf H (1996) Biosynthesis of acylpeptidolactones of the daptomycin type. A comparative analysis of peptide synthetases forming A21978C and A54145. Eur J Biochem 242:665–673
Yeats C, Bentley S, Bateman A (2003) New knowledge from old: in silico discovery of novel protein domains in Streptomyces coelicolor. BMC Microbiol 3:3–20
Zhang JH, Quigley NB, Gross DC (1997) Analysis of the syrP gene, which regulates syringomycin synthesis by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2771–2778
Zotchev SB, Schrempf H (1994) The linear Streptomyces plasmid pBL1: analyses of transfer functions. Mol Gen Genet 242:374–382
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank J. McMenanim and L. Thurston for technical assistance, and S.K. Wrigley for reviewing and discussing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Note: A patent application on the sequence of the A54145 gene cluster was published (PCT Int. Appl., W003060127A2) during the preparation of this manuscript. A small deletion of 67 nucleotides (nucleotides 56952–57018) was observed relative to the sequence assembled in this study. The present sequence, obtained from a library clone, was confirmed by sequencing products from replicate PCR amplifications of the region in question from two stocks of S. fradiae DNA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, V., Brost, R., Chapple, J. et al. The lipopeptide antibiotic A54145 biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces fradiae . J IND MICROBIOL BIOTECHNOL 33, 129–140 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-005-0028-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-005-0028-5