Abstract
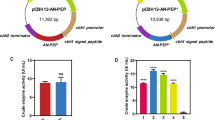
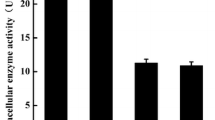
A novel prolyl endopeptidase gene from Aspergillus oryzae was cloned and expressed in Pichia pastoris. Amino acid sequence analysis of the prolyl endopeptidase from Aspergillus oryzae (AO-PEP) showed that this enzyme belongs to a class serine peptide S28 family. Expression, purification and characterization of AO-PEP were analyzed. The optimum pH and temperature were pH 5.0 and 40 °C, respectively. The enzyme was activated and stabilized by metal ion Ca2+ and inhibited by Zn2+, Mn2+, Al3+, and Cu2+. The K m and k cat values of the purified enzyme for different substrates were evaluated. The results implied that the recombinant AO-PEP possessed higher affinity for the larger substrate. A fed-batch strategy was developed for the high-cell-density fermentation and the enzyme activity reached 1,130 U/l after cultivation in 7 l fermentor. After addition of AO-PEP during the fermentation phase of beer brewing, demonstrated the potential application of AO-PEP in the non-biological stability of beer, which favor further industrial development of this new enzyme in beer stabilization, due to its reducing operational costs, as well as no beer losses unlike regeneration process and beer lost with regenerated polyvinylpolypyrrolidone system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews PC, Minth CD, Dixon JE (1982) Immunochemical characterization of a proline endopeptidase from rat brain. Its relationship to proline endopeptidase from other tissues and from other species. J Biol Chem 257:5861–5865
Arentz-Hansen H, McAdam SN, Molberg O, Fleckenstein B, Lundin KEA (2002) Celiac lesion T cells recognize epitopes that cluster in regions of gliadins rich in proline residues. Gastroenterology 123:803–809
Aron PM, Shellhammer TH (2010) A discussion of polyphenols in beer physical and flavour stability. J Inst Brew 116:369–380
Capiralla H, Hiroi T, Hirokawa T, Maeda S (2002) Purification and characterization of a hydrophobic amino acid -specific endopeptidase from Halobacterium halobium S9 with potential application in debittering of protein hydrolysates. Process Biochem 38:571–579
Chevallier S, Goeltz P, Thibault P, Banville D, Gagnon J (1992) Characterization of a prolyl endopeptidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Complete sequence and localization of the active-site serine. J Biol Chem 267:8192–8199
Edens L, Dekker P, Van der Hoeven R, Deen F, De Roos A, Floris R (2005) Extracellular prolyl endoprotease from Aspergillus niger and its use in the debittering of protein hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem 53:7950–7957
Esparza Y, Huaiquil A, Neira L, Leyton A, Rubilar M, Salazar L, Shene C (2011) Optimization of process conditions for the production of a prolyl endopeptidase by Aspergillus niger ATCC 11414 in solid state fermentation. Food Sci Biotechnol 20:1323–1330
Gass J, Ehren J, Strohmeier G, Isaacs I, Khosla C (2005) Fermentation, purification, formulation, and pharmacological evaluation of a prolyl endopeptidase from Myxococcus xanthus: implications for Celiac Sprue therapy. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:674–684
Goertges S (1982) Problematik der Eiweissstabilisierung (Problems with protein stabilization in winemaking). Weinwirtschaft 118:931–935
Goldman BS, Nierman WC, Kaiser D, Slater SC, Durkin AS, Eisen J, Ronning CM et al (2006) Evolution of sensory complexity recorded in a myxobacterial genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15200–15205
Goptar IA, Lysogorskaya EN, Filippova IY, Vinokurov KS, Zhuzhikov DP, Elpidina EN (2005) Prolyl endopeptidases from the midgut of the yellow mealworm Tenebrio molitor. FEBS J 272:154–155
Hough JSBD, Stevens R, Young TW (1982) Malting and brewing science, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, London, 2
Kabashima T, Fujii M, Meng Y, Ito K, Yoshimoto T (1998) Prolyl endopeptidase from Sphingomonas capsulata: isolation and characterization of the enzyme and nucleotide sequence of the gene. Arch Biochem Biophys 358:141–148
Kanatani A, Yoshimoto T, Kitazono A, Kokubo T, Tsuru D (1993) Prolyl endopeptidase from Aeromonas hydrophila: cloning, sequencing, and expression of the enzyme gene, and characterization of the expressed enzyme. J Biochem 113:790–796
Kang C, Yu XW, Xu Y (2013) Gene cloning and enzymatic characterization of an endoprotease Endo-Pro-Aspergillus niger. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:855–864
Kang C, Yu XW, Xu Y (2014) Purification and characterization of a prolyl endopeptidase isolated from Aspergillus oryzae. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:49–55
Siebert KJ (1999) Effects of protein-polyphenol interactions on beverage haze, stabilization, and analysis. J Agric Food Chem 47:353–362
Kubota K, Tanokura M, Takahashi K (2005) Purification and characterization of a novel prolyl endopeptidase from Aspergillus niger. Proc Jpn Acad B Phys 81:447–453
Kuwabara T (1992) Characterization of a prolyl endopeptidase from spinach thylakoids. FEBS Lett 300:127–130
Lopez M, Edens L (2005) Effective prevention of chill-haze in beer using an acid proline-specific endoprotease from Aspergillus niger. J Agric Food Chem 53:7944–7949
Mary Booth WJD, Fhaoláin IN, Jennings PV, O’Cuinn G (1990) Proline-specific peptidases of Streptococcus cremoris AM2. J Dairy Res 57:79–88
Mentlein R (1988) Proline residues in the maturation and degradation of peptide hormones and neuropeptides. FEBS Lett 234:251–256
Nadzeyka A, Altenhofen U, Zahn H (1979) The significance of beer proteins in relationship to cold break and age-related haze formation. Brauwissenschaft 32:167–172
Nierman WC, Pain A, Anderson MJ, Wortman JR, Kim HS et al (2005) Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 438:1151–1156
O’Leary RM, Gallagher SP, O’Connor B (1996) Purification and characterization of a novel membrane-bound form of prolyl endopeptidase from bovine brain. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 28:441–449
O’Leary RM, O’Connor B (1995) Identification and localisation of a synaptosomal membrane prolyl endopeptidase from bovine brain. Eur J Biochem 227:277–283
Oyama H, Aoki H, Amano M, Mizuki E, Yoshimoto T, Tsuru D, Murao S (1997) Purification and characterization of a prolyl endopeptidase from Pseudomonas sp. KU-22. J Ferment Bioeng 84:538–542
Riggle HM, Fisher MA (2009) Purification of a prolyl endopeptidase from Aspergillus oryzae and evaluation of its ability to digest gluten. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society 237
Sattar AK, Yamamoto N, Yoshimoto T, Tsuru D (1990) Purification and characterization of an extracellular prolyl endopeptidase from Agaricus bisporus. J Biochem 107:256–261
Schwede T, Kopp J, Guex N, Peitsch MC (2003) SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucl Acid Res 31:3381–3385
Shan L, Marti T, Sollid LM, Gray GM, Khosla C (2004) Comparative biochemical analysis of three bacterial prolyl endopeptidases: implications for coeliac sprue. Biochem J 383:311–318
Shen GX, Shi JP (1999) Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of prolyl endopeptidase gene from Aeromonas punctata subsp. punctata. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 31:567–571
Soisson SM, Patel SB, Abeywickrema PD, Byrne NJ, Diehl RE et al (2010) Structural definition and substrate specificity of the S28 protease family: the crystal structure of human prolylcarboxypeptidase. BMC Struct Biol 10:16
Sridhar VR, Hughes JE, Welker DL, Broadbent JR, Steele JL (2005) Identification of endopeptidase genes from the genomic sequence of Lactobacillus helveticus CNRZ32 and the role of these genes in hydrolysis of model bitter peptides. Appl Environ Microb 71:3025–3032
Szwajcer-Dey E, Rasmussen J, Meldal M, Breddam K (1992) Proline-specific endopeptidases from microbial sources: isolation of an enzyme from a Xanthomonas sp. J Bacteriol 174:2454–2459
Yoshimoto T, Walter R, Tsuru D (1980) Proline-specific endopeptidase from Flavobacterium. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem 255:4786–4792
Yoshimoto T, Kanatani A, Shimoda T, Inaoka T, Kokubo T, Tsuru D (1991) Prolyl endopeptidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum: cloning and sequencing of the enzyme gene. J Biochem 110:873–878
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2012AA022207), the National Key Basic Research and Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2011CB710800), the High-end Foreign Experts Recruitment Program (GDW20123200113) and the 111 Project (111-2-06) are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, C., Yu, XW. & Xu, Y. Cloning and expression of a novel prolyl endopeptidase from Aspergillus oryzae and its application in beer stabilization. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42, 263–272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1571-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1571-8