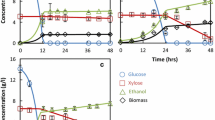
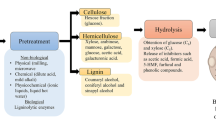
Abstract
This article reviews current co-culture systems for fermenting mixtures of glucose and xylose to ethanol. Thirty-five co-culture systems that ferment either synthetic glucose and xylose mixture or various biomass hydrolysates are examined. Strain combinations, fermentation modes and conditions, and fermentation performance for these co-culture systems are compared and discussed. It is noted that the combination of Pichia stipitis with Saccharomyces cerevisiae or its respiratory-deficient mutant is most commonly used. One of the best results for fermentation of glucose and xylose mixture is achieved by using co-culture of immobilized Zymomonas mobilis and free cells of P. stipitis, giving volumetric ethanol production of 1.277 g/l/h and ethanol yield of 0.49–0.50 g/g. The review discloses that, as a strategy for efficient conversion of glucose and xylose, co-culture fermentation for ethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass can increase ethanol yield and production rate, shorten fermentation time, and reduce process costs, and it is a promising technology although immature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abate C, Callieri D, Rodriguez E, Garro O (1996) Ethanol production by a mixed culture of flocculent strains of Zymomonas mobilis and Saccharomyces sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45:580–583
Abbi M, Kuhad RC, Singh A (1996) Bioconversion of pentose sugars to ethanol by free and immobilized cells of Candida shehatae (NCL-3501): fermentation behavior. Process Biochem 31(6):555–560
Alterthum F, Ingram LO (1989) Efficient ethanol production from glucose, lactose, and xylose by recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1943–1948
Amartey S, Jeffries T (1996) An improvement in Pichia stipitis fermentation of acid-hydrolysed hemicelllulose achieved by overliming (calcium hydroxide treatment) and strain adaptation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 12(3):281–283
Amore R, Kotter P, Kuster C, Ciriacy M, Hollenberg CP (1991) Cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of the NAD(P)H-dependent xylose reductase-encoding gene (XYL1) from the xylose-assimilating yeast Pichia stipitis. Gene 109:89–97
Bader J, Mast-Gerlach E, Popović MK, Bajpai R, Stahl U (2010) Relevance of microbial coculture fermentations in biotechnology. J Appl Microbiol 109:371–387
Beck MJ, Johnson RD, Baker CS (1990) Ethanol production from glucose/xylose mixes by incorporating microbes in selected fermentation schemes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 24–25:415–424
Birol G, Doruker P, Kirdar B, Önsan Zİ, Ülgen K (1998) Mathematical description of ethanol fermentation by immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Process Biochem 33:763–771
Brooks TA, Ingram LO (1995) Conversion of mixed waste office paper to ethanol by genetically engineered Klebsiella oxytoca strain P2. Biotechnol Prog 11:619–625
Bothast RJ, Nichols NN, Dien BS (1999) Fermentations with new recombinant organisms. Biotechnol Prog 15:867–875
Cardona CA, Sánchez ÓJ (2007) Fuel ethanol production: process design trends and integration opportunities. Bioresour Technol 98:2415–2457
Chandrakant P, Bisaria VS (1998) Simultaneous bioconversion of cellulose and hemicelluloses to ethanol. Crit Rev Biotechnol 18(4):295–331
Cho BK, Charusanti P, Herrgård MJ, Palsson BØ (2007) Microbial regulatory and metabolic networks. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:360–364
Chu BCH, Lee H (2007) Genetic improvement of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for xylose fermentation. Biotechnol Adv 25:425–441
Deanda K, Zhang M, Eddy C, Picataggio S (1996) Development of an arabinose-fermenting Zymomonas mobilis strain by metabolic pathway engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4465–4470
De Bari I, Cuna D, Nanna F, Braccio G (2004) Ethanol production in immobilized cell bioreactors from mixed sugar syrups and enzymatic hydrolysates of steam-exploded biomass. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 114:539–557
Delgenes JP, Escare MC, Laplace JM, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1998) Biological production of industrial chemicals, i.e. xylitol and ethanol, from lignocelluloses by controlled mixed culture systems. Ind Crops Prod 1:101–111
Delgenes JP, Laplace JM, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1996) Comparative study of separated fermentations and cofermentation process to produce ethanol from hardwood derived hydrolysates. Biomass Bioenergy 11(4):353–360
Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1988) The ethanol tolerance of Pichia stipitis Y7124 grown on a d-xylose d-glucose and L-arabinose mixture. J Ferment Technol 66:417–422
Department of Energy (2005) From biomass to biofuels: a roadmap to the energy future, based on a workshop, Rockville, 7–9 Dec
Dien BS, Cotta MA, Jeffries TW (2003) Bacteria engineered for fuel ethanol production: current status. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:258–266
Doran JB, Aldrich HC, Ingram LO (1994) Saccharification and fermentation of sugar-cane bagasse by Klebsiella oxytoca P2 containing chromosomally integrated genes encoding the Zymomonas mobilis ethanol pathway. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:240–247
Dumsday GJ, Jones K, Stanley GA, Pamment NB (1997) Recombinant organisms for ethanol production from hemicellulosic hydrolyzates—a review of recent progress. Australas Biotechnol 7(4):285–295
Eliasson A, Christensson C, Wahlbom CF, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Anaerobic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae carrying XYL1, XYL2 and XKS1 in mineral medium chemostat cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3381–3386
Förster J, Famili I, Fu P, Palsson BØ, Nielsen J (2003) Genomescale reconstruction of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic network. Genome Res 13:244–253
Fu N, Peiris P, Markham J et al (2009) A novel co-culture process with Zymomonas mobilis and Pichia stipitis for efficient ethanol production on glucose/xylose mixtures. Enzyme Microb Technol 45(3):210–217
Fu N, Peiris P (2008) Co-fermentation of a mixture of glucose and xylose to ethanol by Zymomonas mobilis and Pachysolen tannophilus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(7):1091–1097
Golias H, Dumsday GJ, Stanley GA, Pamment NB (2002) Evaluation of a recombinant Klebsiella oxytoca strain for ethanol production from cellulose by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation: comparison with native cellobiose-utilising yeast strains and performance in co-culture with thermotolerant yeast and Zymomonas mobilis. J Biotechnol 96:155–168
Gong CS, Cao NJ, Du J, Tsao GT (1999) Ethanol production from renewable resources. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 65:207–241
Gray KA, Zhao L, Emptage M (2006) Bioethanol. Curr Opin Chem Biol 10:141–146
Grootjen DRJ, Meijlink LHHM, van der Lans RGJM, KChAM Luyben (1990) Cofermentation of glucose and xylose with immobilized Pichia stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 12:860–864
Grootjen DRJ, van der Lans RGJM, KChAM Luyben (1990) Effects of the aeration rate on the fermentation of glucose and xylose by Pichia stipitis CBS 5773. Enzyme Microb Technol 12:20–23
Grootjen DRJ, Jansen ML, van der Lans RGJM, Luyben KCAM (1991) Reactors in series for the complete conversion of glucose/xylose mixtures by Pichia stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:828–833
Grootjen DRJ, Meijlink LHHM, Vleesenbeek R, van der Lans RGJM, Luyben KChAM (1991) Cofermentation of glucose and xylose with immobilized Pichia stipitis in combination with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:530–536
Grootjen DRJ, van der Lans RGJM, Luyben KChAM (1991) Conversion of glucose/xylose mixtures by Pichia stipitis under oxygen-limited conditions. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:648–654
Grootjen DRJ, Windemeijer MGA, van der Lans RGJM, Luyben KChAM (1990) The use of a coulter counter to investigate a mixed culture of Pichia stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Tech 4(6):403–408
Hallborn J, Walfridsson M, Airaksinen U, Ojamo H, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Penttila M et al (1991) Xylitol production by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnology 9:1090–1095
Harish Kumar Reddy Y, Srijana M, Madhusudhan Reddy D, Reddy G (2010) Coculture fermentation of banana agro-waste to ethanol by cellulolytic thermophilic Clostridium thermocellum CT2. Afr J Biotechnol 9(13):1926–1934
Ho NW, Chen Z, Brainard AP (1998) Genetically engineered Saccharomyces yeast capable of effective co-fermentation of glucose and xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1852–1859
Hodge DB, Karim MN (2002) Modeling and advanced control of recombinant Zymomonas mobilis fed-batch fermentation. Biotechnol Prog 18:572–579
Ingram LO, Alterthum F, Conway T, Ohta K (1991) Ethanol production by Escherichia coli strains co-expressing Zymomonas pdc and adh genes. US Patent No. 5, 000, 000
Ingram LO, Conway T (1988) Expression of different levels of ethanologenic enzymes from Zymomonas mobilis in recombinant strains of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:397–404
Ingram LO, Conway T, Clark DP, Sewell GW, Preston JF (1987) Genetic engineering of ethanol production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2420–2425
Ingram LO, Gomez PF, Lai X, Moniruzzaman M, Wood BE, Yomano LP, York SW (1997) Metabolic engineering of bacteria for ethanol production. Biotechnol Bioeng 58:204–214
Jeffries TW, Grigoriev IV, Grimwood J, Laplaza JM, Aerts A, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Lindquist E, Dehal P, Shapiro H, Jin YS, Passoth V, Richardson PM (2007) Genome sequence of the lignocellulose-bioconverting and xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Nat Biotechnol 25(3):319–326
Jeffries TW, Jin YS (2004) Metabolic engineering for improved fermentation of pentoses by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:495–509
Jeffries TW (2006) Engineering yeasts for xylose metabolism. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:320–326
Jin YS, Jeffries TW (2004) Stoichiometric network constraints on xylose metabolism by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 6:229–238
Joachimsthal EL, Rogers PL (2000) Characterization of a high productivity recombinant strain of Zymomonas mobilis for ethanol production from glucose/xylose mixtures. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 84(6):343–356
Knauf M, Moniruzzaman M (2004) Lignocellulosic biomass processing: a perspective. Int Sugar J 106:147–150
Kordowska-Wiater M, Targoński Z (2001) Ethanol production on the media containing glucose and xylose by coculture of Pichia Stipitis CCY39501 and respiratory deficient mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae V30. Electr J Pol Agric Univ Food Sci Technol 4(2):15–28
Kordowska-Wiater M, Targoński Z (2002) Ethanol fermentation on glucose/xylose mixture by co-cultivation of restricted glucose catabolite repressed mutants of Pichia stipitis with respiratory deficient mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Acta Microbiol Pol 51:345–352
Krishnan MS, Ho NWY, Tsao GT (1999) Fermentation kinetics of ethanol production from glucose and xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces 1400 (pLNH33). Appl Biochem Biotehcnol 77–79:373–388
Kumar R, Singh S, Singh OV (2008) Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass: biochemical and molecular perspectives. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:377–391
Kuyper M, Hartog MMP, Toirkens MJ, Almering MJH, Winkler AA, Van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005) Metabolic engineering of a xylose-isomerase-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for rapid anaerobic xylose fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res 5:399–409
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R (1992) Alcoholic glucose and xylose fermentations by the coculture process: compatibility and typing of associated strains. Can J Microbiol 38:654–658
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1993) Effects of culture conditions on the co-fermentation of a glucose and xylose mixture to ethanol by a mutant of Saccharomyces diastaticus associated with Pichia stipitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:760–763
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1993) Cofermentation of glucose and xylose to ethanol by a respiratory-deficient mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-cultivated with a xylose-fermenting yeast. J Ferment Bioeng 75:207–212
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1993) Ethanol production from glucose and xylose by separated and coculture process using high cell density systems. Process Biochem 28:519–525
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1991) Combined alcoholic fermentation of d-xylose and d-glucose by four selected microbial strains: process considerations in relation to ethanol tolerance. Biotechnol Lett 13(6):445–450
Latif F, Rajoka MI (2001) Production of ethanol and xylitol from corn cobs by yeasts. Bioresour Technol 77(1):57–63
Lebeau T, Jouenne T, Junter GA (1997) Simultaneous fermentation of glucose and xylose by pure and mixed cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida shehatae immobilized in a two-chambered bioreactor. Enzyme Microb Technol 21:265–272
Lee J (1997) Biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol. J Biotechnol 56:1–24
Lee YS, Lee WG, Chang YK, Chang HN (1995) Modelling of ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae from a glucose and maltose mixture. Biotechnol Lett 17:791–796
Lee WC, Huang CT (2000) Modeling of ethanol fermentation using Zymomonas mobilis ATCC 10988 grown on the media containing glucose and fructose. Biochem Eng J 4:217–227
Leksawasdi N, Joachimsthal EL, Rogers PL (2001) Mathematical modeling of ethanol production from glucose/xylose mixtures by recombinant Zymomonas mobilis. Biotechnol Lett 23:1087–1093
Lin Y, Tanaka S (2006) Ethanol fermentation from biomass resources: current state and prospects. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:627–642
Maki M, Leung KT, Qin W (2009) The prospects of cellulase-producing bacteria for the bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Int J Biol Sci 5:500–516
Martin C, Marcet M, Almazan O, Jonsson LJ (2007) Adaptation of a recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to a sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate with high content of fermentation inhibitors. Bioresour Technol 98(9):1767–1777
Mielenz JR (2001) Ethanol production from biomass: technology and commercialization status. Curr Opin Microbiol 4:324–329
Ng TK, Ben-Bassat A, Zeikus JG (1981) Ethanol production by thermophilic bacteria: fermentation of cellulosic substrates by cocultures of Clostridium thermocellum and Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. Appl Environ Microbiol 41(6):1337–1343
Ohta K, Beall DS, Mejia JP, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (1991) Genetic improvement of Escherichia coli for ethanol production: chromosomal integration of Zymomonas mobilis genes encoding pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase II. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:893–900
Ohta K, Beall DS, Mejia JP, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (1991) Metabolic engineering of Klebsiella oxytoca M5A1 for ethanol production from xylose and glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2810–2815
Qian M, Tian S, Li X, Zhang J, Pan Y, Yang X (2006) Ethanol production from dilute-acid softwood hydrolysate by co-culture. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 134:273–283
Okuda N, Ninomiya K, Katakura Y, Shioya S (2008) Strategies for reducing supplemental medium cost in bioethanol production from waste house wood hydrolysate by ethanologenic Escherichia coli: inoculum size increase and coculture with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng 105(2):90–96
Olsson L, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1995) Kinetics of ethanol production by recombinant Escherichia coli KO11. Biotechnol Bioeng 45:356–365
Patle S, Lal B (2007) Ethanol production from hydrolysed agricultural wastes using mixed culture of Zymomonas mobilis and Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol Lett 29(12):1839–1843
Potera C (2006) Process with biofuels will depend on, drive microbiology research. Microbe 1:317–322
Pramanik J, Keasling JD (1997) Stoichiometric model of Escherichia coli metabolism: incorporation of growth-rate dependent biomass composition and mechanistic energy requirements. Biotechnol Bioeng 56:398–421
Reed LJ, Palsson BØ (2003) Thirteen years of building constraint-based in silicon models of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 185(9):2692–2699
Rouhollah H, Iraj N, Giti E, Sorah A (2007) Mixed sugar fermentation by Pichia stipitis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and an isolated xylose-fermenting Kluyveromyces marxianus and their cocultures. Afr J Biotechnol 6(9):1110–1114
Sánchez S, Bravo V, Castro E, Moya AJ, Camacho F (2002) The fermentation of mixtures of d-glucose and d-xylose by Candida shehatae, Pichia stipitis or Pachysolen tannophilus to produce ethanol. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 77:641–648
Service RF (2007) Cellulosic ethanol: biofuel researchers prepare to reap a new harvest. Science 315:1488–1491
Skoog K, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1990) Effect of oxygenation on xylose fermentation by Pichia stipitis. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3389–3394
Stephanopoulos G (2007) Challenges in engineering microbes for biofuels production. Science 315:801–804
Szambelan K, Nowak J, Czarnecki Z (2004) Use of Zymomonas mobilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae mixed with Kluyveromyces fragilis for improved ethanol production from Jerusalem artichoke tubers. Biotechnol Lett 26:845–848
Taherzadeh MJ, Karimi K (2007) Acid-based hydrolysis processes for ethanol from lignocellulosic materials: a review. BioResources 2(3):472–499
Takuma S, Nakashima N, Tantirungkij M, Kinoshita S, Okada H, Seki T et al (1991) Isolation of xylose reductase gene of Pichia stipitis and its expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 28–29:327–340
Taniguchi M, Itaya T, Tohma T, Fujii M (1997) Ethanol production from a mixture of glucose and xylose by co-culture of Pichia stipitis and a respiratory-deficient mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Bioeng 83:364–370
Taniguchi M, Itaya T, Tohma T, Fujii M (1997) Ethanol production from a mixture of glucose and xylose by a novel co-culture system with two fermentors and two microfiltration modules. J Ferment Bioeng 84(1):59–64
Taniguchi M, Tanaka T (2004) Clarification of interactions among microorganism and development of co-culture systems for production of useful substances. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 90:35–62
Thatipamala R, Rohani S, Hill GA (1992) Effects of high product and substrate inhibitions on the kinetics and biomass and product yields during ethanol batch fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 40:289–297
Varma A, Palsson BØ (1993) Metabolic capabilities of Escherichia coli. I. Synthesis of biosynthetic precursors and cofactors. J Theor Biol 165:477–502
Varma A, Palsson BØ (1993) Metabolic capabilities of Escherichia coli. II. Optimal growth patterns. J Theor Biol 165:503–522
Varma A, Palsson BØ (1994) Stoichiometric flux balance models quantitatively predict growth and metabolic by-product secretion in wild type Escherichia coli W3110. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:3724–3731
Wood BE, Ingram LO (1992) Ethanol production from cellobiose, amorphous cellulose, and crystalline cellulose by recombinant Klebsiella oxytoca containing chromosomally integrated Zymomonas mobilis genes for ethanol production and plasmids expressing thermostable cellulose from Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2103–2110
Zaldivar J, Nielsen J, Olsson L (2001) Fuel ethanol production from lignocelluloses: a challenge for metabolic engineering and process integration. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:17–34
Zhang M, Eddy C, Deanda K, Finkelstein M, Picataggio S (1995) Metabolic engineering of a pentose metabolism pathway in ethanologenic Zymomonas mobilis. Science 267:240–243
Zhou S, Davis FC, Ingram LO (2001) Gene integration and expression and extracellular secretion of Erwinia chrysanthemi endoglucanase CelY (celY) and CelZ (celZ) in ethanologenic Klebsiella oxytoca P2. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:6–14
Zhou S, Ingram LO (1999) Engineering endoglucanase-secreting strains of ethanologenic Klebsiella oxytoca P2. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 22:600–607
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Graduate Research Scholars Program (GRSP) of the Alabama Experimental Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR). Three anonymous referees and the journal editor, Dr. Thomas W. Jeffries, are gratefully acknowledged for their insightful suggestions and valuable comments. Dr. Fred L. Strickland, Dr. Heping Liu, Dr. Shirlaine Koh and Mr. Ronald Putt are highly appreciated for their helpful suggested revisions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y. Development and application of co-culture for ethanol production by co-fermentation of glucose and xylose: a systematic review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 581–597 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0894-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0894-3