Abstract
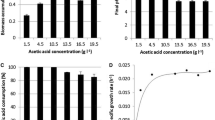
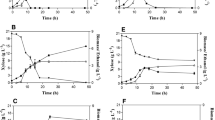
Substrates that contain hexose as well as pentose sugars can form an interesting substrate for the production of ethanol. Pichia stipitis and a respiratory-deficient mutant of Saccharomyces diastaticus were used to convert such a substrate into ethanol under continuous culture conditions. With a sugar mixture (glucose 70%/xylose 30%) at 50 g/l, the xylose was entirely consumed when the dilution rate (D) did not exceed 0.006 h−1 whereas the glucose was entirely consumed whatever the D. The study of influence of initial substrate concentration (S0) was performed at D = 0.015 h−1. Under these conditions the substrate was entirely consumed when its initial concentration did not exceed 20 g/l. With S0 = 80 g/l the residual xylose concentration reached 20.5 g/l. At low D or at low S0, P. stipitis was the dominant species in the fermentor. Increasing the D or S0 resulted in the wash-out of P. stipitis mainly because of its low ethanol tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballesteros M, Ballesteros I, Olivia JM, Cabanas A, Saez F, Carrasco J (1991) Comparative study of different fermentation schemes to produce ethanol from lignocellulosic sugar components. In: Grassi G, Collina A, Zibetta H (eds) Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Biomass for Energy, Industry and Environment. 21–27 April, Athens. Elsevier Applied Science, London and New York, pp 536–540
Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1989) Fermentation of d-xylose, d-glucose, l-arabinose mixture by Pichia stipitis: effect of the oxygen transfer rate on fermentation performance. Biotechnol Bioeng 34:398–402
Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1991) Xylose metabolism by Pichia stipitis: the effect of ethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35:656–661
Du Preez JC, Bosch M, Prior BA (1986) The fermentation of hexose and pentose sugars by Candida shehatae and Pichia stipitis. Appl Microbiol Technol 23:228–233
Grootjen DRJ, Meijlink LHHM, Lans RGJM van der, Luyben KOAM (1990) Cofermentation of glucose and xylose with immobilized Pichia stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 12:860–864
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1991a) Alcoholic fermentation of glucose and xylose by Pichia stipitis, Candida shehatae, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Zymomonas mobilis: oxygen requirement as key factor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:158–162
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1991b) Combined alcoholic fermentation of d-xylose and d-glucose by four selected microbial strains: process considerations in relation to ethanol tolerance. Biotechnol Lett 13:445–450
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1992) Alcoholic glucose and xylose fermentations by coculture process: compatibility and typing of associated strains. Can J Microbiol 38:654–658
Laplace JM, Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1993) Cofermentation of glucose and xylose to ethanol by a respiratory deficient mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cocultivated with a xylose fermenting yeast. J Ferment Bioeng 75(3):207–212
Postma E, Kuiper A, Tomasouw F, Scheffers WA, Dijken JP van (1989) Competition for glucose between the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida utilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:3214–3220
Slonimski PP, Perrodin G, Groft JH (1968) Ethidium bromide induced mutation of yeast mitochondria: complete transformation of cells into respiratory deficient non chromosomal “petites”. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 30:232–239
Urk H van, Postma E, Scheffers WA, Dijken JP van (1989) Glucose transport in Crabtree-positive and Crabtree-negative yeasts. J Gen Microbiol 135:2399–2406
Wickerham LJ (1951) Taxonomy of yeasts. Technical Bulletin no. 1029, U.S. Dept of Agriculture, Washington, D.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: J. P. Delgenes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laplace, J.M., Delgenes, J.P., Moletta, R. et al. Effects of culture conditions on the co-fermentation of a glucose and xylose mixture to ethanol by a mutant of Saccharomyces diastaticus associated with Pichia stipitis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 760–763 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164463
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164463