Abstract
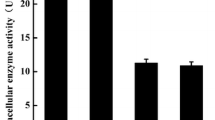
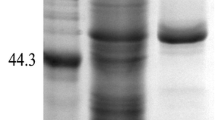
A new fungal strain that was isolated from our library was identified as an Aspergillus oryzae and noted to produce a novel proly endopeptidase. The enzyme was isolated, purified, and characterized. The molecular mass of the prolyl endopeptidase was estimated to be 60 kDa by using SDS-PAGE. Further biochemical characterization assays revealed that the enzyme attained optimal activity at pH 4.0 with acid pH stability from 3.0 to 5.0. Its optimum temperature was 30 °C and residual activity after 30 min incubation at 55 °C was higher than 80 %. The enzyme was activated and stabilized by Ca2+ but inhibited by EDTA (10 mM) and Cu2+. The K m and k cat values of the purified enzyme for different length substrates were also evaluated, and the results imply that the enzyme from A. oryzae possesses higher affinity for the larger substrates. Furthermore, this paper demonstrates for the first time that a prolyl endopeptidase purified from A. oryzae is able to hydrolyze intact casein.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews PC, Hines CM, Dixon JE (1980) Characterization of proline endopeptidase from rat brain. Biochem 19:5494–5500
Arentz-Hansen H, McAdam SN, Molberg Ø, Fleckenstein B, Lundin KE, Jørgensen TJ, Jung G, Roepstorff P, Sollid LM (2002) Celiac lesion T cells recognize epitopes that cluster in regions of gliadins rich in proline residues. Gastroenterology 123:803–809
Aubes-Dufau I, Seris JL, Combes D (1995) Production of peptide hemoglobin hydrolysis: bitterness demonstration and characterization. J Agric Food Chem 43:1982–1988
Capiralla H, Hiroi T, Hirokawa T, Maeda S (2002) Purification and characterization of a hydrophobic amino acid-specific endopeptidase from Halobacterium halobium S9 with potential. Process Biochem 38:571–579
Chang PK, Ehrlich KC (2010) What does genetic diversity of Aspergillus flavus tell us about Aspergillus oryzae. Int J Food Microbiol 138:189–199
Edens L, Dekker P, Van der Hoeven R, Deen F, de Roos A, Floris R (2005) Extracellular prolyl endoprotease from Aspergillus niger and its use in the debittering of protein hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem 53:7950–7957
Esparza Y, Alejandro H, Luz N, Allison L, Monica R, Luis S, Carolina S (2011) Optimization of process conditions for the production of a prolylendopeptidase by Aspergillus niger ATCC 11414 in solid state fermentation. Food Sci Biotechnol 20:1323–1330
Gass J, Ehren J, Strohmeier G, Isaacs I, Khosia C (2005) Fermentation, purification, formulation, and pharmacological evaluation of a prolyl endopeptidase from Myxococcus xanthus: implications for Celiac Sprue therapy. Biotechnol Bioengin 92:674–684
Kabashima T, Fujii M, Meng Y, Ito K, Yoshimoto T (1998) Prolyl endopeptidase from Sphingomonas capsulata: isolation and characterization of the enzyme and nucleotide sequence of the gene. Arch Biochem Biophys 358:141–148
Kanatani A, Yoshimoto T, Kitazono A, Kokubo T (1993) Prolyl endopeptidase from Aeromonas hydrophila: cloning, sequencing, and expression of the enzyme gene, and characterization of the expressed enzyme. J Biochem 113:790–796
Kang C, Yu XW, Xu Y (2013) Gene cloning and enzymatic characterization of an end protease Endo-Pro-Aspergillus niger. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:855–864
Kuwabara T (1992) Characterization of proly endopeptidase from spinach thylakoids. FEBS Lett 300:127–130
Kuwabara T, Suzuki K (1994) A prolyl endoproteinase that acts specifically on the extrinsic 18-kDa protein of photosystem II: purification and further characterization. Plant Cell Physiol 35:665–675
Lopez M, Edens L (2005) Effective prevention of chill-haze in beer using an acid proline-specific endoprotease from Aspergillus niger. J Agric Food Chem 53:7944–7949
Machida M, Yamada O, Gomi K (2008) Genomics of Aspergillus oryzae: learning from the history of koji mold and exploration of its future. DNA Res 15:173–183
Mentlein R (1988) Proline residues in the maturation and degradation of peptide hormones and neuropeptides. FEBS Lett 234:251–256
O’Leary RM, O’ Connor B (1995) Identification and localisation of a synaptosomal membrane prolyl endopeptidase from bovine brain. Eur J Biochem 227:277–283
O’Leary RM, Gallagher SP, O’Connor B (1996) Purification and characterization of a novel membrane-bound form of prolyl endopeptidase from bovine brain. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 28:441–449
Oyama H, Aoki H, Amano M, Mizuki E, Yoshimoto T, Tsuru D, Murao S (1997) Purification and characterization of a prolyl endopeptidase from Pseudomonas sp. KU-22. J Ferment Bioeng 8:538–542
Polgar L (2002) Structure-function of prolyl oligopeptidase and its role in neurological disorders. Curr Med Chem Cent Nerv Syst Agents 2:251–257
Riggle HM, Fisher MA (2009) Purification of a prolyl endopeptidase from Aspergillus oryzae and evaluation of its ability to digest gluten. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society, vol 237
Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sattar AK, Yamamoto N, Yoshimoto T, Tsuru D (1990) Purification and characterization of an extracellular prolyl endopeptidase from Agaricus bisporus. J Biochem 107:256–261
Sridhar VR, Hughes JE, Welker DL, Broadbent JR, Steele JL (2005) Identification of endopeptidase genes from the genomic sequence of Lactobacillus helveticus CNRZ32 and the role of these genes in hydrolysis of model bitter peptides. Apply Environ Microbiol 71:3025–3032
Szwajcer-Dey E, Rasmussen J, Meldal M, Breddam K (1992) Proline-specific endopeptidases from microbial sources: isolation of an enzyme from a Xanthomonas sp. J Bacteriol 174:2454–2459
Verweij PE, Meis JFGM, van den Hurk P, Zoll J, Samson RA, Melchers WJG (1995) Phylogenetic relationships of five species of Aspergillus and related taxa as deduced by comparison of sequences of small subunit ribosomal RNA. Med Mycol 33:185–190
White TJ, Bmns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic, San Diego, pp 315–322
Yoshimoto T, Sattar AK, Hirose W, Tsuru D (1988) Studies on prolyl endopeptidase from Shakashimeji (Lyophyllum cinerascens): purification and enzymatic properties. J Biochem 104:622–627
Yoshimoto T, Walter R, Tsuru D (1980) Proline-specific endopeptidase from Flavobacterium: purification and properties. J Biol Chem 255:4786–4792
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2012AA022207), the National Key Basic Research and Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2011CB710800) and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (111 Project) (111-2-06) are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, C., Yu, XW. & Xu, Y. Purification and characterization of a prolyl endopeptidase isolated from Aspergillus oryzae . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 49–55 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1378-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1378-z